Vomitoxin fluorescence immunochromatography test strip as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technique of fluorescence immunochromatography and vomitoxin, which is applied to the analysis of materials, biological tests, material inspection products, etc. It can solve the problems that positive results cannot be saved, sample background interference, and results are no longer accurate and reliable.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Example 1 Preparation of Deoxynivalenol Hapten, Complete Antigen, Monoclonal Antibody, Goat Anti-mouse Secondary Antibody
[0073] 1. Preparation of vomitoxin hapten
[0074] The synthetic route of vomitoxin hapten of the present invention is as follows Figure 4 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0075] (1) Weigh 23.2 mg of vomitoxin in advance, add 10 mL of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, dissolve it by ultrasonic, and set aside;
[0076] (2) Weigh 0.6g of sodium hydride (because sodium hydride contains kerosene, use 20mL of petroleum ether to stir magnetically for 30s, let it stand for 2min, pour off the petroleum ether; repeat the cleaning 2 to 3 times; after pouring off the petroleum ether for the last time, Blow dry with nitrogen);
[0077] (3) Add dissolved vomitoxin in sodium hydride, stir for 1 hour, add 0.5 g of succinic anhydride, stir for 3 hours, after reacting for 1 hour, slowly add 4 mL of methyl 3-bromopropionate dropwise, react...
Embodiment 2
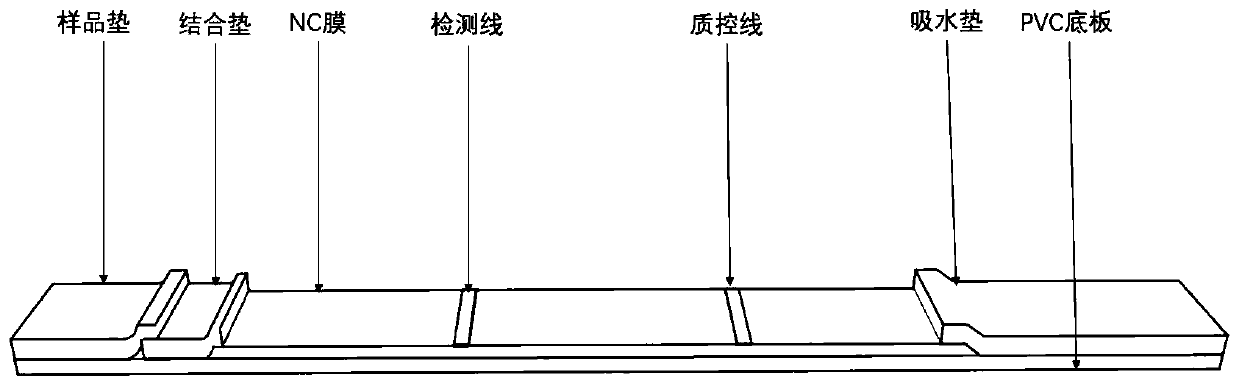
[0108] Embodiment 2 Preparation method of vomitoxin fluorescent immunochromatography test strip
[0109] 1. Preparation of fluorescent probes for DON monoclonal antibody labeled with aggregation-induced luminescence fluorescent microspheres
[0110] a. Take 10 μL of aggregation-induced luminescent fluorescent microsphere solution and 1 mL of MES buffer solution into a centrifuge tube, mix well, centrifuge, and set aside;
[0111] The carboxylated aggregation-induced luminescent fluorescent microspheres have an excitation wavelength of 200 nm and an emission wavelength of 610 nm.
[0112] b. Add 15 μL 0.5 mg / mL EDC and 20 μL 0.5 mg / mL NHS to each tube, use a constant temperature culture shaker to shake, 200 rpm, 25 ° C for 15 min; after the catalysis is completed, 14000 rpm, 25 ° C for 15 min, discard the supernatant solution, redissolve in 1 mL of 0.05M BB buffer solution (pH=8.0);
[0113] c. Add 1 μL of deoxynivalenol monoclonal antibody, place on a constant temperature cu...
