Method for preparing N38M type sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material at low cost
A NdFeB magnetic material technology is applied in the field of low-cost preparation of N38M sintered NdFeB magnetic materials, which can solve the problems of high production cost, non-renewable, economic loss, etc. The effect of magnetic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
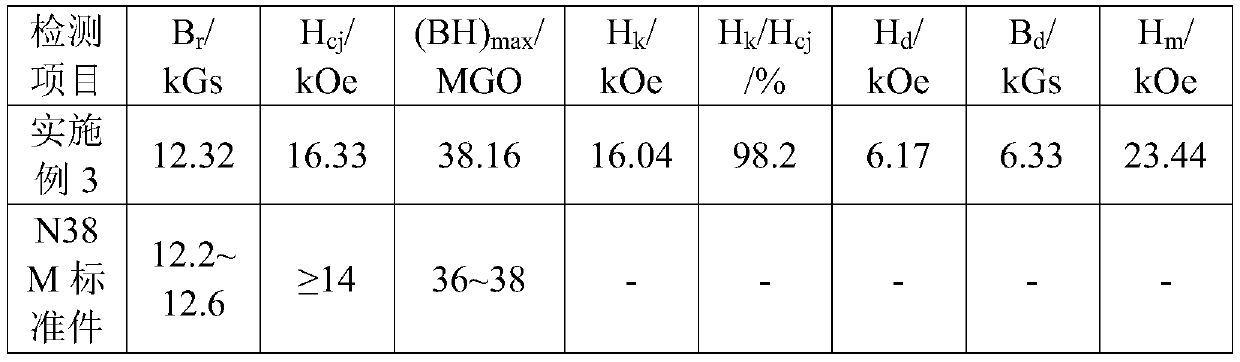
[0038] A low-cost method for preparing N38M type sintered NdFeB magnetic material, comprising the following steps:
[0039] S1: Prepare raw materials, which include 78% by mass of 38M waste, 0.08% of antioxidants, 0.08% of gasoline, and 21.84% of mixed metal virgin materials, wherein the mixed metal virgin materials are made of the following mass fractions of raw materials: praseodymium neodymium alloy 27%, metal cerium 2.5%, gadolinium iron alloy 1.74%, boron 4.74%, copper 0.16%, aluminum 0.53%, zirconium 0.16%, cobalt 0.41%, alloy iron 0.092%, iron is the balance; of which 38M waste It contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 28.5% of praseodymium-neodymium alloy, 2% of gadolinium iron, 4.9% of boron, 0.18% of copper, 0.5% of aluminum, 0.15% of zirconium, 0.4% of cobalt, 2.5% of metal cerium, and the balance of iron.
[0040] S2: Melting the above-mentioned raw materials under vacuum conditions, adjusting the rotation speed of the copper roll to 45m / s, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: Step S1: Prepare raw materials, the raw materials include 82% 38M waste, 0.12% antioxidant, 0.12% gasoline and 17.76% mixed metal virgin materials, wherein the mixed Metal virgin materials are made of raw materials with the following mass fractions:
[0047] praseodymium neodymium alloy 31%, praseodymium neodymium dysprosium alloy 3.3%, gadolinium iron alloy 2.14%, boron 5.74%, copper 0.22%, aluminum 0.93%, zirconium 0.22%, cobalt 0.55%, alloy iron 0.1%, iron as the balance; 38M scrap It contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 29.5% of praseodymium neodymium alloy, 2.5% of gadolinium iron, 5.6% of boron, 0.23% of copper, 0.8% of aluminum, 0.2% of zirconium, 0.5% of cobalt, 3.5% of metal cerium, and the balance of iron.
[0048] Others are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0050] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0051] Step S1: Prepare raw materials, the raw materials include 80% by mass percentage of 38M waste, 0.1% of antioxidants, 0.1% of gasoline and 19.8% of mixed metal virgin materials, wherein the mixed metal virgin materials are made of the following mass fractions of raw materials :
[0052] 29% praseodymium neodymium alloy, 2.9% praseodymium neodymium dysprosium alloy, 1.94% gadolinium iron alloy, 5.2% boron, 0.19% copper, 0.73% aluminum, 0.19% zirconium, 0.48% cobalt, 0.096% alloy iron, iron as the balance;
[0053] The 38M scrap contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: praseodymium neodymium alloy 29%, gadolinium iron 2.3%, boron 5.3%, copper 0.2%, aluminum 0.65%, zirconium 0.18%, cobalt 0.45%, metal cerium 3%, iron as the balance .
[0054] Others are with embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic energy product | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com