Strontium titanate/strontium ruthenate ferroelectric superlattice film material and preparation method thereof
A thin-film material, superlattice technology, applied in metal material coating process, ion implantation plating, coating and other directions, can solve problems such as no practical value, and achieve the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
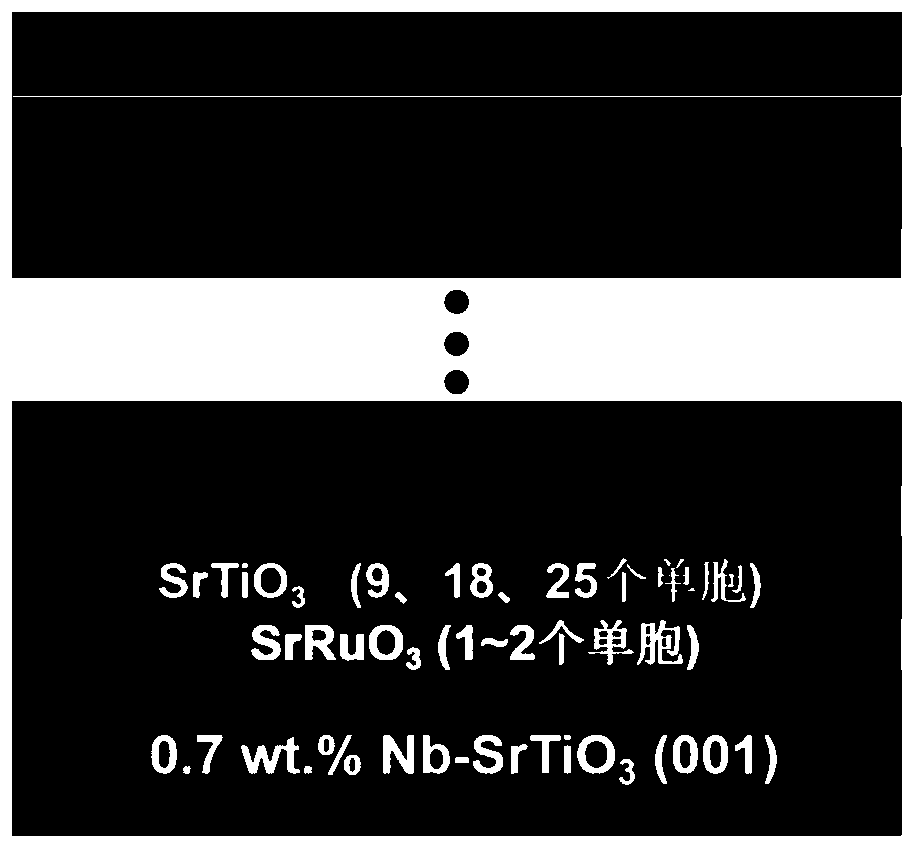
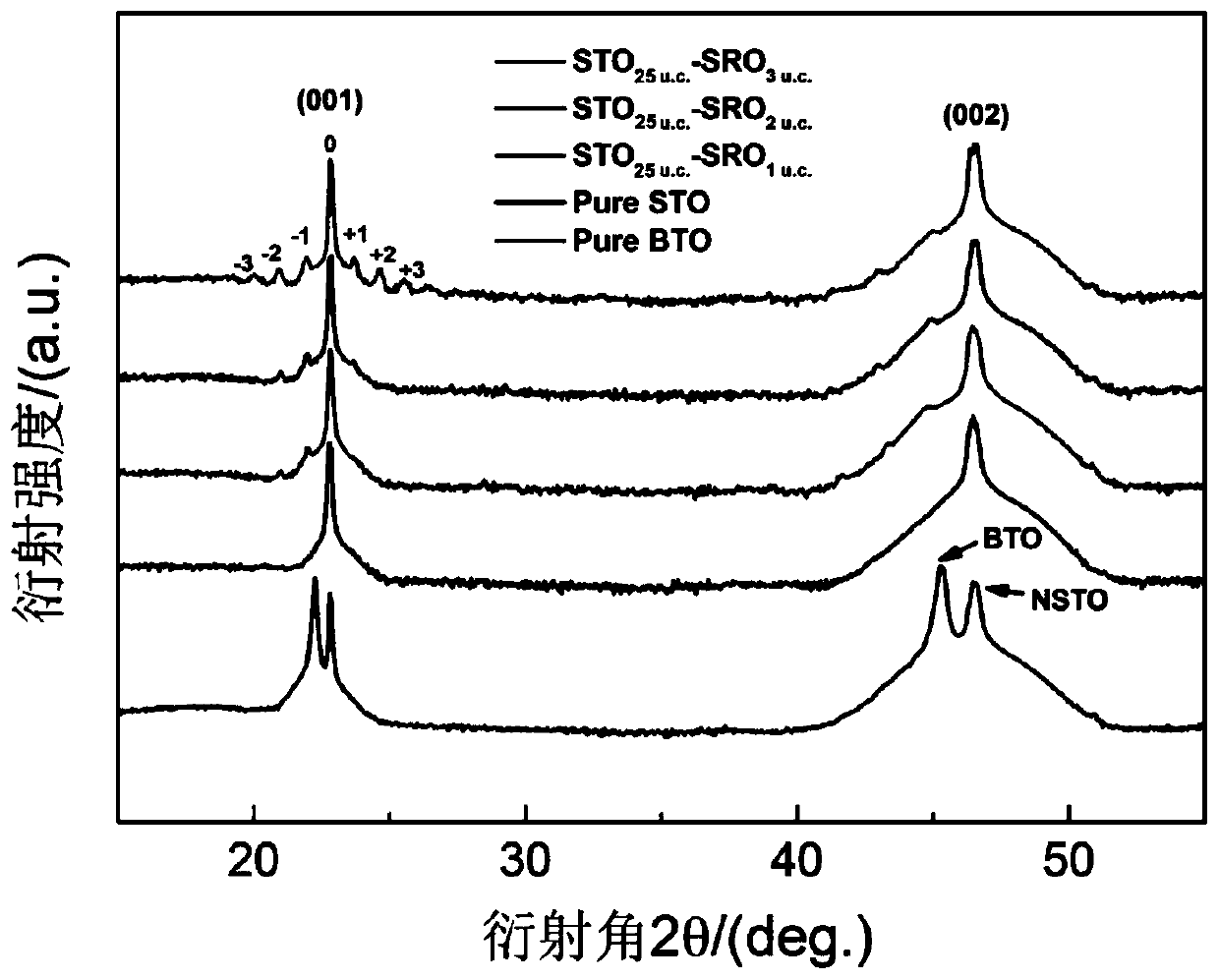
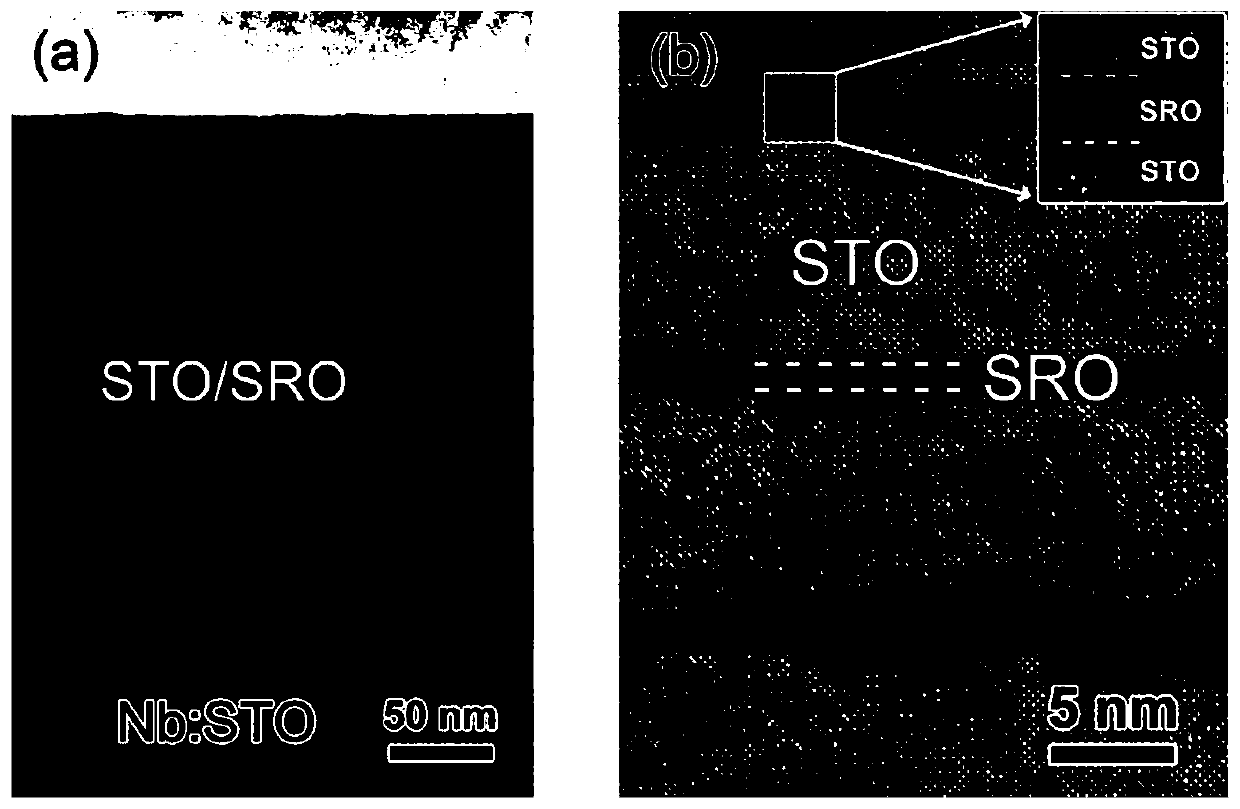
[0032] STO-25 / SRO-1 ferroelectric superlattice material
[0033] (1) Nb-SrTiO 3 (001) The substrate was cleaned with acetone and ethanol for 10 minutes respectively, then placed in the deposition chamber, heated to 750° C. in vacuum, and kept for 30 minutes;
[0034] (2) Under the conditions of a deposition temperature of 650°C and an oxygen pressure of 20Pa, the strontium ruthenate target was bombarded with a pulsed laser, so that the Nb-SrTiO 3 A strontium ruthenate layer with a thickness of 1 unit cell is deposited on the (001) substrate. Then convert the target to strontium titanate, and deposit a strontium titanate layer with a thickness of 25 unit cells on the strontium ruthenate layer;
[0035] (3) Repeat the process of (2) 25 times to prepare the STO-25 / SRO-1 ferroelectric superlattice thin film material.
