Method for treating aluminum electrolytic cell anode carbon slag by using nacl molten salt extraction method
An aluminum electrolytic cell and anode carbon technology, which is applied in the fields of metallurgy and environmental protection, can solve the problems of high labor intensity of workers, complex process, loss of secondary dissolution of aluminum, etc., and achieves saving pretreatment time and cost, simple treatment process, and easy acquisition. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
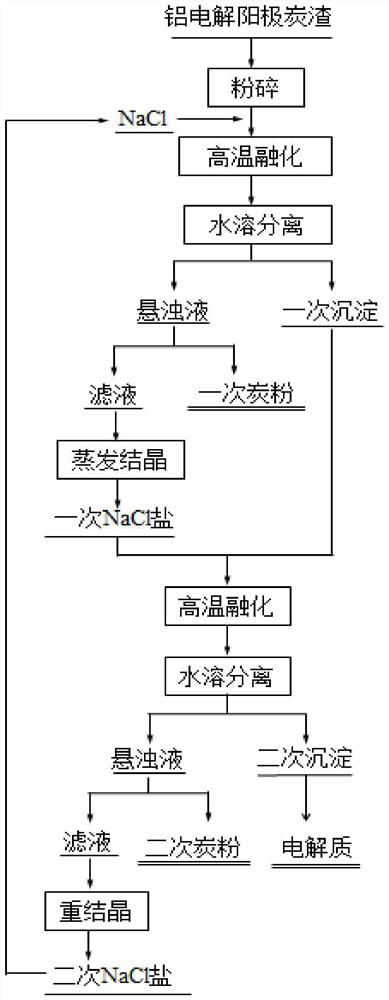
[0038] Process such as figure 1 shown;
[0039] Crush the large pieces of anode carbon slag in the aluminum electrolytic cell to make crushed carbon slag with a particle size of ≤20mm; the elemental composition of the anode carbon slag in the aluminum electrolytic cell contains 29.7% of C, 16.6% of Na, 11.3% of Al, F 34.1%; where Na, Al and F are electrolyte components;
[0040] Mixing the pulverized carbon residue and NaCl evenly to make a mixed material, the mass ratio of NaCl and the pulverized carbon residue in the mixed material is 4;
[0041] Put the mixed material into the crucible, then place it in an electric furnace and raise the temperature to 880°C. When the mixed material is completely melted, a mixed molten salt consisting of NaCl, electrolyte and carbon is obtained;