Embodiment 3
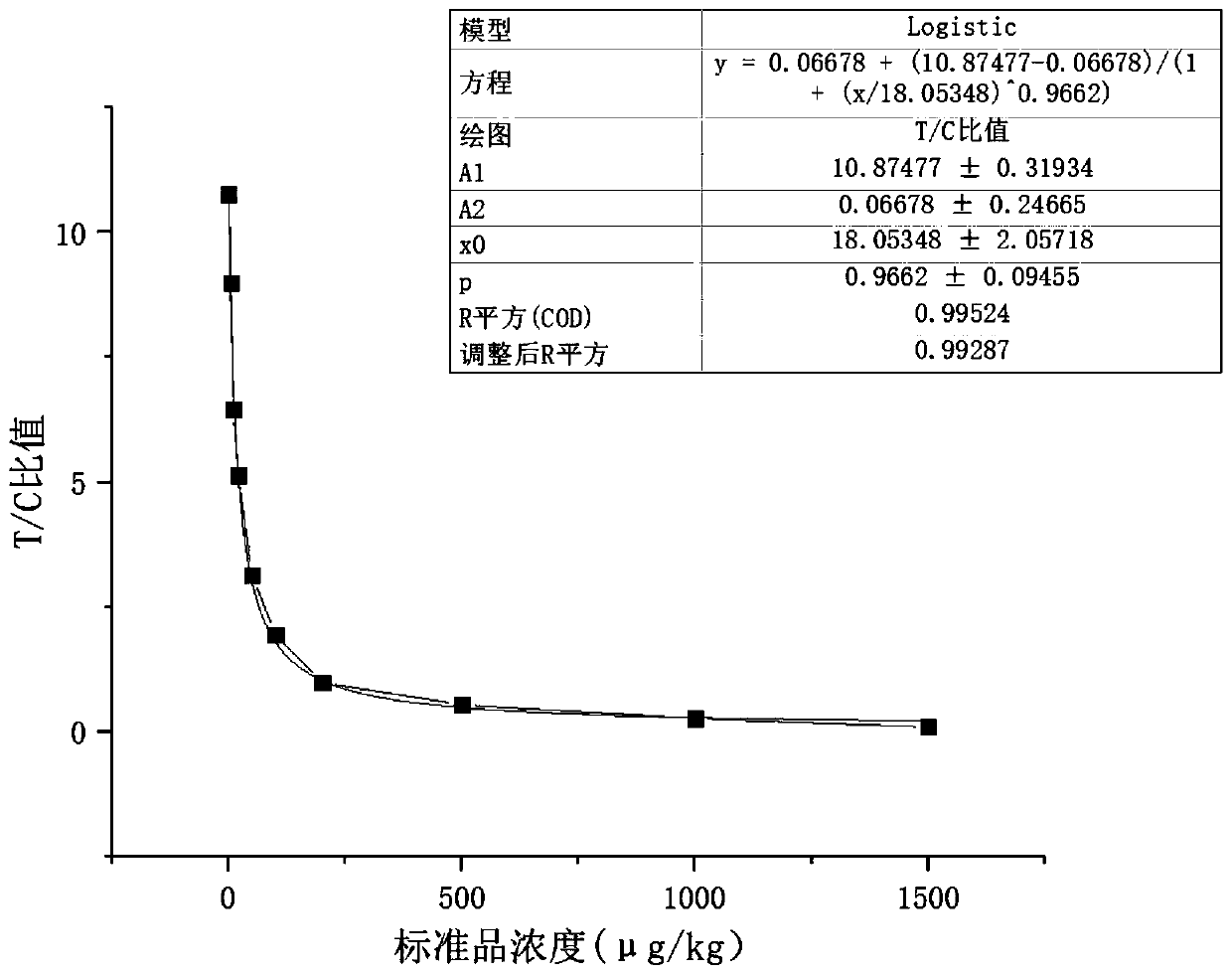
[0142] Example 3 Using the above-mentioned fluorescent immunochromatographic test strips to detect vomitoxin residues
[0143] 1. Sample pretreatment
[0144] Grind the sample (feed) to be tested into powder; weigh 1.00±0.05g of the crushed sample into a 10mL centrifuge tube; add 6mL of 70% methanol-water solution, vortex for 3min, and centrifuge at 4000rpm for 5min; take 50μL of the supernatant, Add 450 μL of sample diluent, mix well, and test.
