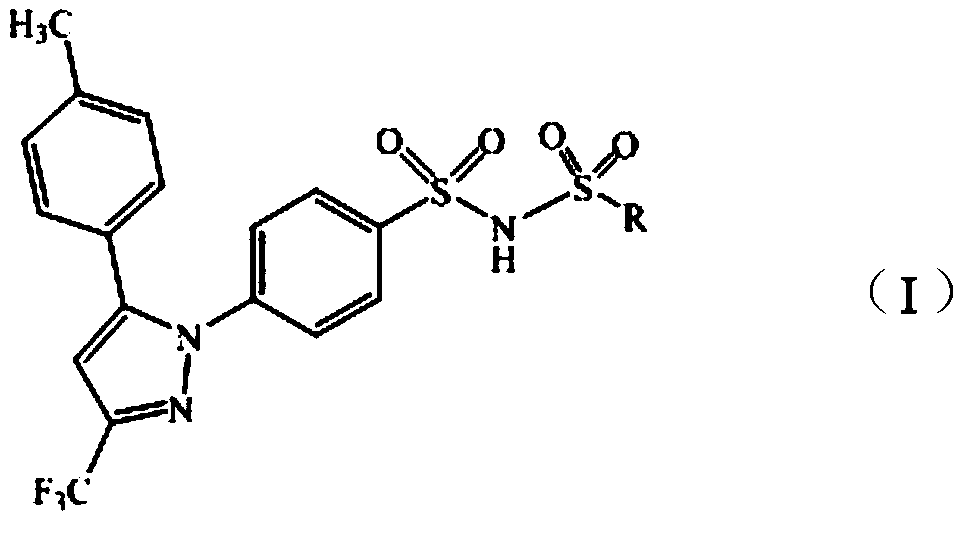
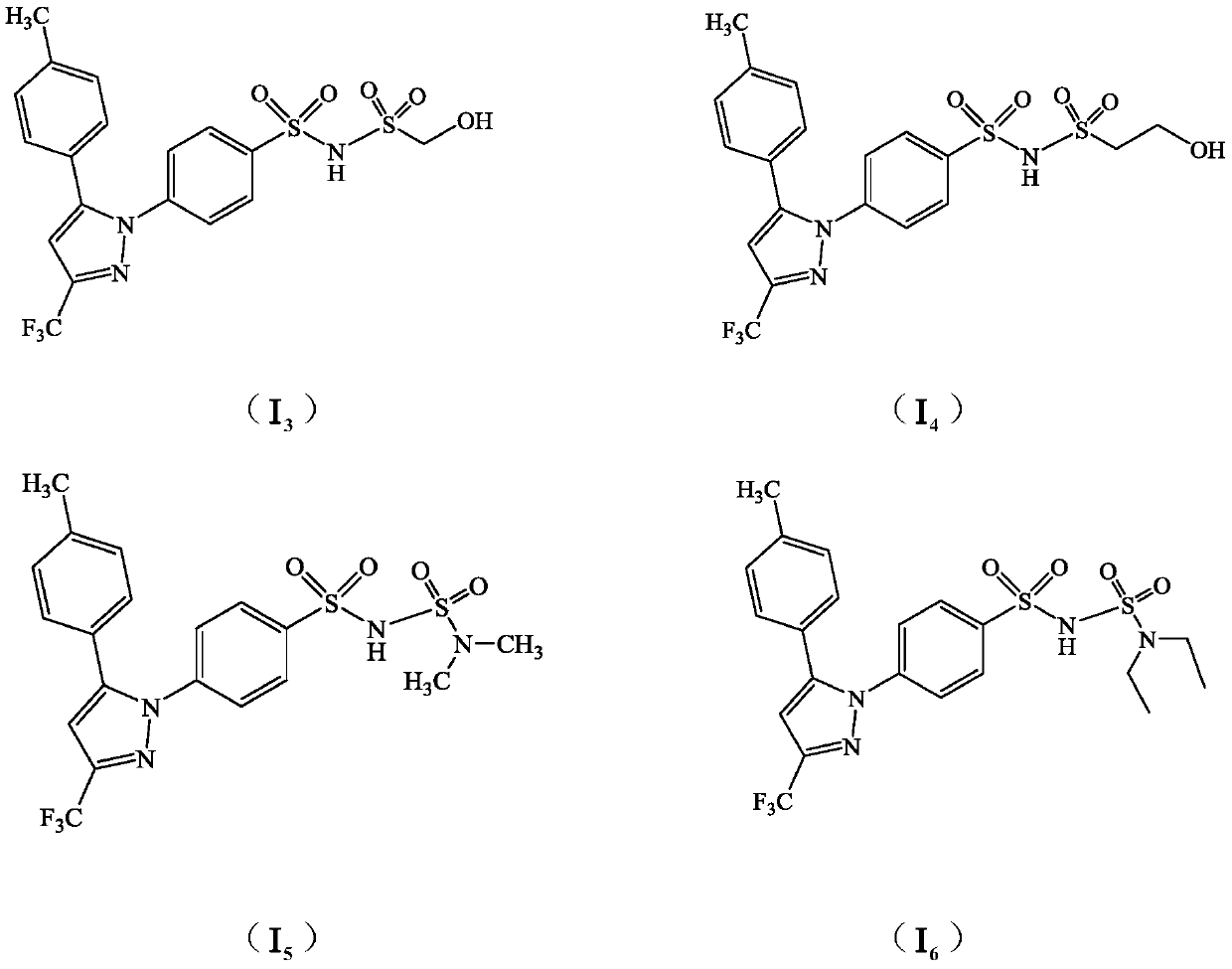
Celecoxib derivative and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of celecoxib and derivatives, which is applied in the field of celecoxib derivatives and their preparation, can solve the problems of low absorption and poor dissolution, and achieve good medicinal biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
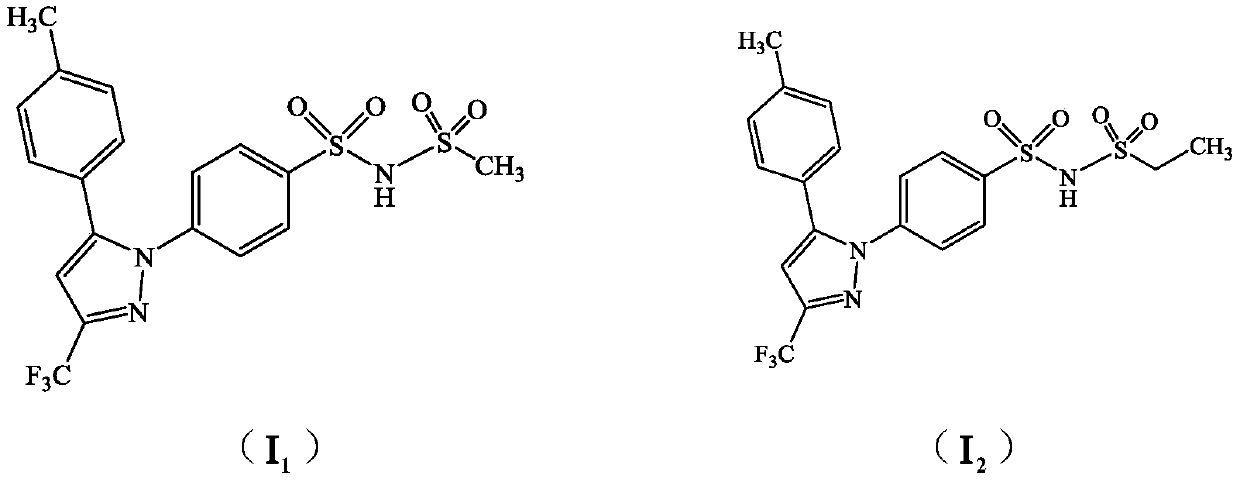
[0021] Example 1 Compound I 1 preparation of
[0022] 100mL dry three-necked flask, install stirrer, thermometer, add celecoxide (95g, 0.249mol) and dry anhydrous acetonitrile 570mL and potassium carbonate (36g, 0.26mol) to wherein, stir; Slowly add the methanesulfonic acid to 30g The acetonitrile solution of acid chloride (60mL, 0.262mmol) was heated to 75-80°C and reacted for 8h, and the end point of the reaction was identified by TLC (thin layer development conditions (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5:1)); the reaction was completed, and the reaction solution was Cool and crystallize at 0°C to 5°C for 2 hours, filter, wash the solid with an appropriate amount of acetonitrile, and dry it in vacuum at 65°C to 70°C for 6 hours to obtain 95 g of a light yellow crystalline powder solid with a yield of 83.1% and an HPLC content of 98.9%. Table 1 is compound Ⅰ 1 elemental analysis.
