Remediation method and application of chromium-polluted water body
A remediation method and technology for chromium pollution, applied in the fields of water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of easy agglomeration of nZVI, aging of nZVI, decrease in reduction and removal ability, etc., so as to improve the removal efficiency and avoid cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: Preparation of a biochar-loaded aging nanometer zero-valent iron and cultivation of Shewanella MR-1 bacteria
[0020] 1. Preparation of biochar:
[0021] Step 1): Wash the fresh palm biomass with distilled water, dry it at 80°C, and break it into pieces to obtain biomass fragments;
[0022] Step 2): Put the biomass fragments in a vacuum tube furnace, raise the temperature to 500°C under a nitrogen atmosphere, and the heating rate is 10°C / min, stop heating after keeping for 2 hours, and take it out at room temperature to obtain biochar;
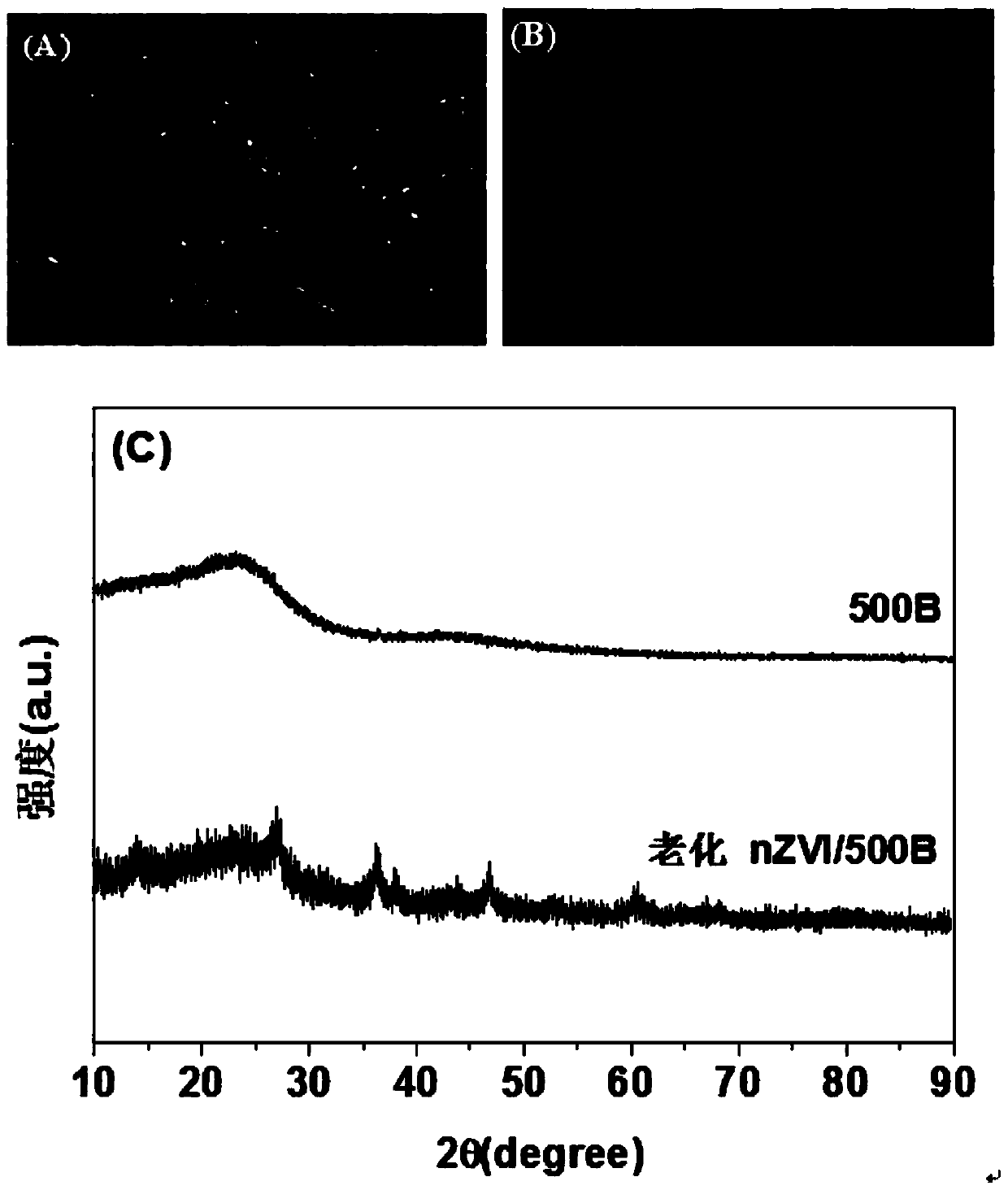
[0023] Step 3): Then soak the prepared biochar in 1mol / L HCl solution, shake at 200rpm for 5 hours to remove excess impurities, and finally rinse with deionized water until the pH of the solution remains unchanged, and dry at 80°C to obtain the final product The biochar (referred to as BC, XRD see figure 1 in C).