[0145] 2. Test with test strips
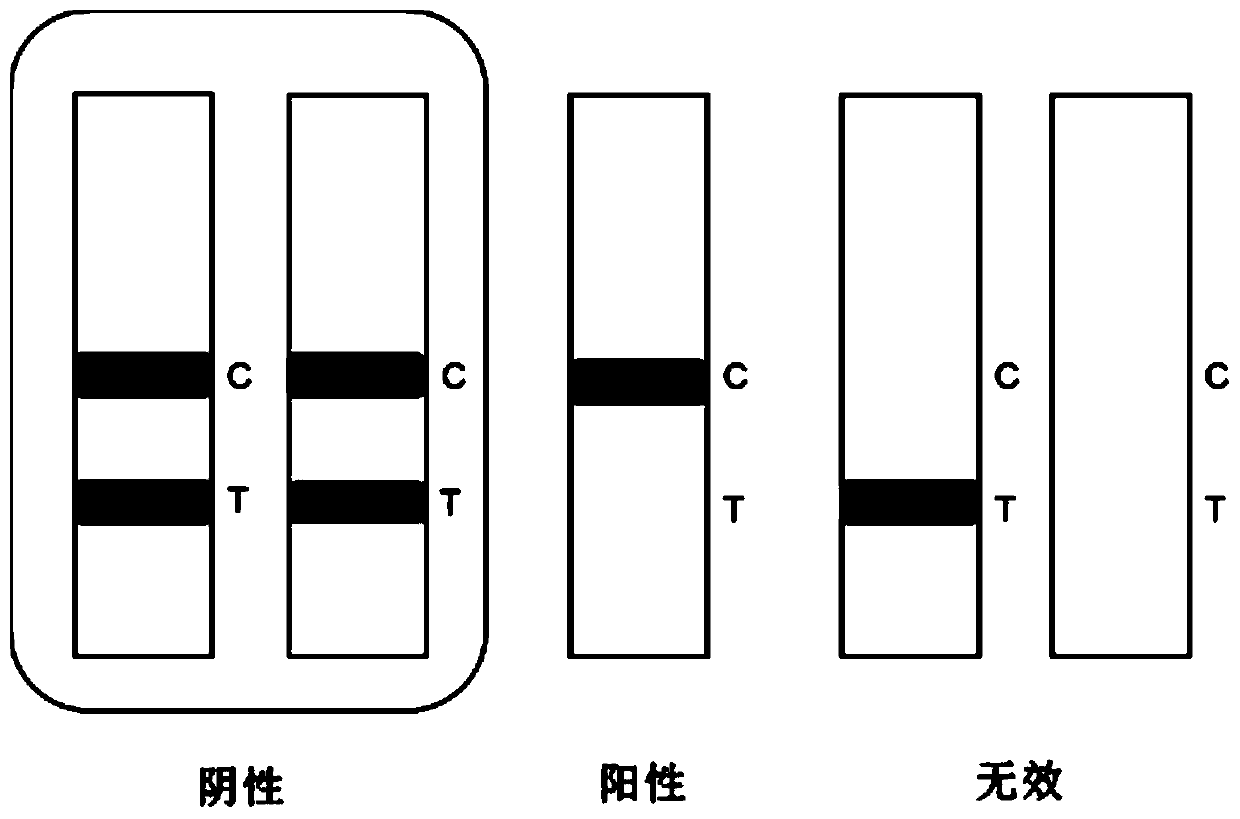
[0146] Open the test paper cylinder, take out the test paper strip prepared in Example 2, mark it and place it on the table (note: after taking out the micropore and the test paper strip, cover the cylinder cover immediately to prevent moisture); absorb 100 μL of the sample to be tested , drop the test strip into the micropore of the fluorescent probe, fully immerse the sample pad in the sample, and react for 5 minutes; take out the test strip, and interpret the result in a dry fluorescence analyze...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com