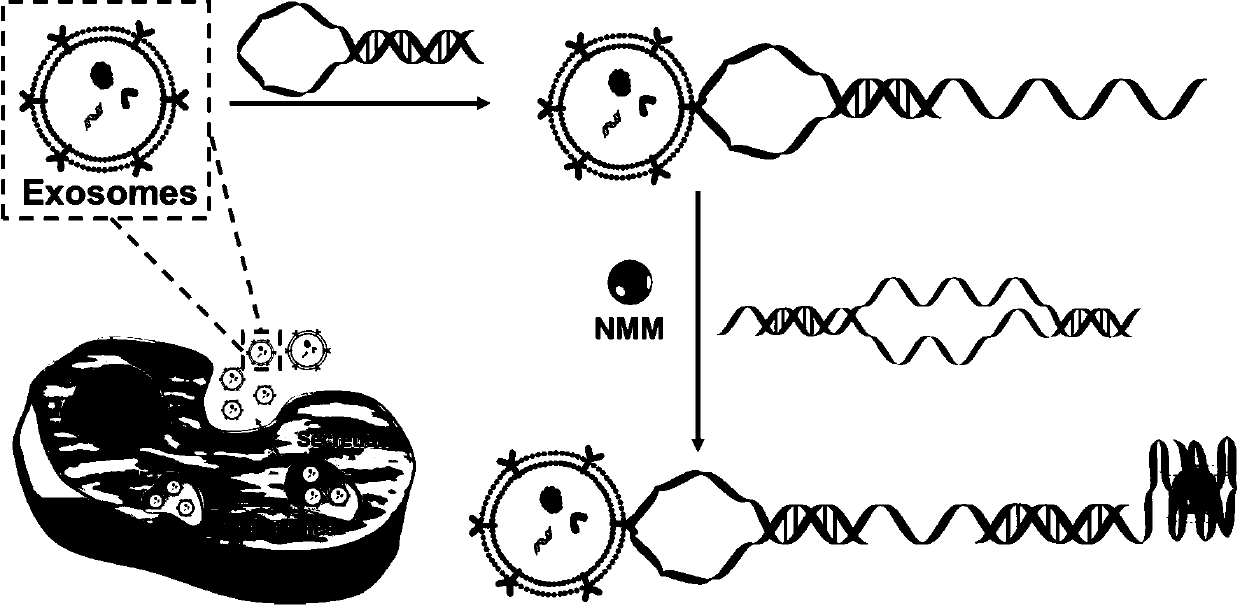
Self-assembly probe based on configuration change and unlabeled detection method for exosomes thereof
A technology for configuration change and detection method, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as background interference and affecting the efficiency of identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In this example, a self-assembly probe based on configuration change is used for a label-free detection method of exosomes, and the steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Cell culture: CCRF-CEM, Ramos, Hela, B16F1 and HL-7702 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% exosomes (fetal bovine serum removed) and 100IU / mL penicillin or streptomycin cultured at 37 °C with 5% wt / vol CO 2 Incubate in a humid incubator for 48 hours, and collect the cell supernatant when the cells grow to 80-90%;
[0038] (2) Isolation of exosomes: The cell supernatant obtained in step (1) was centrifuged at 3,000g for 30 minutes at 4°C, and filtered through a syringe-driven filter unit to remove intact cells and cell debris, collected by filtration and concentrated using 100KDaMWCO at 5,000g at 4°C for 30 minutes, then the filtered medium was ultracentrifuged at 160,000g for 2 hours at 4°C, the supernatant was discarded, and the exosome pellet was resuspended in phosphate buffered...
Embodiment 2
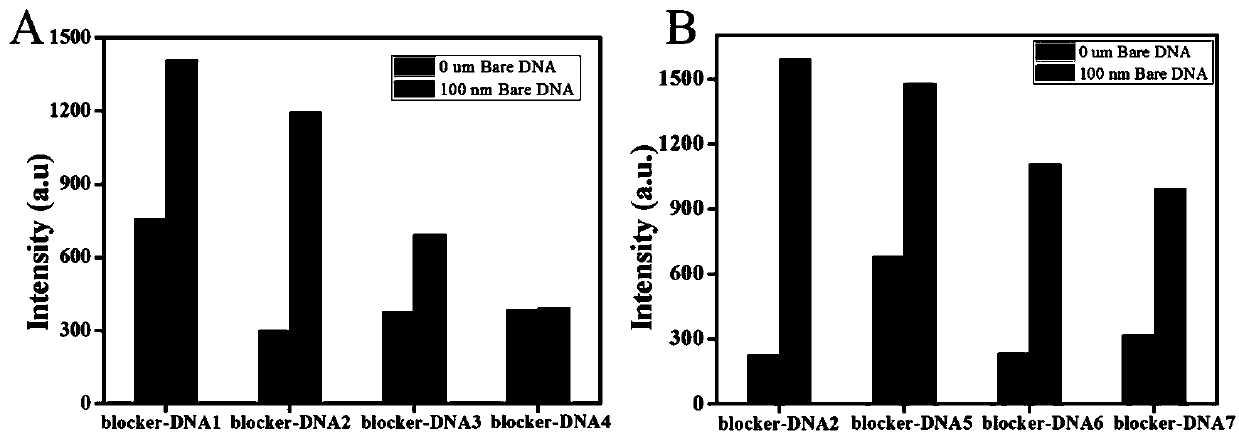
[0042] In this embodiment, in order to further study the hybridization and binding ability of G4-DNA and different blocker-DNAs, eight sets of Blocker DNA sequences are designed such as SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.5, SEQ ID NO .6, shown in SEQ ID NO.7, SEQ ID NO.8, SEQ ID NO.9 and SEQ ID NO.10; refer to the steps of Example 1 for fluorescence detection. First, a Bare DNA strand is designed, which contains the complete priming region bases, to simulate the probe recognition of exosomes, which can be used to trigger the strand displacement reaction and release G4. Test results such as figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that by using BlockerDNA-2, when there is Bare DNA, the maximum fluorescence enhancement can be obtained, which is significantly higher than that of blocker DNA-1, blockerDNA-3, blocker DNA-4, Blocker DNA-5, Blocker DNA-6 and Blocker DNA- 7. Therefore, blocker DNA-2 was selected as the best blocker DNA for subsequent experiments, and it was nam...
