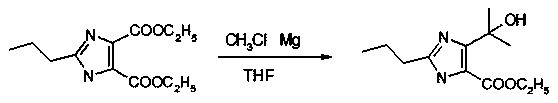
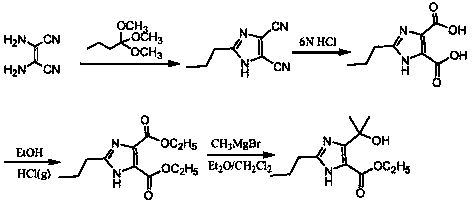
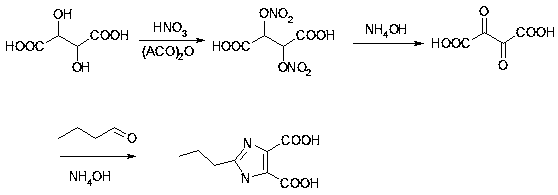
Synthesis method of olmesartan intermediate
A synthetic method and intermediate technology, applied in the field of pharmaceutical intermediate synthesis, can solve the problems of many by-products in the oxidation ring-opening reaction, difficult to control, and high ring-closing temperature, and achieve easy control of the overall steps, low production costs, and side reactions. little effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] A kind of synthetic method of olmesartan intermediate, take tartaric acid as raw material, make through cyclization reaction, esterification reaction and methylation reaction, wherein,
[0062] The chemical reaction equation for the cyclization reaction is:
[0063]
[0064] The chemical reaction equation of the esterification reaction is:
[0065]
[0066] The chemical reaction equation for the methylation reaction is:
[0067]
[0068] The cyclization reaction includes the following steps:
[0069] Step 1, put dehydrating agent into the ring-closure reaction kettle, cool down to 0°C; add fuming nitric acid dropwise, control the temperature in the kettle to drop at 3°C-6°C, add dropwise in 4 hours, and keep warm at 5°C for 1-2 Hours; then add tartaric acid in batches, 25 parts per batch, feed once every 30 minutes, and keep warm for 10-12 hours between 5-10°C; When it exceeds 5°C, add alkaline solution dropwise to adjust to PH7-7.5, the temperature does not...
Embodiment 2
[0087] The reaction steps and the amount of each substance added in this example are almost the same as those in Example 1, the difference being that the dehydrating agent in the cyclization reaction of this example is concentrated sulfuric acid. The alkaline solution used for the cyclization reaction in this embodiment is 5% sodium hydroxide solution. The acidic solution in the cyclization reaction of this embodiment is dilute sulfuric acid. The catalyst in the esterification reaction of this embodiment is oxalyl chloride, and the alkaline solution in the esterification reaction of this embodiment is 5% sodium hydroxide solution. The monohalomethane in the methylation reaction of this embodiment is methyl bromide; the first organic solvent in the methylation reaction of this embodiment is 2-methyltetrahydrofuran; the second organic solvent in the methylation reaction of this embodiment The solvent is ethanol.
Embodiment 3
[0089] The reaction steps and the amount of each substance added in this embodiment are almost the same as those in Example 1, the difference being that the dehydrating agent in the cyclization reaction of this embodiment is polyphosphoric acid. The alkaline solution used for the cyclization reaction in this embodiment is 10% sodium carbonate solution. The acidic solution in the cyclization reaction of this embodiment is acetic acid. The catalyst in the esterification reaction of this embodiment is concentrated sulfuric acid, and the alkaline solution in the esterification reaction of this embodiment is 10% sodium carbonate solution. The monohalomethane in the methylation reaction of this embodiment is methyl bromide; the first organic solvent ether in the methylation reaction of this embodiment; the second organic solvent in the methylation reaction of this embodiment is acetone.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com