Method for extracting flavonoid compounds from wild rice by using deep eutectic solvent
A deep eutectic solvent and medium flavonoid technology, which can be used in the fields of antidote, organic chemistry, drug combination, etc., can solve the problems of toxic organic solvents, low vapor pressure, easy volatility, etc., to promote dissolution, strong polarity, and low detection limit. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] In the present invention, the preparation method of the deep eutectic solvent preferably includes the following steps: first mixing the choline chloride and the hydrogen bond donor, and then adding water for the second mixing to obtain the deep eutectic solvent. In the present invention, the method of the first mixing and the second mixing is preferably stirring and mixing; the rotating speed of the stirring and mixing is preferably 200-800 rpm, more preferably 350-550 rpm; the temperature of the first mixing is preferably 45 ~80°C, more preferably 60~80°C, most preferably 80°C; the first mixing time is preferably 30~360min, more preferably 60~240min; the second mixing temperature is preferably 25~35 °C, the time is preferably 10 to 60 minutes. In the present invention, the deep eutectic solvent is a stable, uniform and transparent liquid. The deep eutectic solvent provided by the invention is an extractant with strong polarity, which can effectively break the wild ric...
Embodiment 1
[0056] (1) Preparation of deep eutectic solvent
[0057] Add choline chloride and 1,4-butanediol into a round-bottomed flask at a molar ratio of 1:6, add magnets into the round-bottomed flask, and use an IKA magnetic stirrer to magnetically stir at 80°C for 60 minutes. The choline chloride-1,4-butanediol mixed solution was obtained, and 30 wt% of water was added to the obtained mixed solution to obtain a deep eutectic solvent (abbreviated as DES-1).
[0058] (2) Wild rice pretreatment
[0059] Grind wild rice with a pulverizer, dry at 40°C until constant weight, and store wild rice powder at -20°C in the dark for future use.
[0060] (3) Analysis of wild rice powder
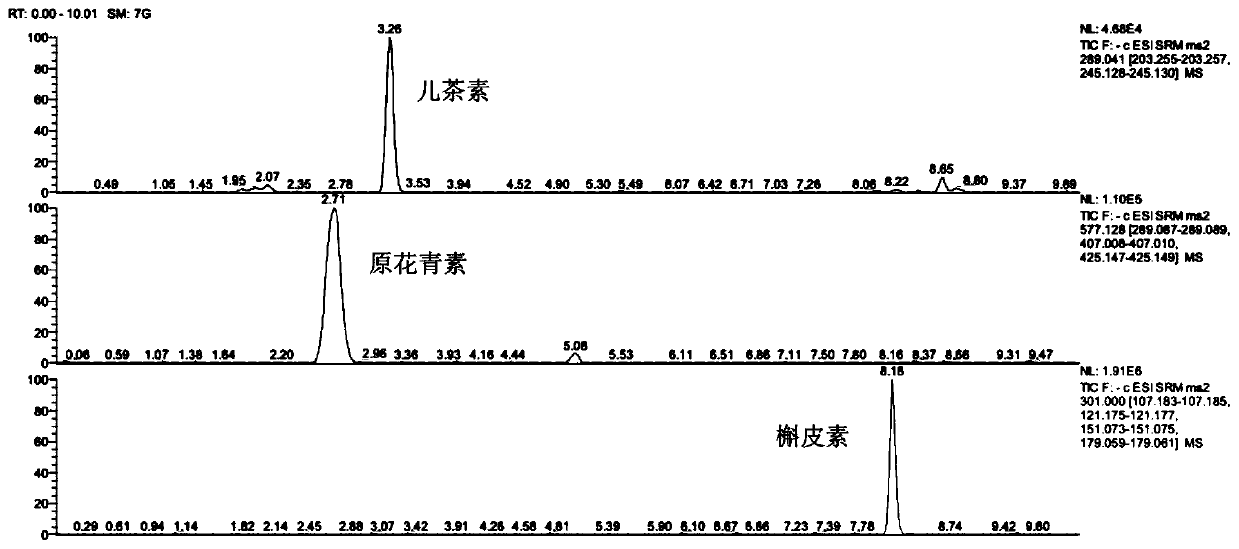
[0061] Use BSA124S-CW electronic balance to weigh 500 mg of wild rice powder, add 10 mL of deep eutectic solvent and mix well, place it in a KQ-500GVDV double-combined constant-temperature numerical control ultrasonic generator, at 50 ° C, ultrasonic power 200 W, ultrasonic frequency Under the condition of 25k...
