Method for analyzing aflatoxin B1 by fluorescence anisotropy of sensitive aptamer
A kind of aflatoxin and anisotropic technology, applied in the direction of material analysis, material analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc. through optical means, can solve the problems of poor antibody stability, high antibody preparation cost, cumbersome and time-consuming operation, etc., to achieve Ease of high-throughput analysis, easy introduction of labels, convenient storage and transportation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1, the preparation of nucleic acid aptamer and complementary nucleic acid sequence
[0055] 1. Preparation of nucleic acid aptamers
[0056] A nucleic acid aptamer that can specifically bind aflatoxin B1 (as shown in sequence 1 in the sequence listing) is artificially synthesized, and the 5' end of the nucleic acid aptamer is labeled with fluorescein (FAM).
[0057] 2. Screening and preparation of complementary nucleic acid sequences
[0058] 1. For the nucleic acid aptamer prepared in step 1, design the following single-stranded DNA molecules that can complementarily bind to the nucleic acid aptamer:
[0059] Ⅰ: 5'-AGA GAC AAC ACG TGC A-3' (sequence 2 of the sequence listing);
[0060] Ⅱ: 5'-GAG ACA ACA CGT GCA-3' (sequence 3 of the sequence listing);
[0061] Ⅲ: 5'-AGA CAA CAC GTG CA-3' (sequence 4 of the sequence listing);
[0062] Ⅳ: 5'-GAC AAC ACG TGC A-3' (sequence 5 of the sequence listing);
[0063] V: 5'-ACA ACA CGT GCA-3' (sequence 6 of the seq...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2. Establishment of a method for detecting aflatoxin B1 using fluorescein-labeled nucleic acid aptamers and streptavidin-labeled single-stranded DNA molecules
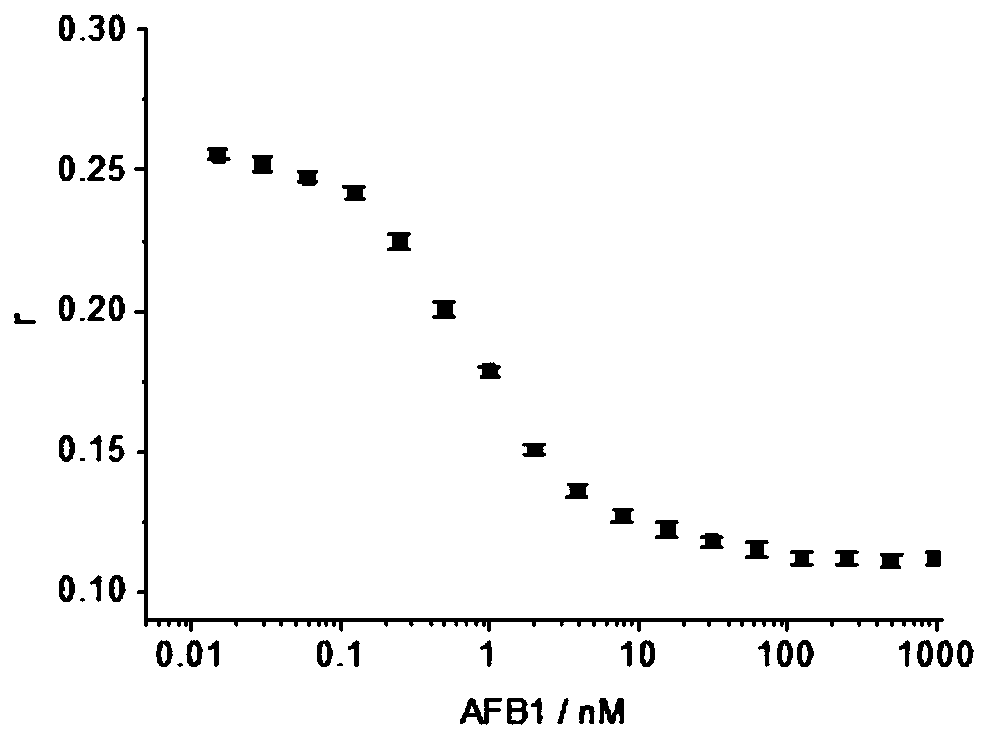
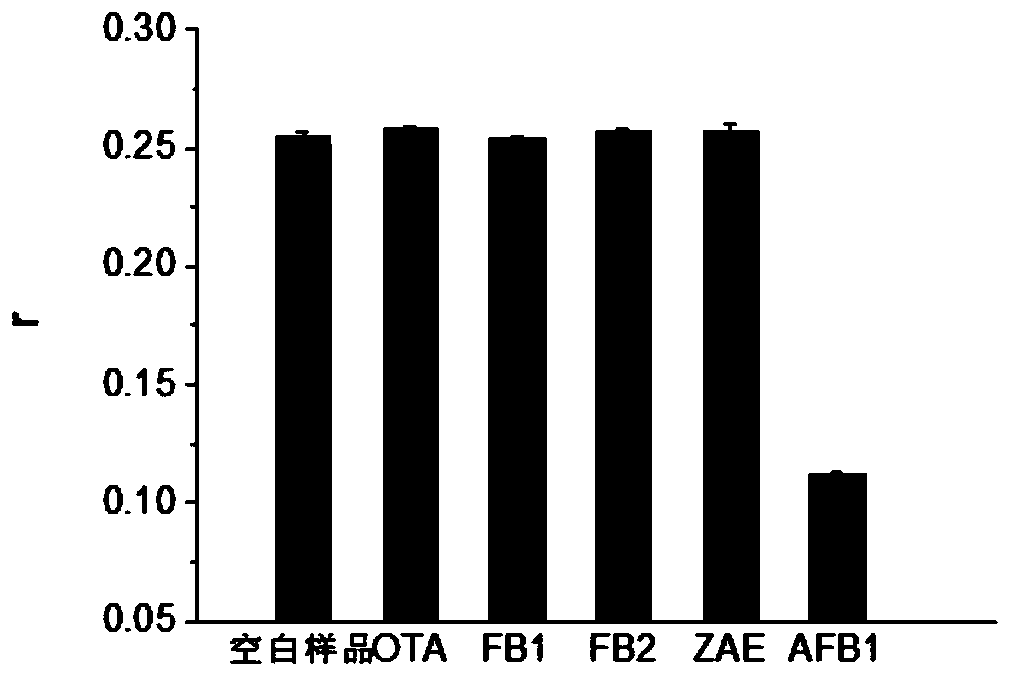
