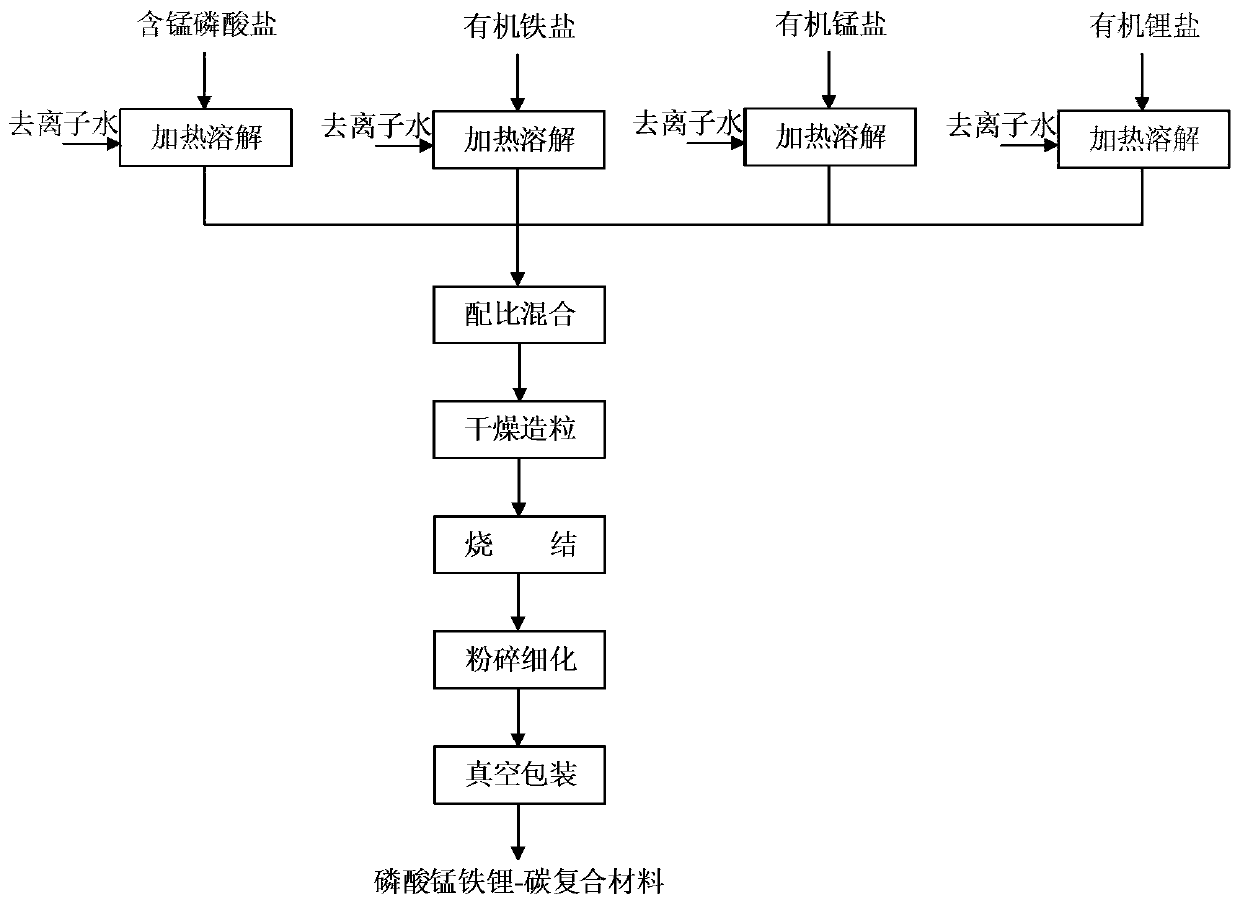
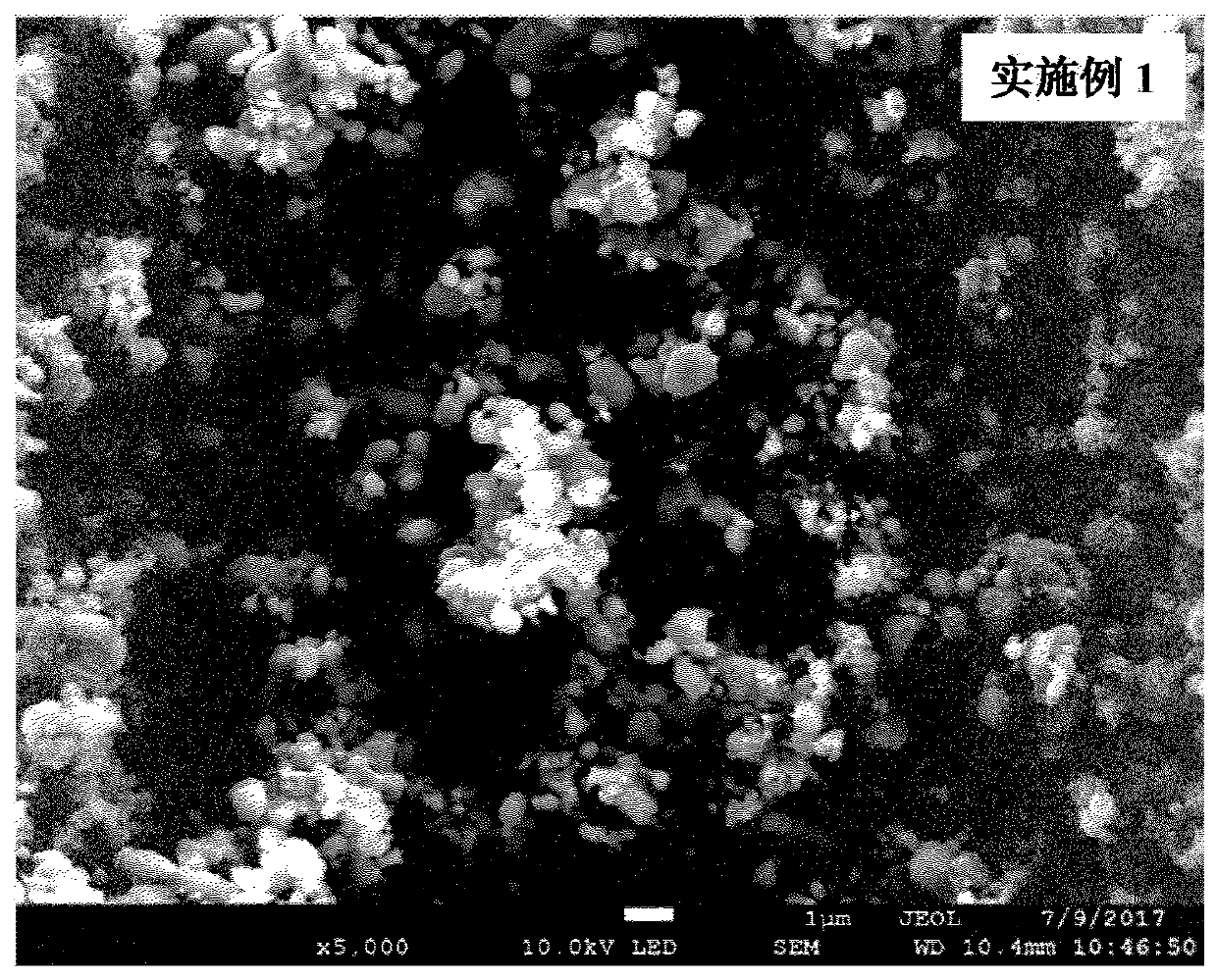
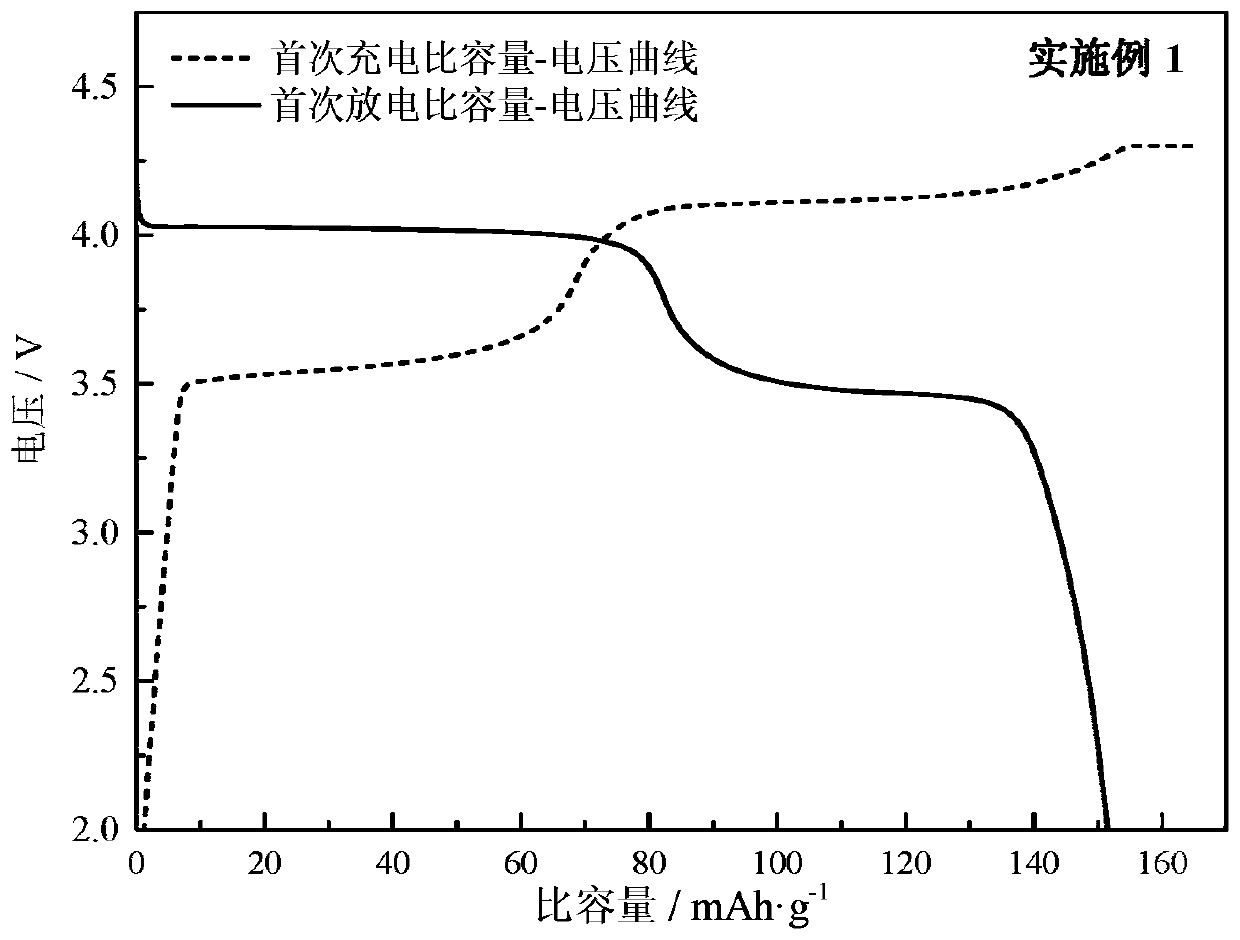
Method for preparing manganese phosphate iron phosphate-carbon composite material and manganese phosphate iron phosphate-carbon composite material
A technology of lithium manganese iron phosphate and carbon composite materials, applied in structural parts, electrical components, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of poor cycle performance, low specific capacity, high resistivity, etc., and achieve simple preparation method and short process flow , the effect of reducing the difficulty of preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0089] 1.1 Preparation of soluble manganese-containing phosphate solution
[0090]Soluble manganese-containing phosphate is added to deionized water according to the solute mass fraction of 10% to 60%, and phosphoric acid can optionally be added as a regulator of phosphorus content and pH value to prevent the generation of solid insolubles. Phosphoric acid (according to pure Phosphoric acid) is added in an amount no more than 15% of the manganese-containing phosphate mass, and solution A is prepared.
[0091] The soluble manganese-containing phosphate may be manganese dihydrogen phosphate.