[0036] (4) Before the electrical performance test, the surface of the ferroelectric superlattice film obtained by magnetron sputtering is coated with an area of ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] STO-25 / SRO-2 Ferroelectric Superlattice Materials
[0040] (1) Nb-SrTiO 3 (001) The substrate was cleaned with acetone and ethanol for 10 minutes respectively, then placed in the deposition chamber, heated to 750° C. in vacuum, and kept for 30 minutes;
[0041] (2) Under the conditions of a deposition temperature of 650°C and an oxygen pressure of 20Pa, the strontium ruthenate target was bombarded with a pulsed laser, so that the Nb-SrTiO 3 A strontium ruthenate layer with a thickness of 2 unit cells was deposited on the (001) substrate. Then bombard the strontium titanate target with a pulsed laser, and deposit a strontium titanate layer with a thickness of 25 unit cells on the strontium ruthenate layer;
[0042] (3) Repeat the process of (2) 24 times to prepare the STO-25 / SRO-2 ferroelectric superlattice thin film material.
[0043] (4) Before the electrical performance test, the surface of the ferroelectric superlattice film obtained by magnetron sputtering is coa...
Embodiment 3
[0046] STO-18 / SRO-1 Ferroelectric Superlattice Materials
[0047] (1) Nb-SrTiO 3 (001) The substrate was cleaned with acetone and ethanol for 10 minutes respectively, then placed in the deposition chamber, heated to 750° C. in vacuum, and kept for 30 minutes;
[0048] (2) Under the conditions of a deposition temperature of 650°C and an oxygen pressure of 20Pa, the strontium ruthenate target was bombarded with a pulsed laser, so that the Nb-SrTiO 3 A strontium ruthenate layer with a thickness of 1 unit cell is deposited on the (001) substrate. Then use a pulsed laser to bombard the strontium titanate target, and deposit a strontium titanate layer with a thickness of 18 unit cells on the strontium ruthenate layer;
[0049] (3) Repeat the process of (2) 33 times to prepare the STO-18 / SRO-1 ferroelectric superlattice thin film material.
[0050] (4) Before the electrical performance test, the surface of the ferroelectric superlattice film obtained by magnetron sputtering is coa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Remanent polarization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Remanent polarization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Remanent polarization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com