Small proteins and application thereof
A protein and G protein technology, applied in the field of small proteins, can solve the problems of poor structural stability of polypeptide inhibitors, not conducive to the design of small molecule inhibitors, and no deep binding pockets, etc., to achieve weak IgG binding ability and no T cells Depleted side effects, good tissue penetration effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1 Comparison of the preferred small protein sequence and the wild-type GB1 backbone sequence
[0069] Table 1 lists the 11 mutant small proteins and skeleton protein GB1 involved in this example. Each of the mutant small proteins can be obtained through simple prokaryotic expression, and the prokaryotic expression vector of the small protein is obtained by molecular cloning, and then expressed by prokaryotic, and the pure mutant small protein can be obtained by affinity purification. Wherein, the prokaryotic expression process of the small protein is as follows: the prokaryotic expression plasmid of each mutant small protein can be obtained by molecular cloning. After the plasmid sequence is correct, it is chemically transformed into BL21(DE3) competent E. coli cells, and the cells are cultured overnight in LB medium containing antibiotics consistent with the plasmid resistance gene (such as LB medium containing kanamycin for pET28a) , to obtain overnight bacte...
Embodiment 2
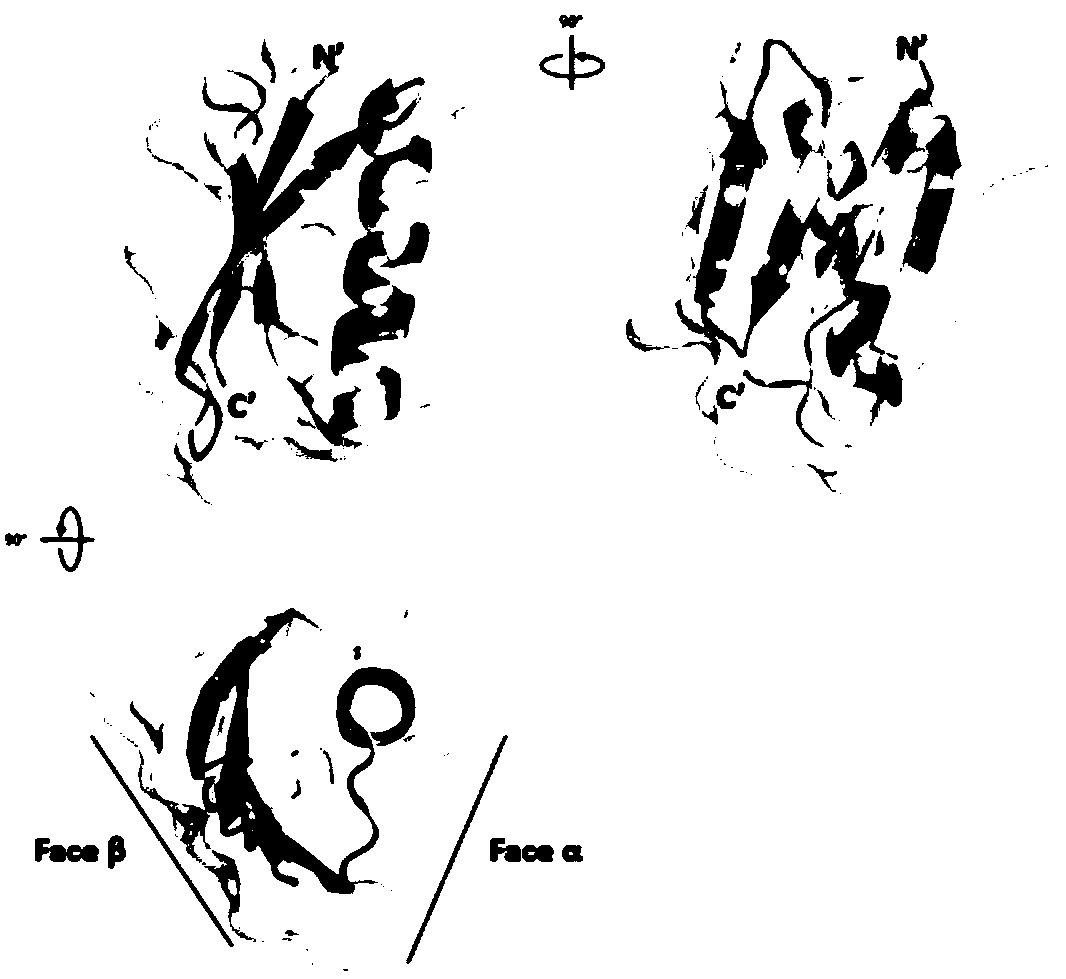
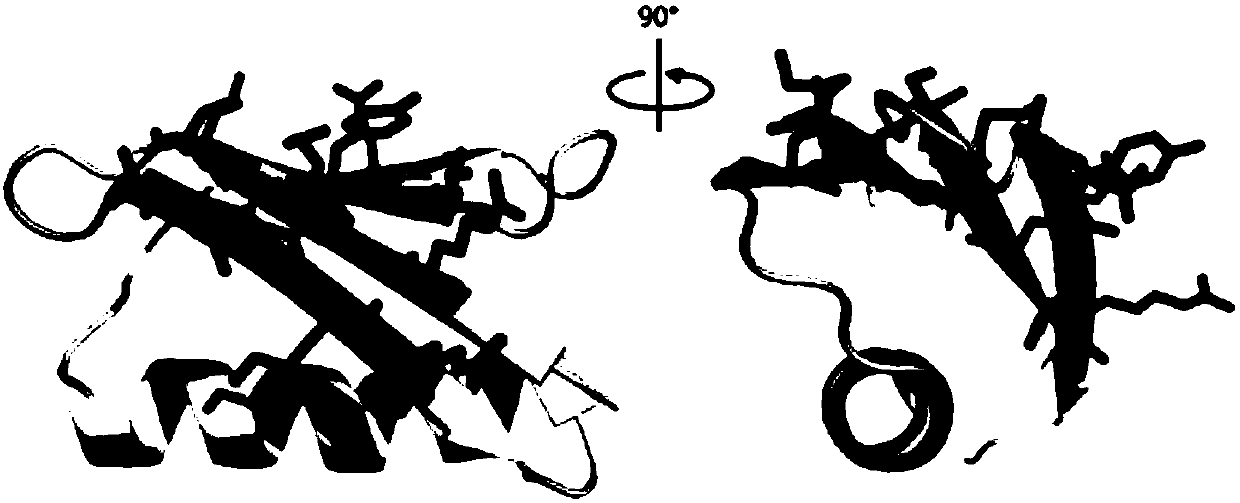
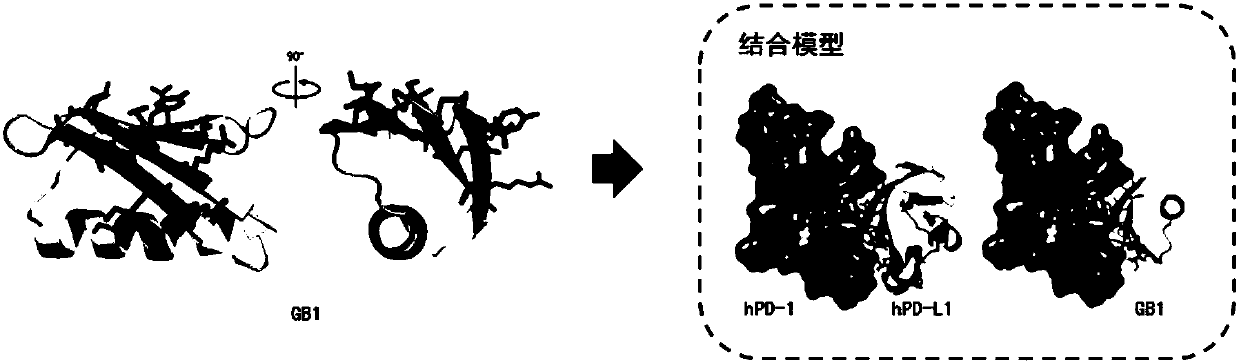
[0073] Example 2 Comparison of conformation similarity between small protein backbone and PD-L1 protein