[0024] 2. Preparation of biochar-loaded aged nano zero-valent iron:
[0025] Step 1): Add the biochar (0.9g)...
Embodiment 2
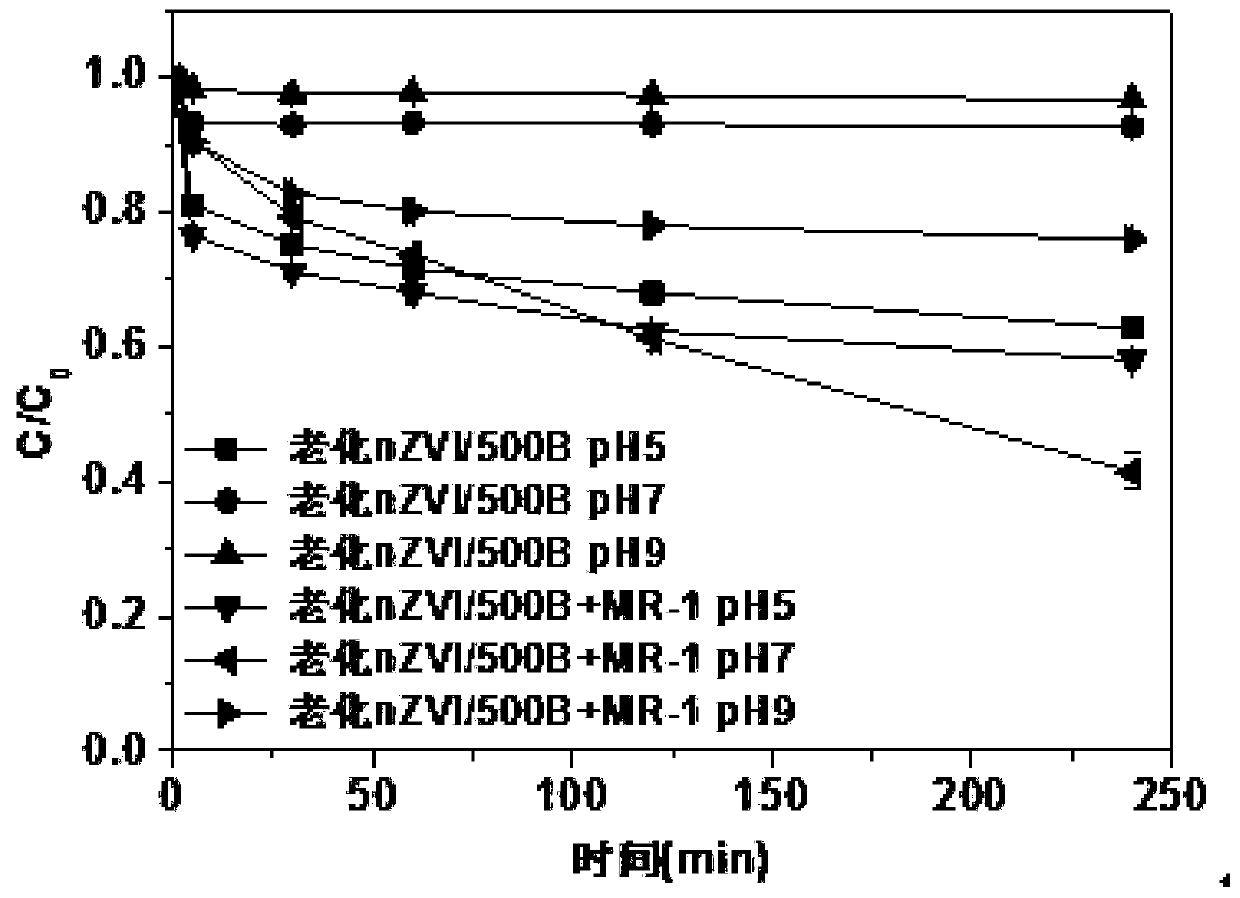
[0031] Example 2: Anaerobic removal of Cr(VI) from water by biochar-loaded aging nanometer zero-valent coupling Shewanella MR-1 bacteria under different pH conditions
[0032] Step 1): Prepare a Cr(VI) solution with a concentration of 12 mg / L, and the solvent is oxygen-free deionized water;
[0033] Step 2): Take the biochar-loaded aging nano-zero-valent iron prepared in Example 1 and Shewan's MR-1 bacteria for Cr(VI) adsorption kinetics experiment, the dosage of nZVI / 500B is 1g / L, and Shewan's The OD600 of MR-1 bacteria was set to 0.2 and no addition, and the concentration of sodium lactate was 20mmol / L. The initial pH value of the chromium solution was adjusted to 5, 7 and 9 with 0.1M HCI solution and 0.1M NaOH solution for the experiment, and the reaction system 40mL, react in a 100mL vial, and the entire reaction process is carried out in an anaerobic box;
[0034] Step 3): start timing after feeding, and take samples at specified time points, and the sampling times are 0...
