Method for detecting and identifying pathogens of children infectious diseases based on metagenomic sequencing
A technology for infectious diseases and metagenomics, which is applied in the field of pathogen detection and identification of infectious diseases in children, and can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining, few applications, and small sample size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] This embodiment provides a method for detecting and identifying pathogens of infectious diseases in children based on metagenomic sequencing. The specific processing method includes the following steps:
[0065] (1) Process the collected cerebrospinal fluid: take 1.5ml of the sample to be tested and centrifuge at 20000G for 5min, discard the supernatant, and obtain the processed sample;
[0066] (2) Use the Qiagen UCP Pathogen Small Kit to extract the DNA of the treated sample; then use the Qubit fluorescence quantitative instrument to measure the concentration of the obtained DNA, and use agarose gel electrophoresis for quality control. It is required that the sample DNA can be clearly The band of genomic DNA was observed, and the sample DNA was obtained;
[0067] (3) The steps of using the KAPA DNA library preparation kit to construct the sample sequencing library include DNA fragmentation, end repair, adapter ligation, screening of DNA with a fragment size of 250-450...
Embodiment 2
[0073] This embodiment provides a method for detecting and identifying pathogens of infectious diseases in children based on metagenomic sequencing. The specific processing method includes the following steps:
[0074] (1) Process the collected throat swab samples: first, shake and squeeze, first add 2 mL of sterile PBS to soak the throat swab for 10 minutes, and shake for 30 seconds every 2 minutes, squeeze the throat swab cotton swab to fully obtain the eluent , and then draw 2mL of eluent as the processed sample;
