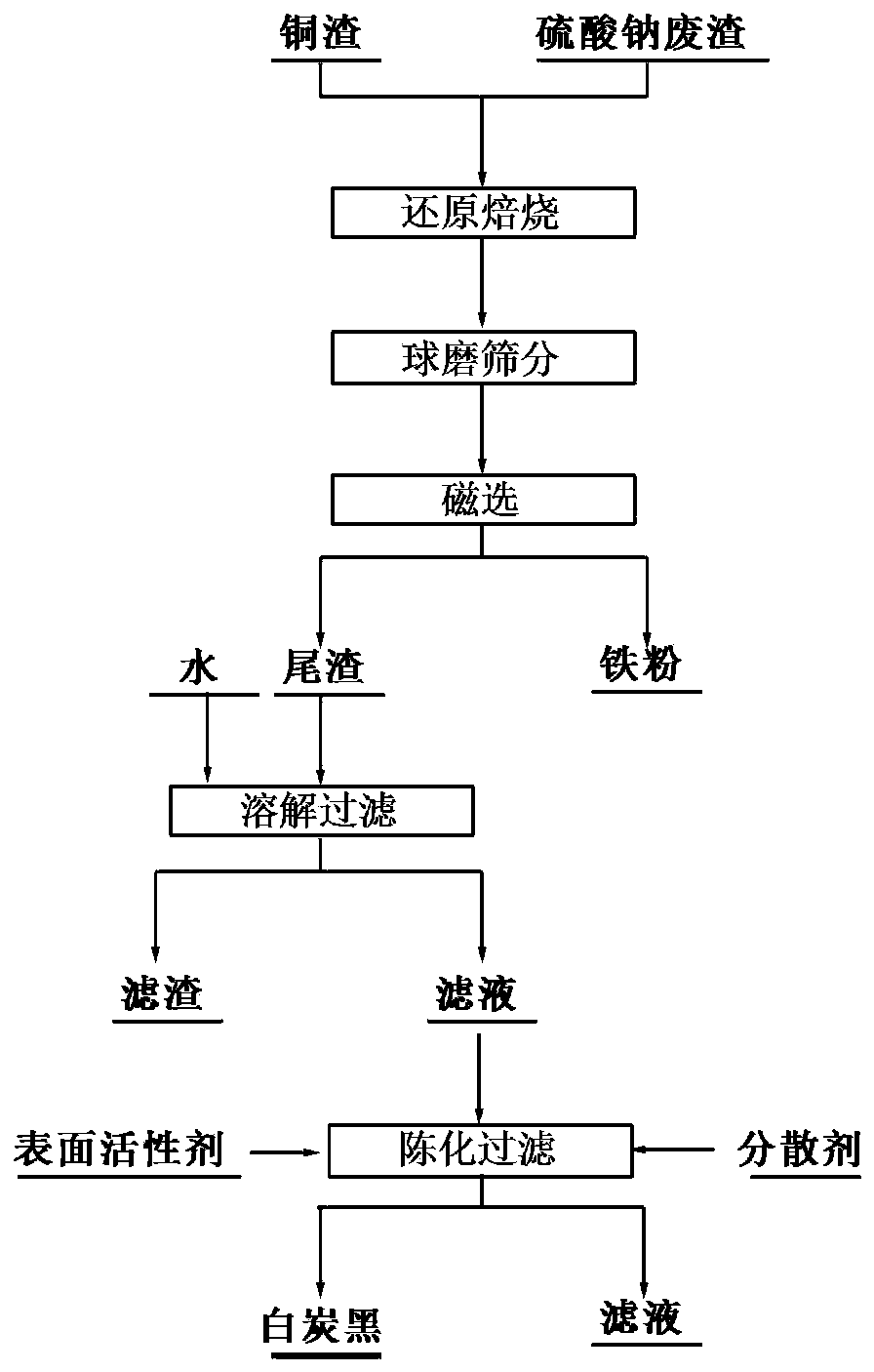
Method for cooperatively recycling copper slag and sodium sulfate waste residues
A sodium sulfate and recycling technology, applied in the direction of silicon oxide, silicon dioxide, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of bulk consumption and processing difficulties, high site requirements, easy water absorption and deliquescence, etc., and achieve technical operability Strong, heavy metal grade improvement, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
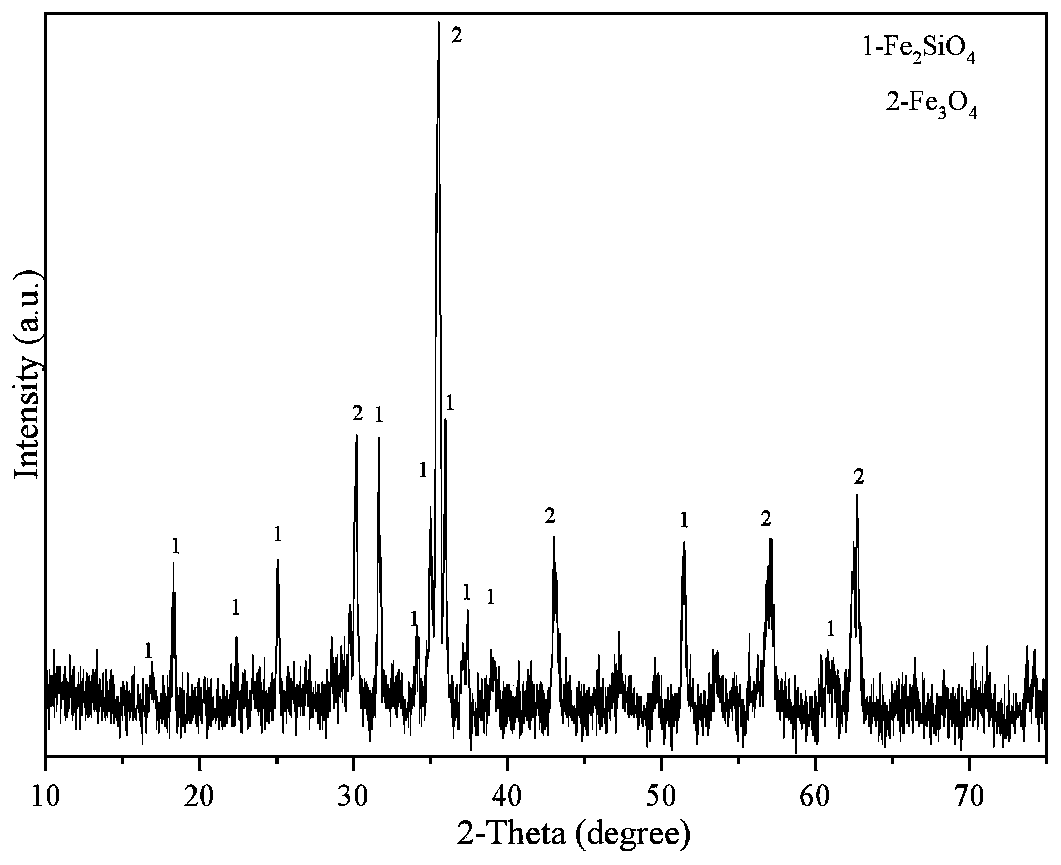
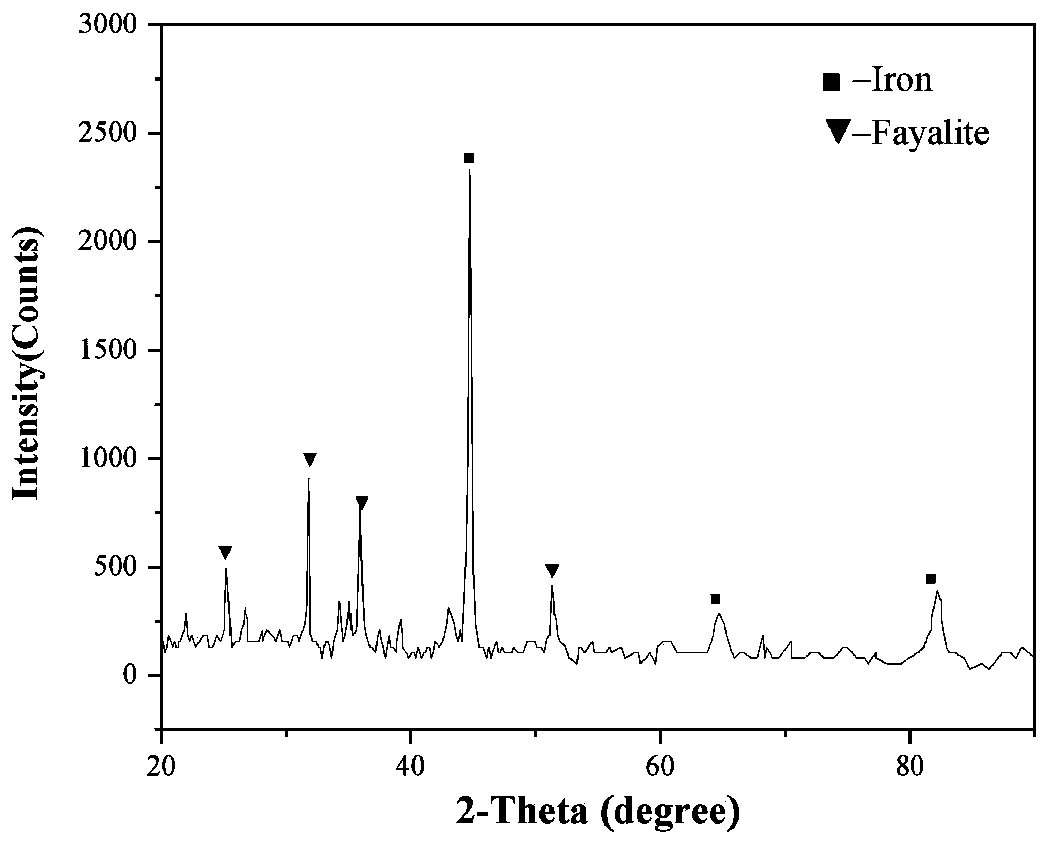
[0047] First, weigh 1 kg of copper slag ball mill and pass it through a 200-mesh sieve, mix it with sodium sulfate waste slag at a mass ratio of 1:1, and keep it warm for 120 minutes in a CO atmosphere at 1000°C; Magnetic separator, magnetic separation under 1200G field strength, to obtain iron