Microbacterium oxidans and its application in degrading organic pollutants
A technology for oxidizing microbacteria and organic pollutants, applied in the field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants, can solve the problems of maintaining high efficiency, not meeting high-efficiency production, and low degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
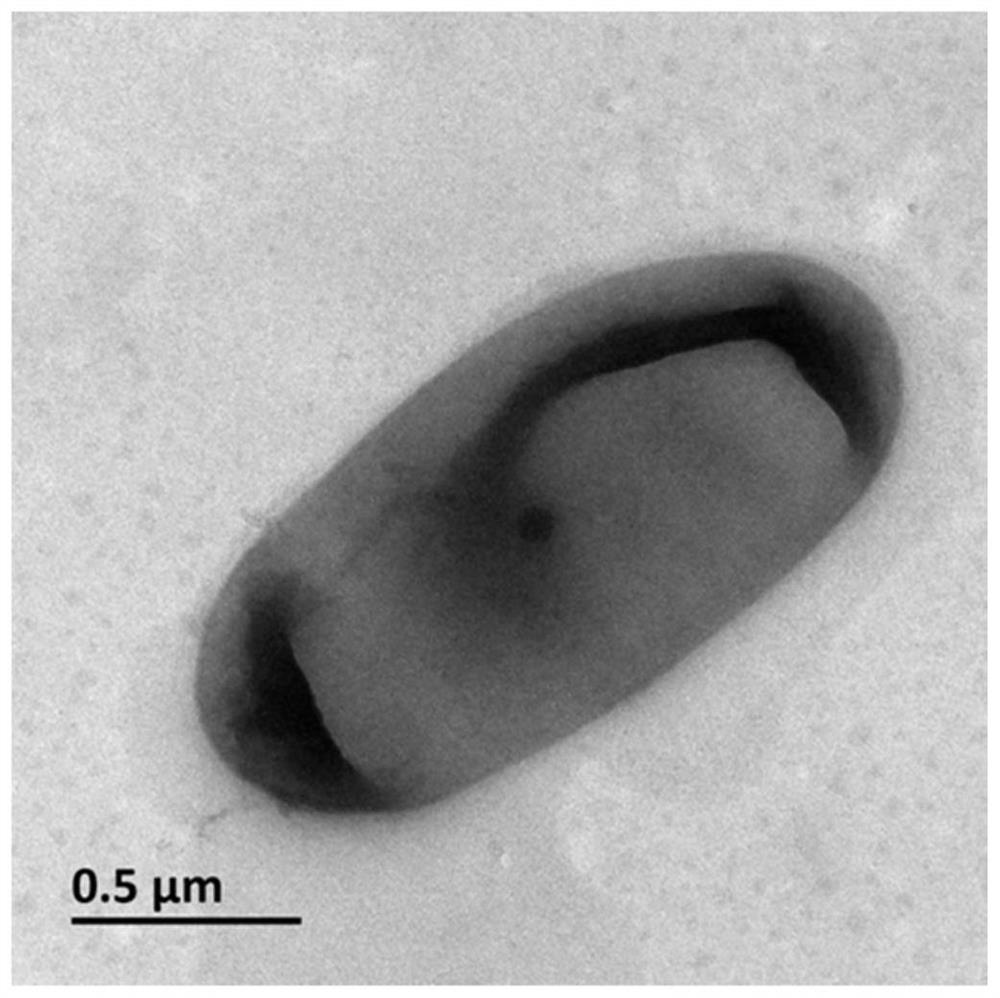
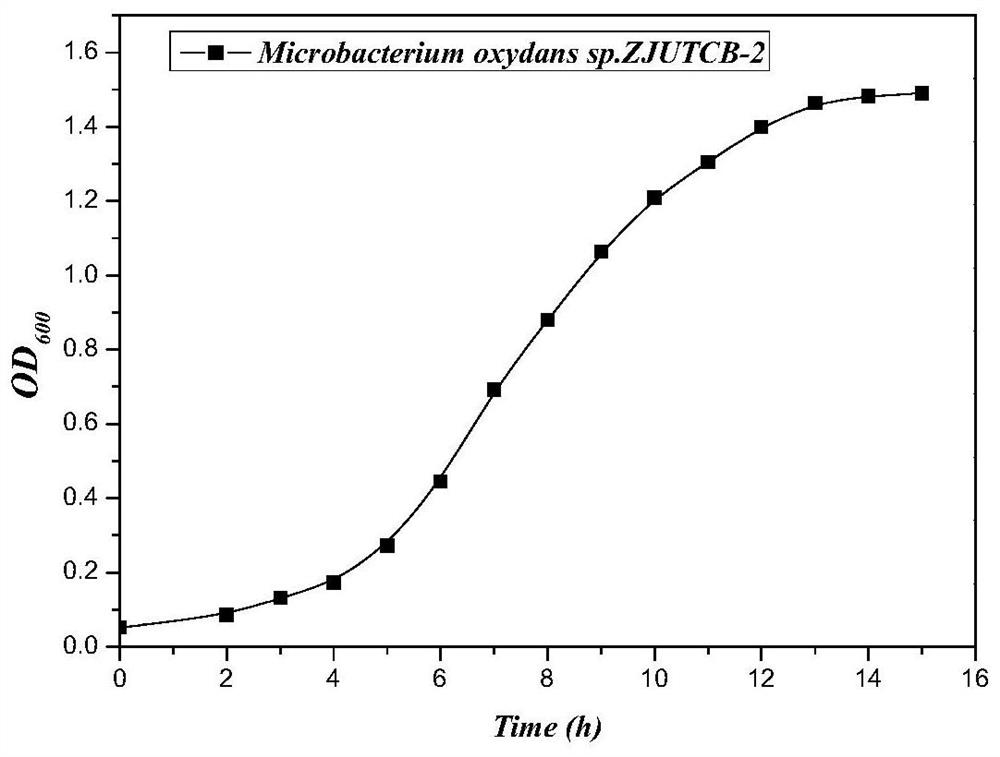
[0018] Example 1: Isolation, purification, identification and preservation of Microbacterium oxydans ZJUTCB-2
[0019] 1. Screening of strain ZJUTCB-2
[0020] Strain ZJUTCB-2 is a Gram-positive bacterium domesticated and isolated from the activated sludge of Hangzhou Qige Wastewater Treatment Plant. Specific steps are as follows:
[0021]Add 200ml of inorganic salt culture solution to a 340mL serum bottle, pass high-purity nitrogen gas (40mL / min) for 30min to remove the dissolved oxygen in the inorganic salt culture solution and the air at the top of the serum bottle, add 20mL of activated sludge and 987μmol / L Chlorobenzene, at 30°C, 160rpm for enrichment culture. When the concentration of chlorobenzene is 50% of the initial concentration, take out 20mL of the enrichment solution and add it to 200mL of fresh inorganic salt culture solution, then add 987μmol / L chlorobenzene, and cultivate anaerobically at 30°C and 160rpm to the concentration of chlorobenzene 50% of the init...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Changes in the concentration of Microbacterium oxydansZJUTCB-2 degrading chlorobenzene in the domestication stage
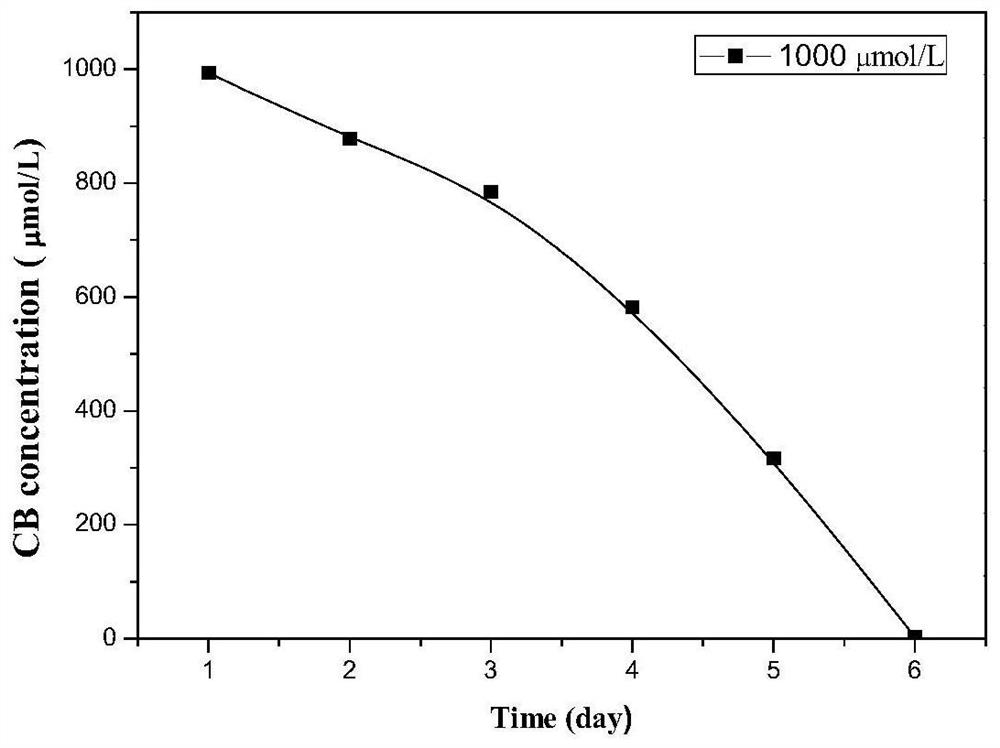