[0092] The phosphoric acid can be pure phosphoric acid or phosphoric acid aqueous solution, such as concentrated phosphoric acid.
[0093] In this field, commonly used manganese sources can be divided into insoluble manganese sources and soluble manganese sources according to water solubility. Insoluble manganese sources mainly include manganese oxalate, manganese carbonate, manganese dio...
Embodiment 1
[0148] (1) Preparation of soluble salt solution
[0149] a. Take by weighing 27.92kg manganese dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate (wherein by mass, Mn content is 15.01%, P content is 21.90%, the same below), 1.44kg concentrated phosphoric acid (mass fraction is 85%) in 100kg deionized water , at a temperature of 45°C, stirring and dissolving to obtain a manganese dihydrogen phosphate solution;
[0150] b. Weigh 28.00kg ferric citrate pentahydrate (by mass, purity ≥ 99.5%, the same below) in 60kg deionized water, stir and dissolve at a temperature of 30°C to obtain ferric citrate solution;
[0151] c. take by weighing 11.93kg manganese acetate tetrahydrate (by mass, purity ≥ 99.5%, the same below) in 20kg deionized water, stir and dissolve to obtain manganese acetate solution;
[0152] d. Weigh 21.46kg lithium acetate dihydrate (by mass, purity ≥ 99.5%, the same below) in 40kg deionized water, stir and dissolve to obtain lithium acetate solution;
[0153] (2) According to the ele...
Embodiment 2
[0158] The main difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that ferrous lactate is used instead of ferric citrate pentahydrate as the soluble organic iron salt to prepare lithium manganese iron phosphate-carbon composite material. details as follows:
[0159] (1) Preparation of soluble salt solution
[0160] a. Take by weighing 27.92kg manganese dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 0.46kg concentrated phosphoric acid (mass fraction is 85%) in 80kg deionized water, at a temperature of 65°C, stir and dissolve to obtain manganese dihydrogen phosphate solution;
[0161] B. take by weighing 22.86kg ferrous lactate trihydrate (by mass, purity ≥ 99.5%, the same below), 1.14kg ascorbic acid in 200kg deionized water, at a temperature of 65 ° C, stir and dissolve to obtain ferrous lactate solution;
[0162] c. take by weighing 10.39kg manganese acetate tetrahydrate in 35kg deionized water, stir and dissolve to obtain manganese acetate solution;
[0163] d. Take by weighing 22.27kg lithi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com