Method of determining major elements in ferrotitanium through X-fluorescence fuse piece method
A titanium-iron alloy and fusing technology, which is applied in the field of physical and chemical detection, can solve the problems of low ammonium iodide residue, fast decomposition and volatilization speed, and fragmentation of samples, so as to eliminate the risk of corrosion, solve the particle size effect, and improve the oxidation ability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0027] 2), preparation and storage of composite oxidizing agent: bake the required reagents potassium nitrate, boric acid, and sodium carbonate solid at 105°C for 1 hour respectively, take them out and place them in a desiccator to cool, and the three kinds of potassium nitrate, boric acid, and sodium carbonate The solid reagent is mixed and prepared according to the mass 1: (1-1.2): (3-5);
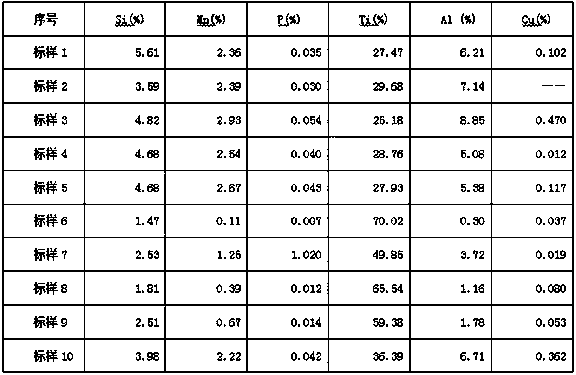
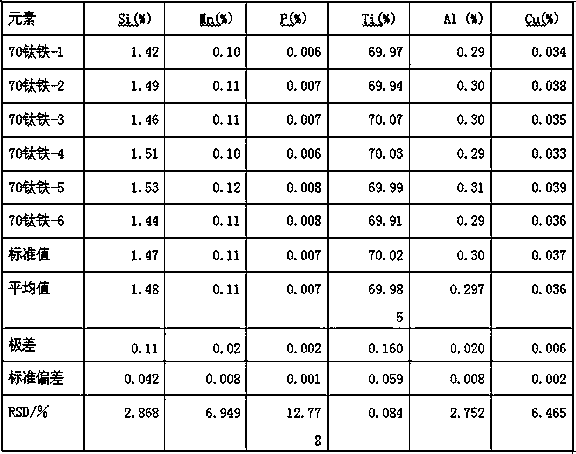
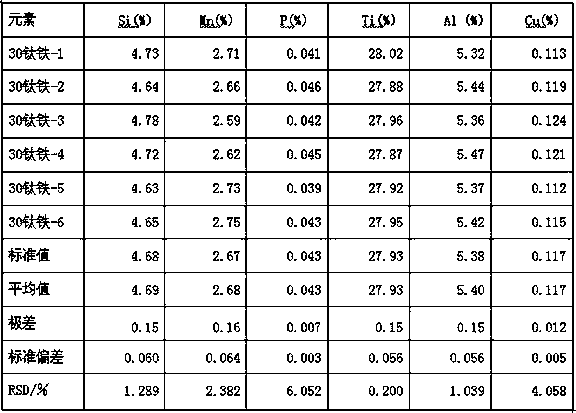
[0028] 3), preparation of working curve standard sample: Weigh 0.1-0.3g standard sample in a porcelain crucible, add compound oxidant and 0.2-0.5g viscosity reducer relative to the quality of standard sample 10-20 times, stir evenly, in Weigh into the platinum crucible the flux lithium tetraborate 10 to 50 times the mass of the standard sample, stir evenly, and make the central area slightly depressed, completely pour the standard sample in the porcelain crucible into the depression, place it in the muffle furnace from room temperature to The speed of 15-20°C / min is raised from room tempe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com