Embodiment 2~3
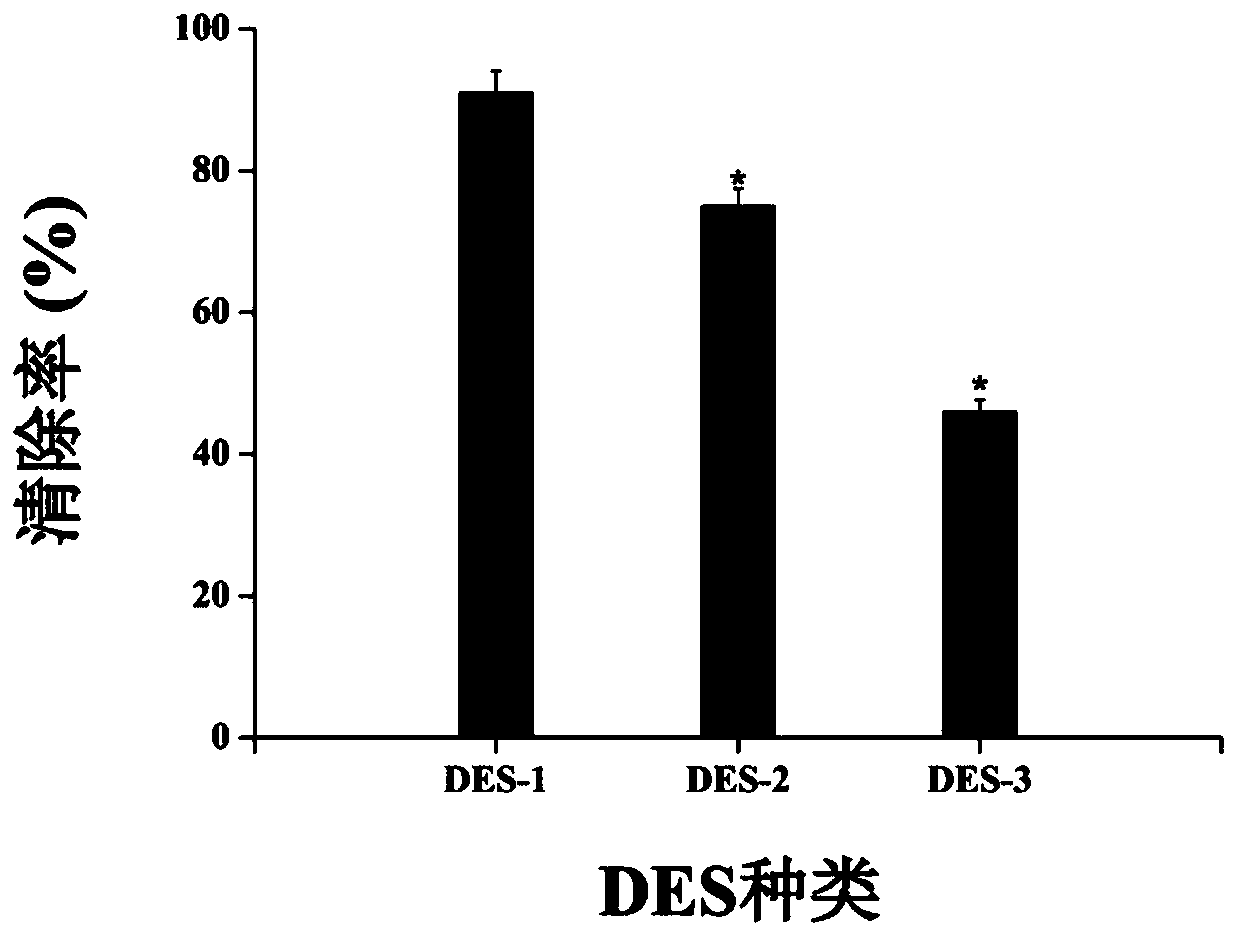
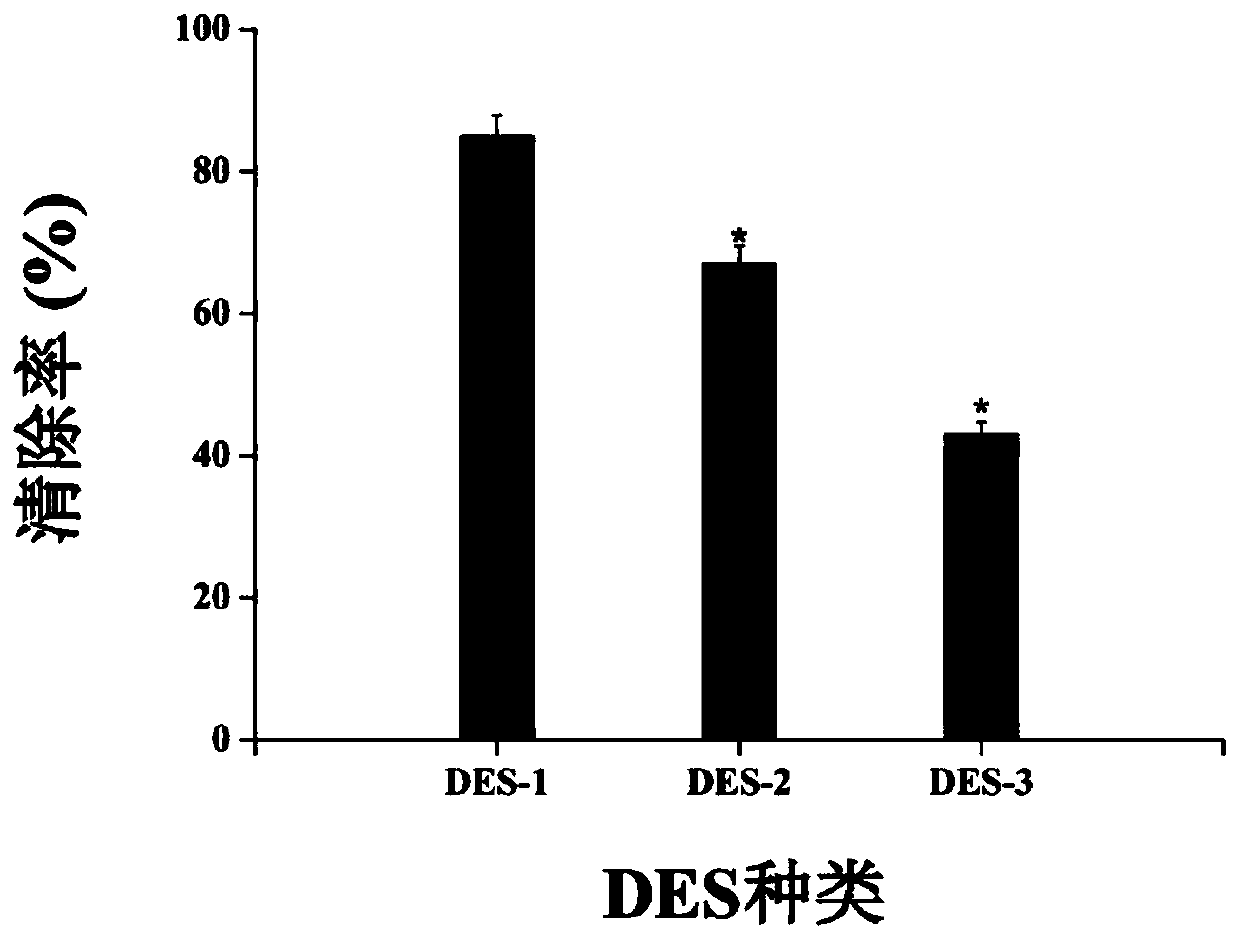
[0080] The flavonoids are extracted and detected according to the method of Example 1. The difference from Example 1 is that the deep eutectic solvent is different. The composition of the deep eutectic solvent in Examples 1 to 3 is as shown in Table 3. Catechin, proanthocyanidin and quercetin The extraction amounts of the three flavonoids of corticosteroids are shown in Table 4.
[0081] Deep eutectic solvent composition in table 3 embodiment 1~7
[0082]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com