Method of detecting extracellular vesicle surface PD-L1 protein by aptamer of programmed death receptor-ligand 1 (PD-L1)
A PD-L1 and programmed death technology is applied in the field of the detection of PD-L1 protein on the surface of extracellular vesicles by nucleic acid aptamer of programmed death receptor-ligand 1, which can solve the problem of cumbersome steps, complicated and time-consuming detection methods. , large sample consumption, etc., to achieve the effect of economical price, fast and efficient detection, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Extraction of exosomes secreted by melanoma cell line A375 by differential centrifugation
[0036] For the exosomes extracted from the culture supernatant of the melanoma cell line A375 cells, avoid the interference from the exosomes in the fetal bovine serum, by centrifuging the fetal bovine serum overnight at 100000×g to remove the exosomes, and obtain bovine-free exosomes. Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS). Then, the cells were cultured at 37°C in a medium supplemented with 10% exosomal depleted FBS and 1% (v / v) penicillin-streptomycin. After 60 hours of incubation, collect the cell culture supernatant and centrifuge at 2000×g for 20 minutes at 4°C (Eppendorf, 5424R) to remove cells and cell debris. Collect the supernatant and centrifuge at 16500×g for 45 minutes at 4°C To remove a large number of microvesicles (Eppendorf, 5424R). The microvesicle pellet was resuspended in PBS and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. The supernatant was centrifuged at 100000g for 2 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Morphological characterization of exosomes secreted by melanoma cell line A375
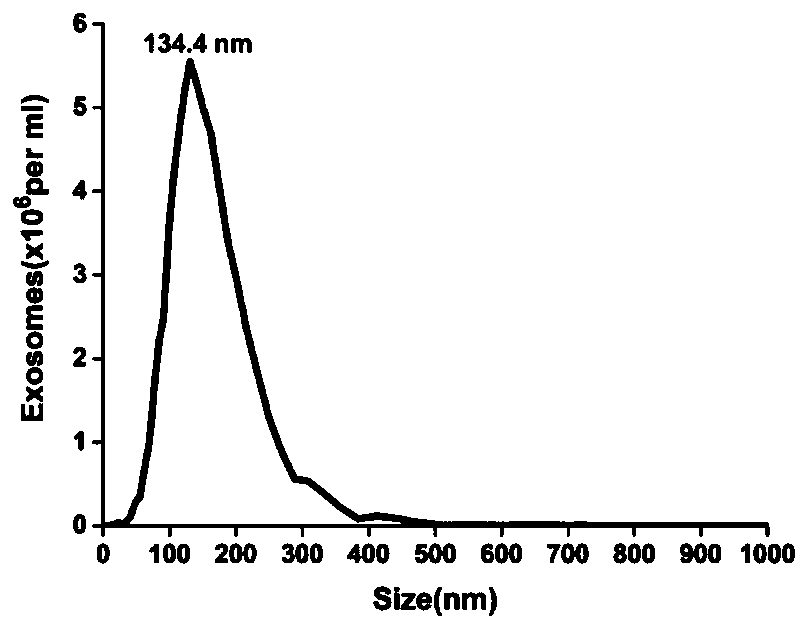
[0038] In order to identify exosomes, morphological analysis of exosomes is required. Then, in order to characterize the purified small vesicles as exosomes, they can be characterized by transmission electron microscopy and nanoparticle tracking analyzer. First, the morphology and size of the exosomes are characterized by transmission electron microscopy. The specific operation: the exosomes are dropped on the carbon-coated copper grid and left for 1 minute (the copper grid should be lightly clamped with tweezers to prevent the copper grid Clipped), after staining with 2% uranyl acetate at room temperature for 1 minute, blot the dye solution with filter paper along the edges, put the copper mesh under a lamp and bake for 10 minutes, use a transmission electron microscope (Tecnai, G2spirit FEI, USA) Observe and take pictures. The concentration and particle size distribution of exoso...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Verification of the expression of PD-L1 in exosomes secreted by the melanoma cell line A375
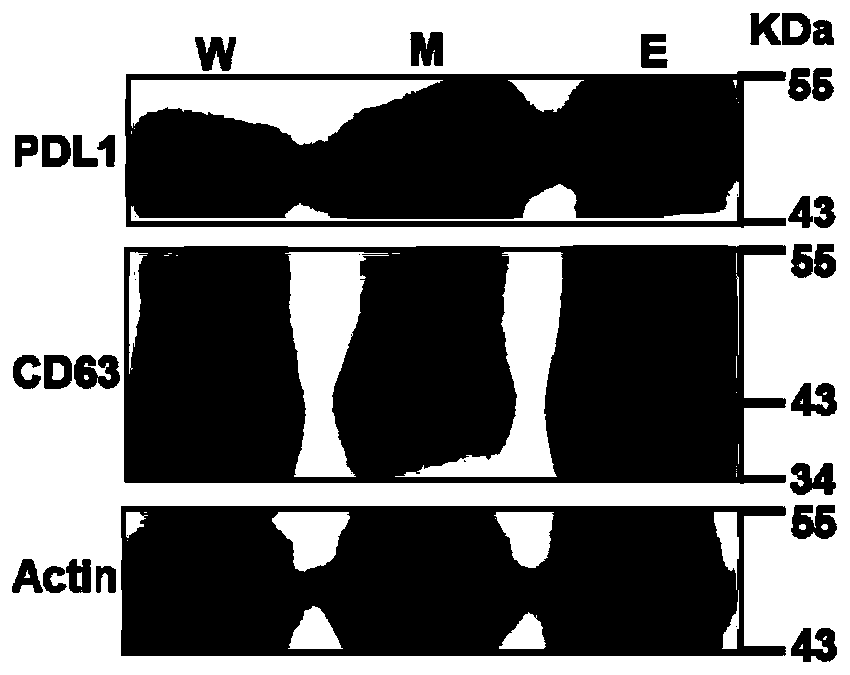
[0041] After successfully extracting exosomes, it is important to characterize the proteins expressed by exosomes, such as CD63 and PD-L1, which can be identified by Western blotting. Using 12% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis analysis, load cell lysate (W) microvesicles (M) and exosomes (E) respectively, load the same total amount of protein, and run three gels in parallel; then transfer to nitric acid On the cellulose membrane, the blot was blocked with blocking buffer (Beyotime Biotechnology) for 1 hour at room temperature. After washing, it was incubated with PD-L1, CD63 and Actin primary antibodies at 4°C overnight. After washing, it was conjugated with HRP The secondary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) was incubated together at room temperature for 2 hours; after washing, the blot on the membrane was developed with ECL detection reagent (Pierce), and the chemiluminesce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com