[0075] (2) Use the Qiagen UCP Pathogen Mini Kit to extract the DNA of the treated sample, measure the concentration of the obtained DNA with a Qubit fluorescence quantitator, and use electrophoresis for quality control to obtain the sample DNA;
[0076] (3) The steps of using the KAPA DNA library preparation kit to construct the sequencing library of the sample DNA include DNA fragmentation, end repair, adapter connection, screening of DNA with a fragment size of...
Embodiment 3
[0082] This embodiment provides a method for detecting and identifying pathogens of infectious diseases in children based on metagenomic sequencing. The specific processing method includes the following steps:
[0083] (1) Process the collected whole blood samples: First, separate the plasma, take 2ml of whole blood and centrifuge at 1600G, 4°C for 10min, separate the plasma without touching the buffy coat, then centrifuge at 16000G, 4°C for 10min, and absorb the supernatant as processed samples;
[0084] (2) Extract the DNA of the processed sample: extract the processed sample DNA from whole blood, use the MagMAX free DNA separation kit, then use the Qubit fluorescence quantitator to measure the concentration of the obtained DNA, and use electrophoresis to determine the quality Control, obtain sample DNA;
[0085] (3) Use the KAPA DNA library preparation kit to construct the sample sequencing library: the steps of constructing the sequencing library from the sample DNA obtai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
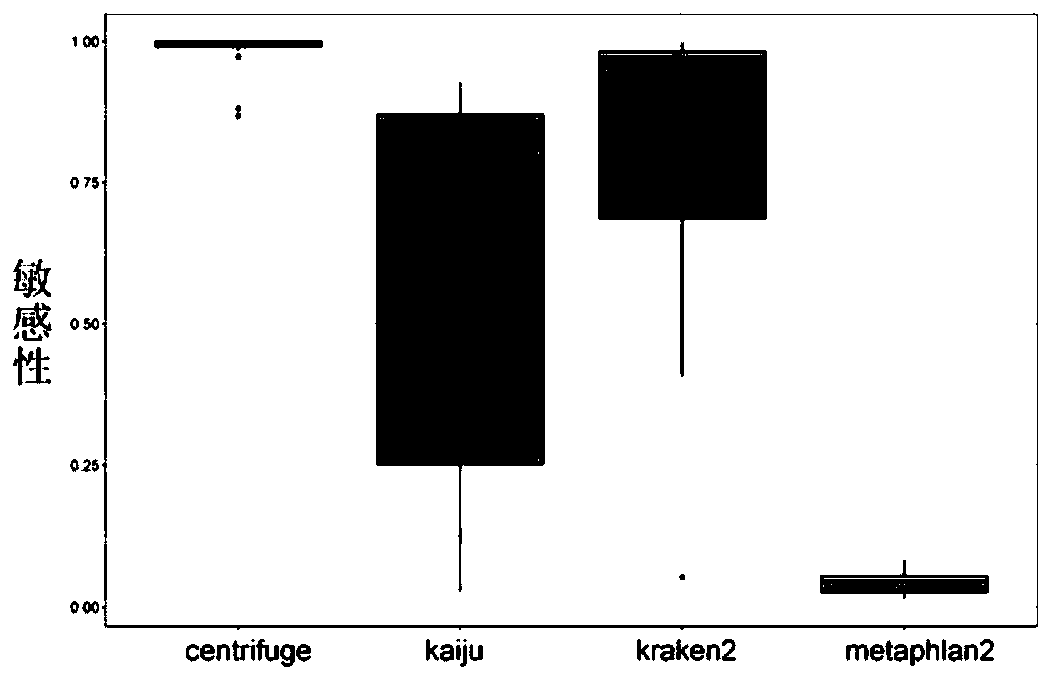
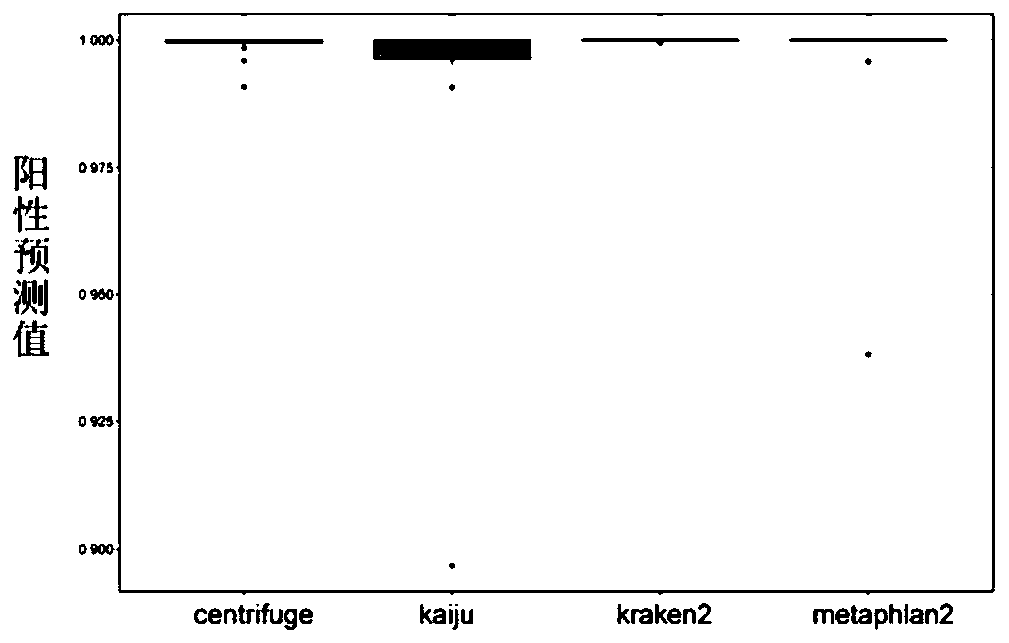
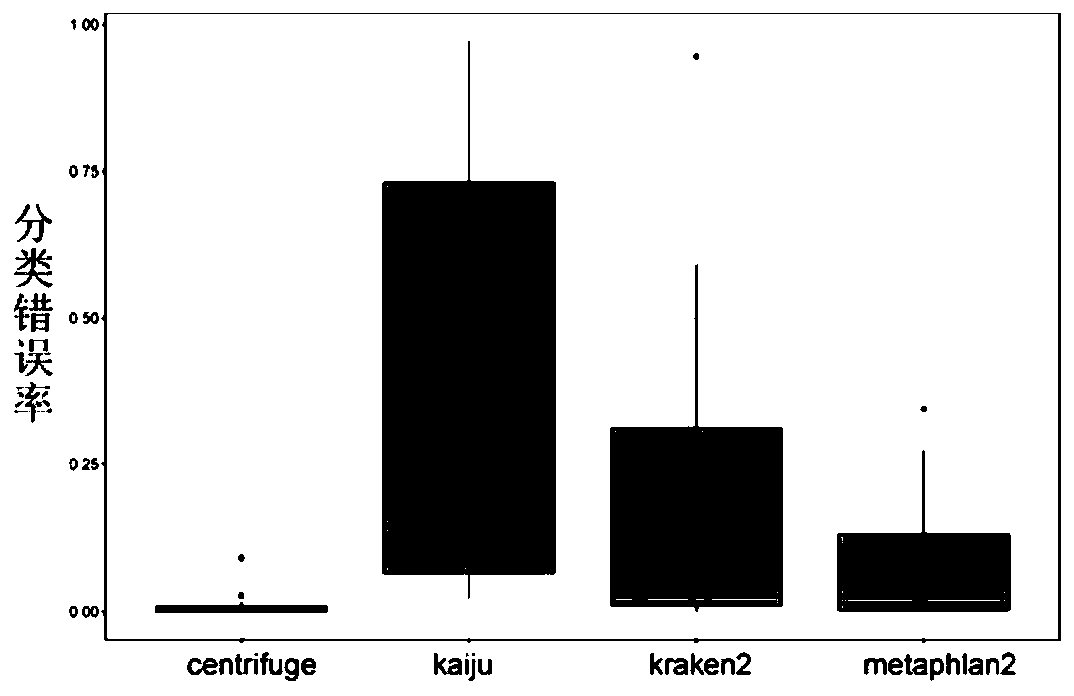
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com