[0069] 1. Mix the FAM-labeled nucleic acid aptamer prepared in Example 1, the single-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 4 marked by streptavidin, and aflatoxin B1 in 100 μl of reaction buffer solution, and incubate at 4°C for 60 min . The concentration of the FAM-labeled nucleic acid aptamer in the reaction system is 1nM, the concentration of the streptavidin-labeled single-stranded DNA molecule in the reaction system is 20nM, and the aflatoxin B1 in the reaction system is set at different concentrations (each Concentration set 2 replicates). At the same time, set a blank control without adding the sample to be tested.
[0070] 2. After the reaction in step 1, the fluorescence anisotropy (fluorescence polarization) value was measured using a multifunctional microplate reader (Synergy H1 Microplate...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3, the impact of streptavidin labeling on detection sensitivity
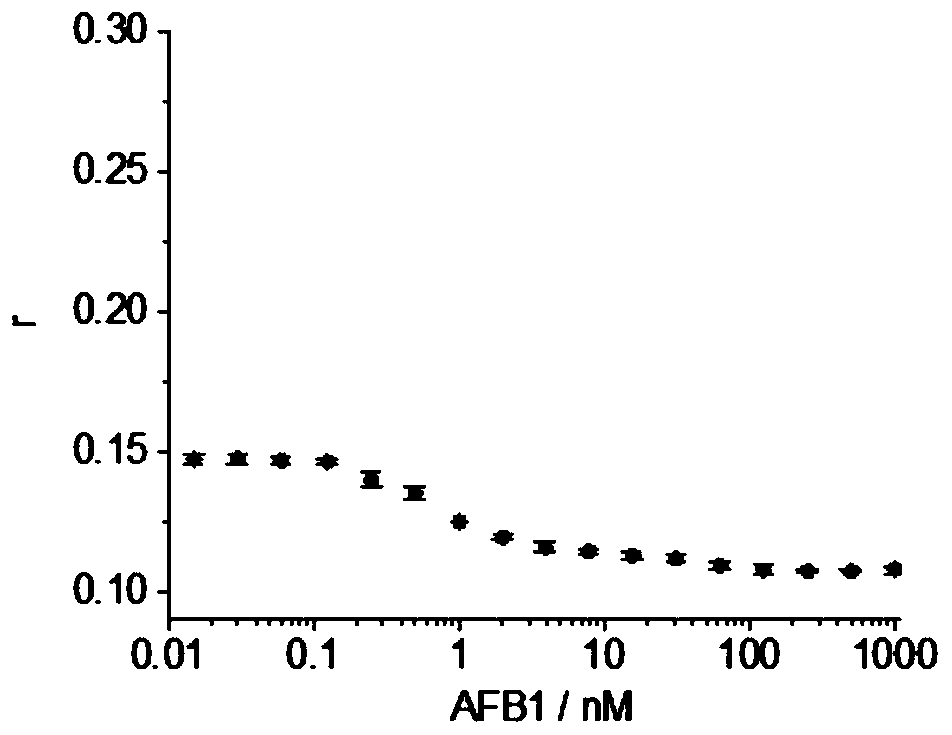
[0075] 1. The FAM-labeled nucleic acid aptamer prepared in Example 1, only the single-stranded DNA molecule (not labeled with streptavidin) shown in sequence 4 using biotin-labeled reaction with aflatoxin B1 in 100 μl Mix in the buffer solution and incubate at 4°C for 60 min. The concentration of FAM-labeled nucleic acid aptamer in the reaction system was 1nM, and the concentration of only biotin-labeled single-stranded DNA molecules (without streptavidin labeling) in the reaction system was 20nM. Yellow in the reaction system Different concentrations of Aspergillus toxin B1 were set (two replicates were set for each concentration). At the same time, set a blank control without adding the sample to be tested.
[0076] 2. After the reaction in step 1, the fluorescence anisotropy (fluorescence polarization) value was measured using a multifunctional microplate reader (Synergy H1 Microplate read...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com