Antioxidant polypeptide and preparation method thereof
A technology for antioxidant polypeptides and seeds, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as cost reduction, inability to achieve, and complex preparation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
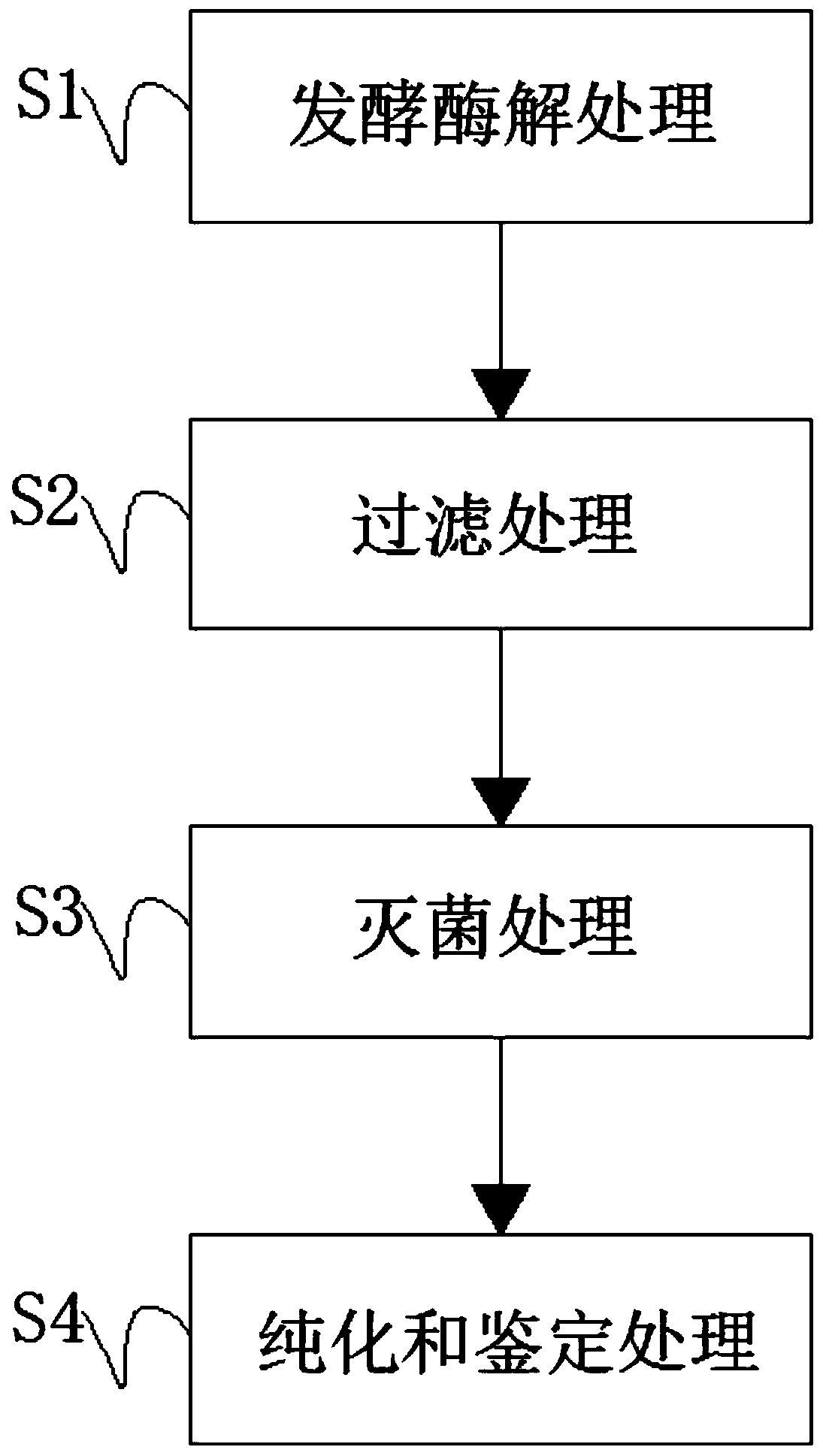
[0027] S1. Fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis treatment: firstly, 7 parts of animal serum albumin, 7 parts of zein, 7 parts of ovalbumin, 7 parts of wheat prolamin, 15 parts of casein, 15 parts of oilseed protein and 15 parts of soybean were selected Pour the protein into the fermenter respectively, then add 35mL of warm water, then inoculate the fermentation strain, start the heating equipment, control the temperature of the fermenter at 30°C, and adjust the pH within the range of 6, then add 16mL of hydrolyzate to the fermenter The protease was stirred for 25 minutes by a stirring device at a speed of 250r / min. After the mixing was completed, the fermenter was sealed and fermented for 14 hours. The oilseed proteins were peanut seed protein, sesame seed protein, rapeseed The composition of flower seed protein and coconut seed protein, animal serum albumin is the composition of porcine serum albumin, sheep serum albumin and bovine serum albumin;
[0028] S2. Filtration trea...
Embodiment 2
[0032]S1. Fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis treatment: firstly, the selected 5 parts of animal serum albumin, 5 parts of zein, 5 parts of ovalbumin, 5 parts of wheat prolamin, 20 parts of casein, 20 parts of oilseed protein and 20 parts of soybean Pour the protein into the fermenter respectively, then add 30mL of warm water, then inoculate the fermentation strain, start the heating equipment, control the temperature of the fermenter at 26°C, and adjust the pH within the range of 5, then add 12mL of hydrolyzate to the fermenter The protease was stirred by a stirring device at a speed of 200r / min for 20 minutes. After the mixing was completed, the fermenter was sealed and fermented for 12 hours. The oilseed protein was peanut seed protein, and the animal serum albumin was porcine serum albumin;
[0033] S2. Filtration treatment: transfer the material after the fermentation in step S1 to a filtration device, perform filtration treatment through an ultrafiltration membrane, fil...
Embodiment 3
[0037] S1. Fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis treatment: first, 10 parts of animal serum albumin, 10 parts of zein, 10 parts of ovalbumin, 10 parts of wheat prolamin, 10 parts of casein, 10 parts of oilseed protein and 10 parts of soybean were selected Pour the protein into the fermenter respectively, then add 40mL of warm water, then inoculate the fermentation strain, start the heating equipment, control the temperature of the fermenter at 33°C, and adjust the pH within the range of 7, then add 20mL of hydrolyzate to the fermenter The protease was stirred for 30 minutes by a stirring device at a speed of 300 r / min. After the mixing was completed, the fermenter was sealed and fermented for 16 hours. The oil seed protein was coconut seed protein, and the animal serum albumin was bovine serum albumin;
[0038] S2. Filtration treatment: transfer the material after the fermentation in step S1 to a filtration device, perform filtration treatment through an ultrafiltration membran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com