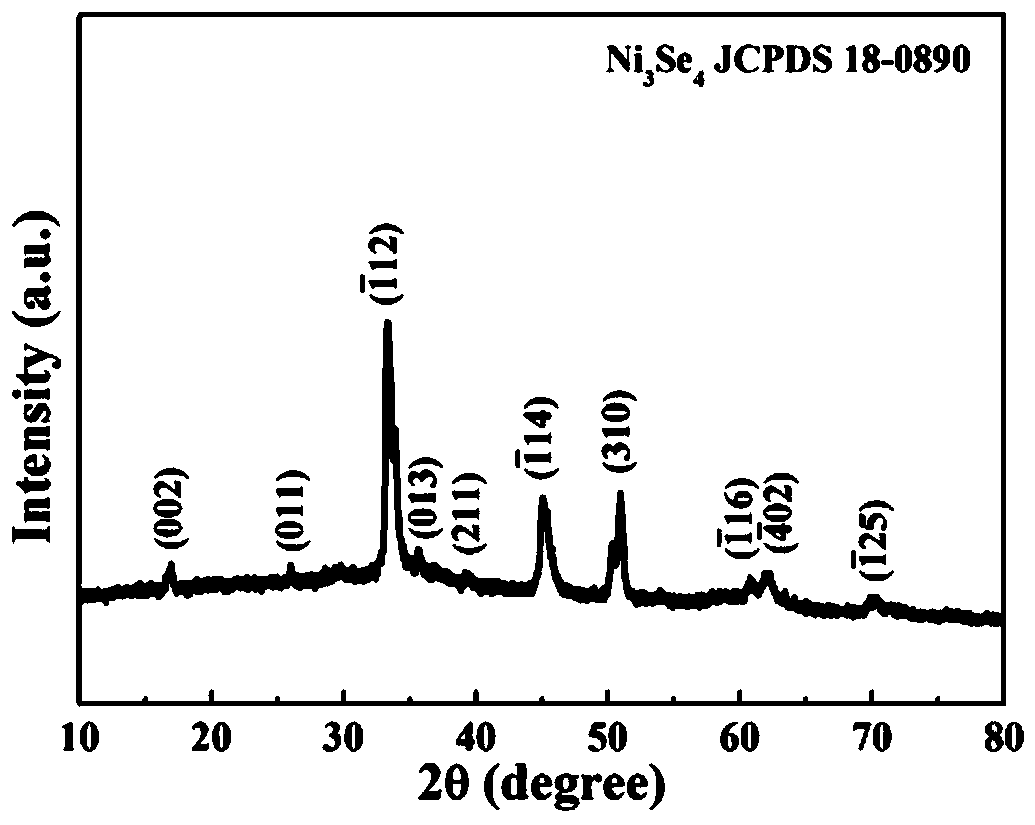
Fe-doped Ni3Se4 nanorod/nanosheet grading array structure material, preparation method and application of material
An array structure, nanosheet technology, applied in catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, nanotechnology, etc., to achieve the effects of enhanced electrical conductivity, fast interfacial charge transfer, and promotion of chemical adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A Fe-doped Ni 3 Se 4 A method for preparing a nanorod / nanosheet hierarchical array structure material, comprising the following steps:
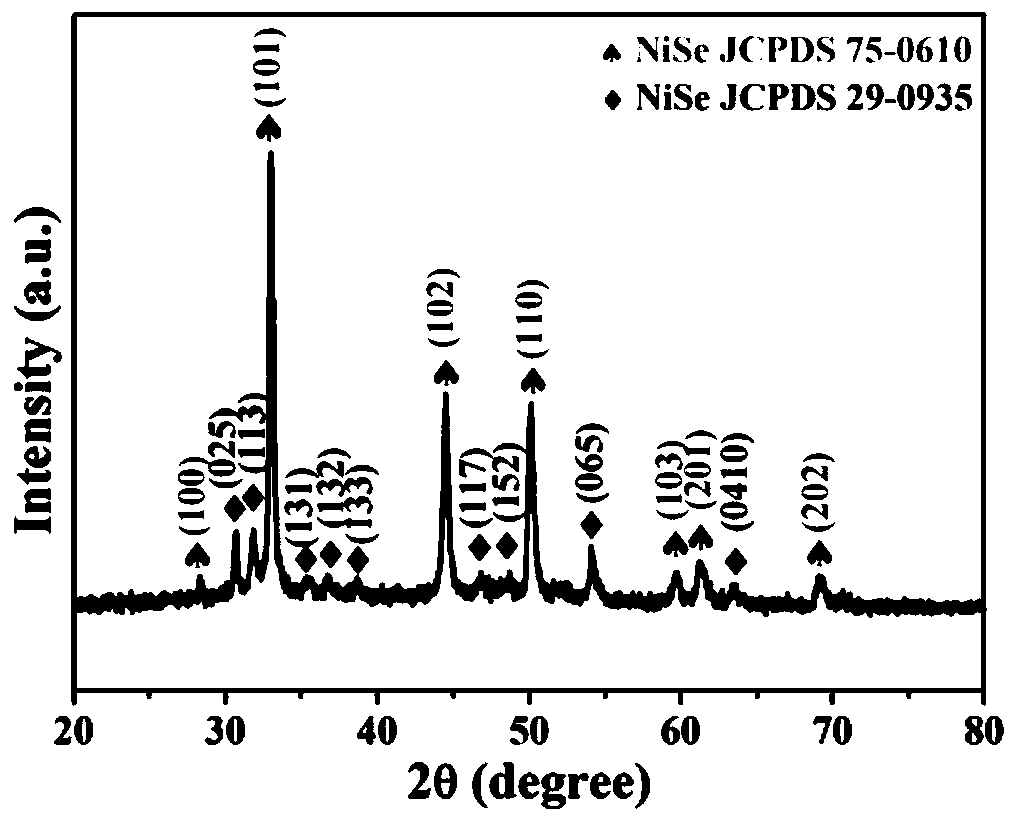
[0047] (1) Soak a piece of nickel foam (NF) with an area of 2×3cm in 6M hydrochloric acid for 15min, and then wash it three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol. Measure 15mL of ammonia water and add it to 25mL of deionized water. After stirring evenly, accurately weigh 1mmol of Se powder and 2.5mmol of NaBH 4 Add the above mixed solution, ultrasonically stir for 30min, then transfer the reddish-brown solution to a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel reaction kettle, put the pre-treated foamed nickel into the solution obliquely, and react in an oven at 120°C 8h. After the reaction is finished, cool down to room temperature naturally, and the foamed nickel A covered by the black sample 1 Wash with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times each, and dry the obtained precursor samples in a vacuum ove...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A Fe-doped Ni 3 Se 4 Application of Nanorod / Nanosheet Hierarchical Array Structure Materials as Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) Catalysts.