[0023] HPLC method: using octadecylsilane bonded silica gel as filler, buffer solution (2.7g / ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Compound I 1 Preparation of sodium salt
[0030] 100mL three-neck flask, add Ⅰ 1 Compound 53g and ethanol 400mL, at room temperature, add 22mL of 50% sodium hydroxide solution, stir at 45°C-50°C for 30min, stand at 5°C-10°C overnight, filter, use cold ethanol for solid, vacuum at 70°C-75°C Drying, white crystalline powdery solid 49.4g, yield: 89.6%, HPLC content 99.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3 Compound I 2 preparation of
[0032] With reference to the method of Example 1, ethanesulfonyl chloride was used instead of methanesulfonyl chloride to obtain 87g of white crystalline solid compound I 2 , HPLC content 97.4% (method is the same as embodiment 1). Table 2 is compound Ⅰ 2 elemental analysis.
[0033]
[0034] Table 2
[0035] 1 H—NMR (500MHz, CH 3 OH-d 3 / TMS):
[0036] δ H (ppm): 1.226(2H, m) 2.379(3H, s), 3.458(3H, t, J=7.5Hz; J=1.5Hz, J=8.0Hz), 4.978(2H, s), 6.739(1H, s), 7.109 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz); 7.718 (2H, d, J = 8.0Hz); 7.471 (2H, d, J = 8.5Hz); 7.898 (2H, d, J = 8.5Hz)
[0037] MS: m / z: 474.5 (M+H) + .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com