powder, iron powder XRD analysis see image 3 . Pour the magnetic separation tailings into 1.5L water and stir for a certain period of time before filtering; obtain about 1.2L filtrate and age at a constant temperature for 720min at 50°C, then heat up to 80°C in a water bath; while stirring, add 120mL of 10wt% dispersant NaCl, 120ml concentration is 70wt% surfactant n-butanol; While stirring the obtained solution, add sulfuric acid with a concentration of 5wt% dropwise, adjust the pH value to 8-9, keep 80°C for constant temperature aging for 180min and then filter; filter residue with deionized Wash and filter with water for 6 times, and then dry at 100°C to obtain white carbon black. ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] First, weigh 1 kg of copper slag ball mill and pass it through a 200-mesh sieve, mix it with sodium sulfate waste slag at a mass ratio of 2:1, and keep it warm at 900°C for 60 minutes in natural gas; Separator, conduct magnetic separation under 1200G field strength to obtain iron powder, pour the magnetic separation tailings into 1.5L water and stir for a certain period of time, then filter; obtain about 1.2L filtrate, age at a constant temperature of 60°C for 900min, and then heat up to 70°C in a water bath ℃; while stirring, adding 120ml concentration of 15wt% dispersant NaCl and 100ml concentration of 80wt% surfactant n-butanol respectively; while stirring the gained solution, adding concentration dropwise is 10wt% sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value to 8~ 9. Keep aging at a constant temperature of 50°C for 240 minutes and then filter; wash the filter residue with deionized water repeatedly-filter 5 times, and then dry the filter residue at 90°C to obtain white carbo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com