Lithium supplementing additive for lithium ion battery, battery electrode and preparation method and application thereof
A lithium-ion battery and additive technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, hidden safety hazards, and complicated operation processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0065] The preparation method of the lithium supplement additive includes: a high-temperature solid-phase method, a liquid-phase method, a vapor-phase method, and the like.
[0066] The lithium sources used in the preparation method include but are not limited to lithium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, lithium nitrate, lithium chloride, lithium sulfide, lithium fluoride, lithium oxide, metallic lithium, organic lithium sources (including but not limited to butyl lithium, phenyllithium, ethyllithium).
[0067] A lithium ion battery, containing the above-mentioned lithium supplement additive, positive electrode material and negative electrode material, its positive electrode material is lithium cobaltate, lithium manganate, lithium nickelate, lithium nickel manganate, lithium nickel cobalt manganate, nickel cobalt Lithium aluminate, lithium-rich lithium manganate, lithium iron phosphate, lithium vanadium phosphate, lithium manganese phosphate, lithium cobalt phosphate, or a combin...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1 Lithium supplement additive, positive electrode material and application in lithium ion battery
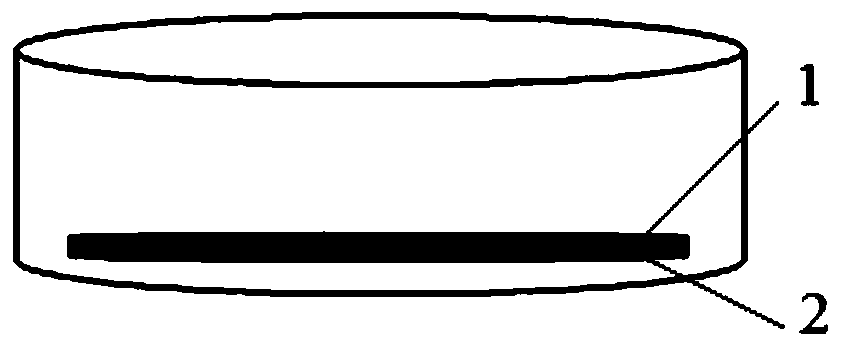
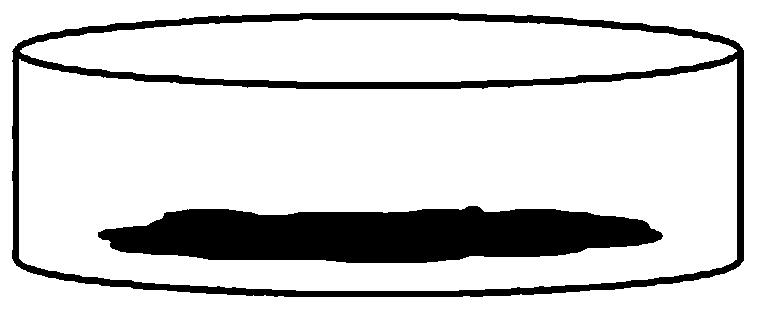
[0077] Get 0.3g lithium sheet in iron crucible, 0.46g red phosphorus (analytical pure) is tiled on the surface of lithium sheet (such as figure 1 shown), placed on a heating table, heated at 300°C for 1 h in an Ar atmosphere in a glove box, cooled naturally and fully ground, then heated at 300°C for 0.5 h in an Ar atmosphere in a glove box, and then heated to 450°C 1h (obtained product such as figure 2 shown), get Li 3 P additive.
[0078] Preparation of positive electrode slurry: this embodiment obtains Li 3 P additive and positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate (LFP), conductive carbon black (SP), binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) according to the required weight ratio of 5:70:15:10, a total of 2.0g was added to 6.6mlN - In methylpyrrolidone (NMP), after fully mixing, a positive electrode slurry is obtained.
[0079]Preparation of neg...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Example 2 Lithium-supplementing additives, positive electrode materials and their application in lithium-ion batteries
[0087] Take 0.3g of lithium flakes in an iron crucible, spread 1.35g of red phosphorus (analytical pure) on the surface of the lithium flakes, place on a heating platform, heat at 200°C for 5h in an Ar atmosphere in a glove box, cool naturally and grind fully, In a glove box, heat at 200° C. for 5 hours under an Ar atmosphere, and then raise the temperature to 400° C. and heat for 5 hours to obtain the LiP additive.
[0088] Using the LiP prepared in this example as the lithium supplement additive, refer to the steps in Example 1, select lithium cobaltate as the positive electrode active material to prepare the positive electrode slurry, refer to the assembly process of Example 1 to assemble the battery, and the electrochemical performance test results are shown in the table 3, wherein the discharge capacity of this embodiment is similar to that of em...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com