Mesa etching method for III-nitride semiconductor light-emitting device
A technology for nitride semiconductors and light-emitting devices, which is applied to semiconductor devices, semiconductor lasers, structural details of semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in manufacturing mesa, and achieve the effects of avoiding lattice damage, high crystal quality, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
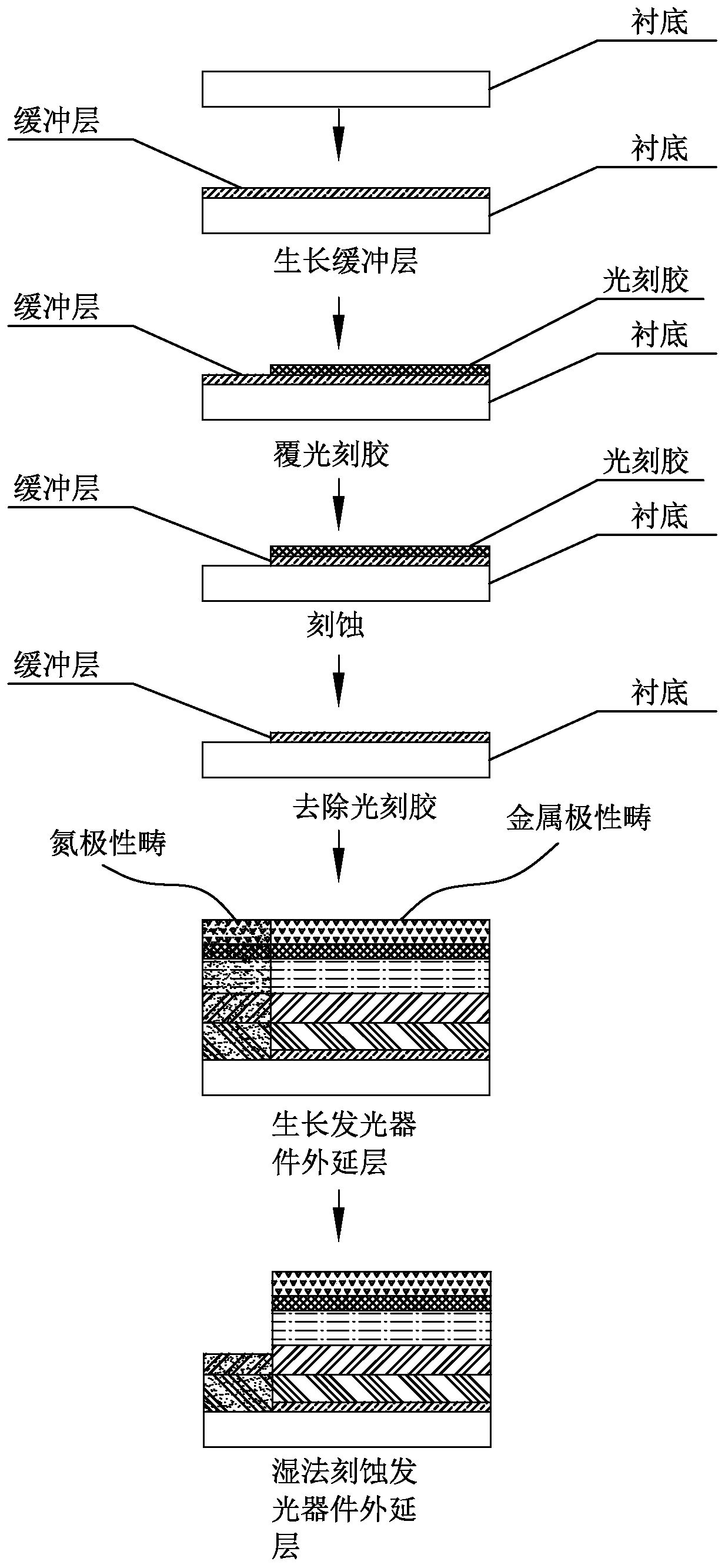
[0026] a) A buffer layer with a thickness of 50 nm is grown on a silicon substrate based on MOCVD technology, and a patterned buffer layer substrate is obtained based on photolithography and plasma etching processes, such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, photolithography is used to remove part of the buffer layer to realize the patterning of the buffer layer, but the patterning scheme is not limited, and any patterning scheme in the existing patterning technology can be used specifically.