[0034] Under the optimal environmental factor conditions (culture solution pH=7, culture temperature 30℃), the degradation performance and bacterial growth of the strain ZJUTCB-2 to the initial concentration of 1000μmol / L chlorobenzene were investigated under aerobic conditions. The results showed that the strain could completely degrade 1000μmol / L chlorobenzene, and after the chlorobenzene was completely degraded, the quality of the bacteria ZJUTCB-2 also increased significantly, and the bacterial solution was turbid at this time. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0035] Prepare inorganic salt culture solution (same as Example 1), adjust the pH to 7 with sodium hydroxide or dilute hydrochloric acid solution, and distribute it in serum bottles with an average volume of 340 mL, 50 mL per bottle.
[0036] Inoculate the strain ZJ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: The degradation of Microbacterium oxydansZJUTCB-2 to different concentrations of chlorobenzene under aerobic conditions
[0039] Under the optimal environmental factor conditions (culture solution pH=7, culture temperature 30℃), the degradation performance and bacterial growth of the strain ZJUTCB-2 to the initial concentration of 700-1500μmol / L chlorobenzene were investigated under aerobic conditions. The results showed that the strain could completely degrade 700-1500 μmol / L of chlorobenzene. After the chlorobenzene was completely degraded, the quality of the bacteria ZJUTCB-2 also increased significantly, and the bacterial solution was turbid at this time. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0040] Prepare inorganic salt culture solution (same as Example 1), adjust the pH to 7 with sodium hydroxide or dilute hydrochloric acid solution, and distribute it in serum bottles with an average volume of 340 mL, 50 mL per bottle.
[0041] The pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com