[0042] Cool the molten salt mixture with the furnace until it solidifies to obtain a solidified mixed salt; put the solidified mixed salt in water and stir to dissolve the water-soluble component...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The method is the same as the embodiment, the difference is:
[0050] (1) The mass ratio of NaCl and pulverized carbon residue in the mixed material is 2;
[0051] (2) The mixture is heated to 900°C and melted;
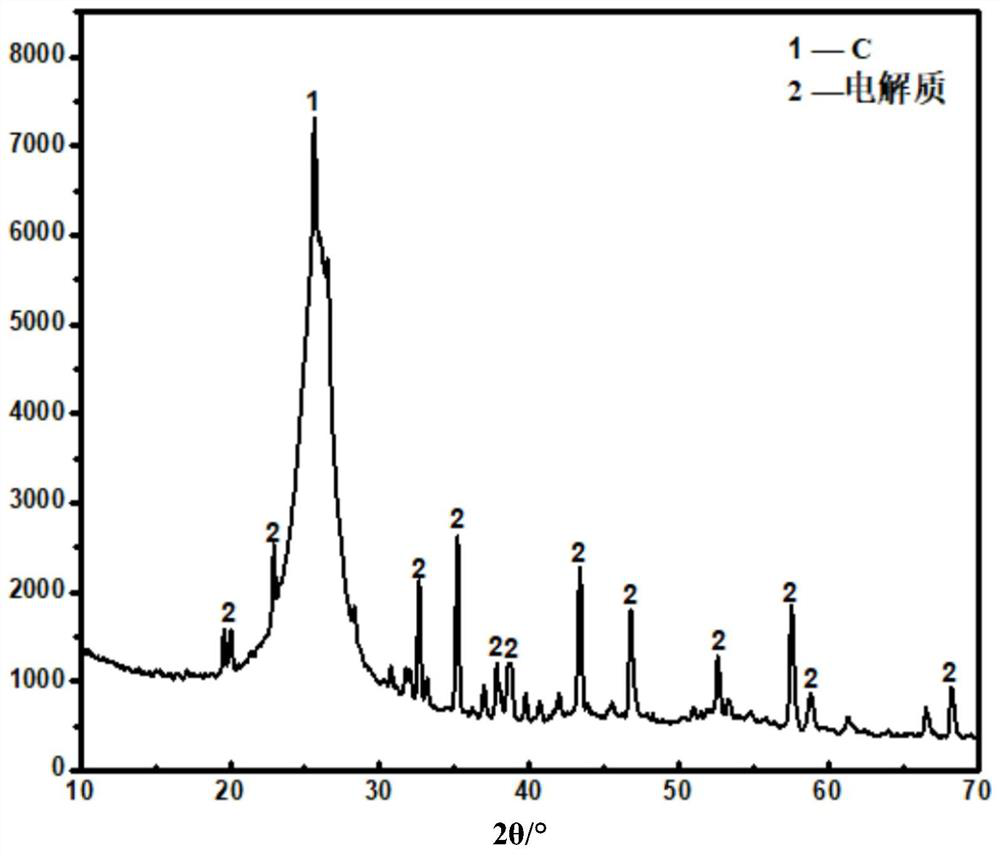
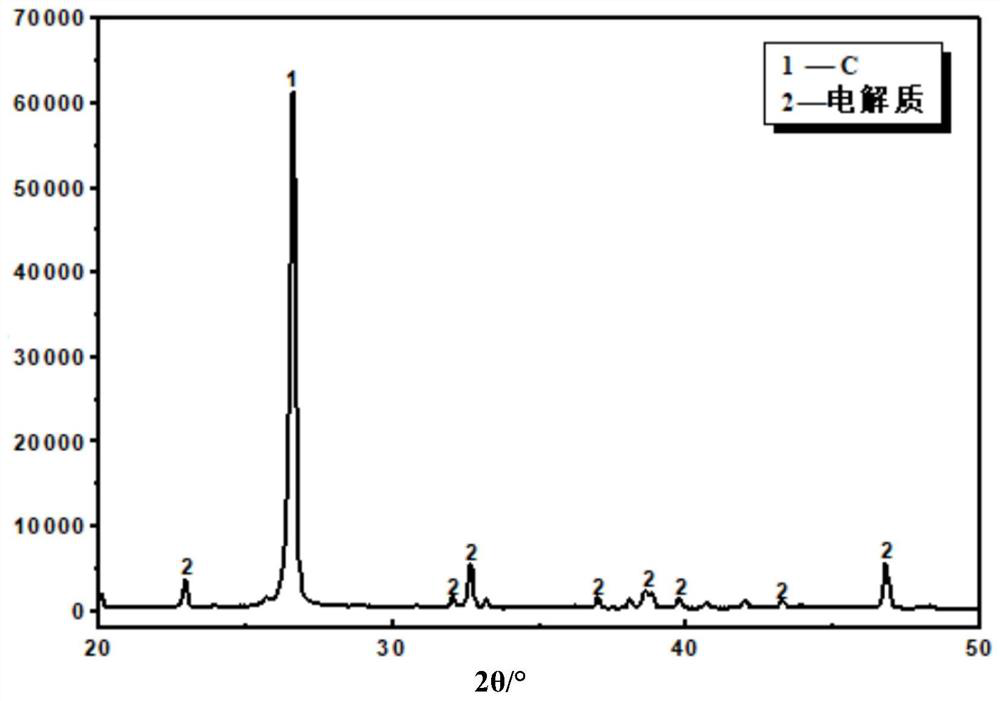
[0052] (3) The purity of the electrolyte is 90.3%; the C recovery rate of the primary carbon powder and the secondary carbon powder is 85%; the mixture of the primary carbon powder and the secondary carbon powder contains 88% of C by mass percentage.
Embodiment 3
[0054] The method is the same as the embodiment, the difference is:
[0055] (1) the mass ratio of NaCl and pulverized carbon residue in the mixed material is 3;
[0056] (2) The mixture is heated to 950°C and melted;
[0057] (3) The purity of the electrolyte is 90.6%; the C recovery rate of the primary carbon powder and the secondary carbon powder is 86%; the mixture of the primary carbon powder and the secondary carbon powder contains 86% of C by mass percentage.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com