[0063] The specific application method is: use Fe-doped Ni with an area of 0.5×0.5cm 3 Se 4 The nanorod / nanosheet hierarchical array structure material is used as the working electrode, and platinum wire and Ag / AgCl electrode are used as the counter electrode and reference electrode, respectively. Electrochemical tests were performed at room temperature (25 °C) using a CHI760E electrochemical workstation in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte solution. Commercial RuO 2 The loaded electrode was used as a benchmark to compare the OER performance. Using linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) at 2.0mV s -1 Polarization curves were obtained at a scan rate of 90% and an ohmic compensation of 90%. Such as Figure 11 As shown, Fe-doped Ni 3 Se 4 The nanorod / nanosheet hierarchical array structure has remarkable OER activity, and only needs a low over...
Embodiment 3
[0065] A Fe-doped Ni 3 Se 4 Applications of Nanorod / Nanosheet Hierarchical Array Structure Materials as Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) Catalysts.
[0066] The specific application method is: use Fe-doped Ni with an area of 0.5×0.5cm 3 Se 4 The nanorod / nanosheet hierarchical array structure material is used as the working electrode, and the carbon rod and Ag / AgCl electrode are used as the counter electrode and the reference electrode, respectively. Electrochemical tests were performed at room temperature (25 °C) using a CHI760E electrochemical workstation in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte solution. Using linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) at 2.0mV s -1 The scan rate is obtained at 90% ohmic compensation. Such as Figure 15 As shown, Fe-doped Ni 3 Se 4 The nanorod / nanosheet hierarchical array structure exhibits excellent HER activity, requiring only a low potential of 153 mV to reach 10 mA cm -2 The current density is better than that of NiSe nanorods at 182mV. Although commer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com