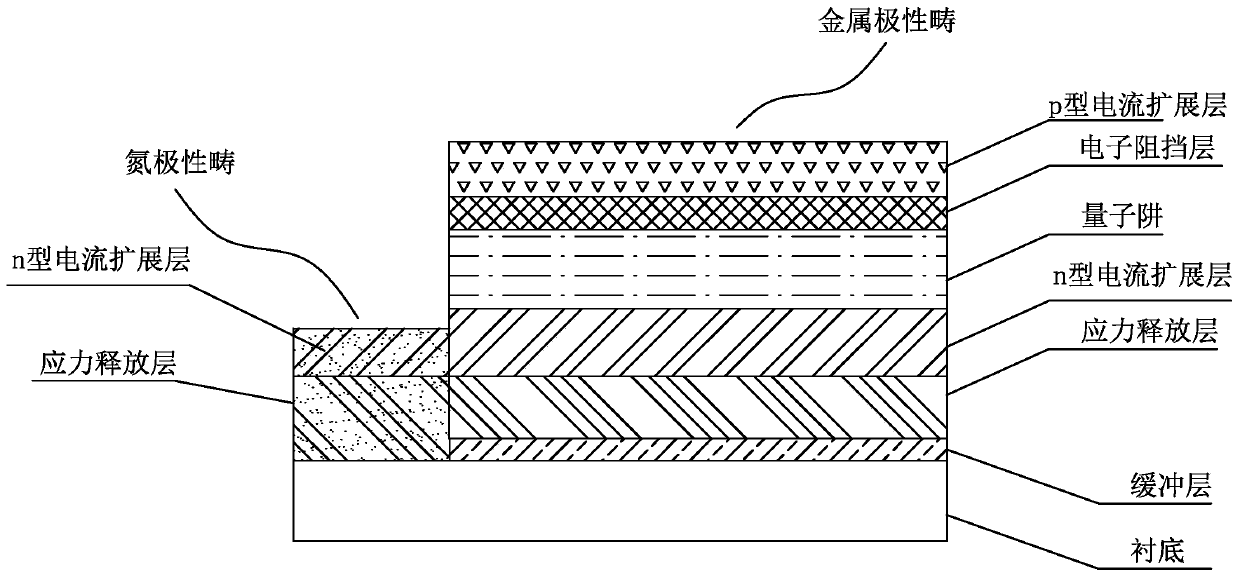
[0027] b) growing an LED epitaxial layer based on a patterned buffer layer substrate. The LED epitaxial layer is sequentially composed of an AlN stress release layer, an n-type current spreading layer, a multilayer quantum well, an electron blocking layer, and a p-type current spreading layer from the bottom layer to the top layer, such as figure 2 shown. The portion of the LED epitaxial layer corresponding to the buffer layer on the substrate is a metal polar domain, and the por...
Embodiment 2
[0032] a) A buffer layer with a thickness of 5 nm was grown on a sapphire substrate based on MBE technology, and a patterned buffer layer substrate was obtained based on photolithography and KOH etching processes.
[0033] b) growing a laser diode epitaxial layer based on a patterned buffer layer substrate. The epitaxial layer of the laser diode is sequentially composed of an AlGaN stress release layer, an n-type current spreading layer, a waveguide layer, a multilayer quantum well, an electron blocking layer, a waveguide layer, and a p-type current spreading layer from the bottom layer to the top layer; the laser diode epitaxial layer The part corresponding to the buffer layer on the substrate is the metal polar domain, and the part corresponding to the no buffer layer on the substrate is the nitrogen polar domain.
[0034] c) Using H at 70°C 3 PO 4 / H 2 o 2 The solution (3M, 0.5M respectively) etched the laser diode epitaxial layer for 5 minutes, the nitrogen polar domai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com