[0074] Using the pair fitting function of the PyMOL software Wiazrd menu, select the C of 12 key amino acids on the binding surface of PD-L1 and PD-1 α Position C corresponding to the β sheet of the small protein backbone α For comparison, according to the root mean square deviation (root-mean-square deviation, RMSD, the unit is ) to evaluate the similarity between the small protein surface and the PD-L1 structure, the smaller the value, the closer the spatial structure, when , the representative structure is completely overlapped. The RMSD comparison values of selected small protein backbones and PD-L1 were all within Left and right, the RMSD value of the GB1 skeleton and PD-L1 selected in the present invention is only Such as Figure 5 As shown in Table 2, Table 2 lists the RMSD values obtained from the comparison of the conformational similarity between t...
Embodiment 3
[0078] 1) Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) detection of mutant small protein 8 inhibiting PD-1 / PD-L1 binding
[0079] SPR detection is to detect the change of the chip's refractive index and reflect the change of the weight of the binding substance on the chip surface. When the analyte flows through the chip surface and binds to the coupled ligand on the chip, the chip's refractive index changes, and the instrument records the response of the change. Value (Response Unit, RU). The RU value reflects the change in the weight of the conjugate on the chip surface, reflecting the binding or dissociation of the analyte and the ligand. Such as Figure 6As shown, the PD-1 protein was coupled on the chip, and different concentrations of GB1 mutant GBM8 were mixed in the analyte PD-L1. With the increase of the concentration of GB1 mutant GBM8, the combination of PD-L1 and PD-1 decreased, It reflects the inhibitory effect of GB1 mutant GBM8 on the binding of PD-1 / PD-L1.
[0080] 2) Sur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com