Embodiment 3
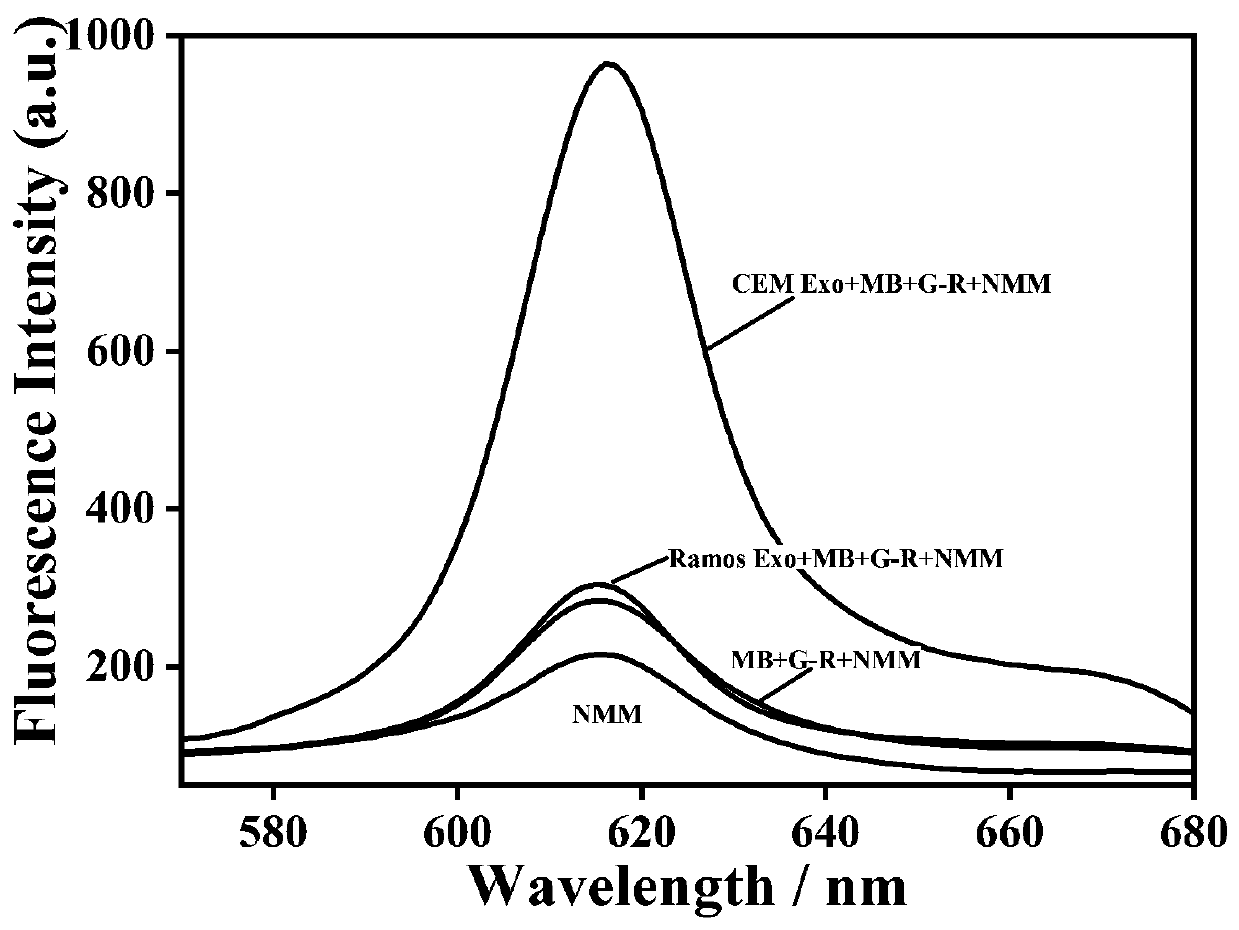
[0044] In this example, in order to prove the feasibility of the experimental principle, the fluorescence intensity of the system under different conditions was studied. The test results are shown in image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen that in the absence of target exosomes (red curve) and control exosomes (blue curve), there is no obvious fluorescence signal, indicating that the present invention has a lower fluorescence background. After the target exosomes were introduced into the above mixed solution, a significant fluorescence enhancement could be observed around 615 nm (green curve), which indicated that the G-rich sequence was exposed and folded into a quadruple structure. These results demonstrate that this experimental platform can be used for the specific detection of leukemia-associated exosomes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com