Embodiment 3
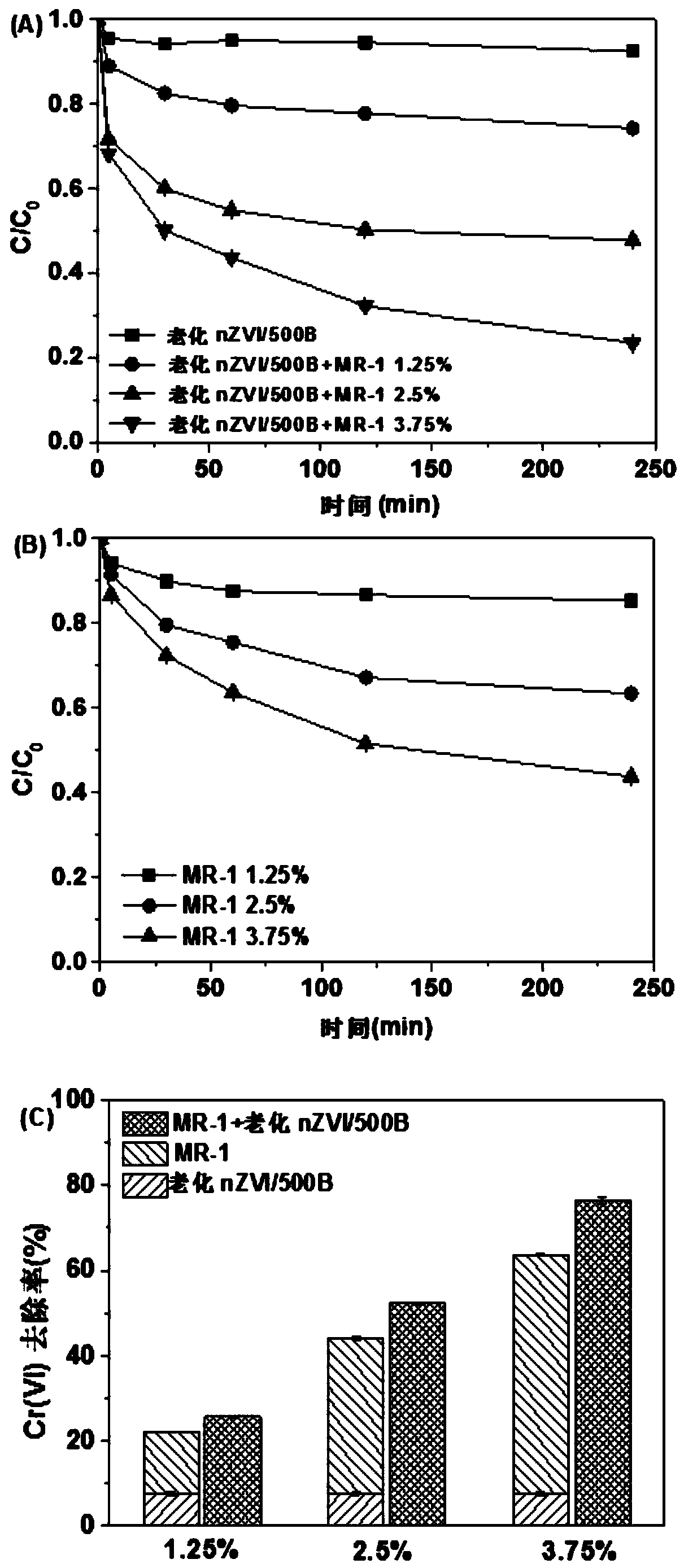
[0037] Example 3: Anaerobic removal of Cr(VI) in water by biochar loaded with aged nanometer zero-valent coupling Shewanella MR-1 bacteria with different dosages of bacteria
[0038] Step 1): Prepare a Cr(VI) solution with a concentration of 12 mg / L, and the solvent is oxygen-free deionized water;
[0039]Step 2): Take the biochar-loaded aging nano-zero-valent iron prepared in Example 1 and Shewan's MR-1 bacteria for Cr(VI) adsorption kinetics experiment, the dosage of nZVI / 500B is 1g / L, and Shewan's MR-1 bacterium OD600 is set to 0.2, 0.4 and 0.6 respectively, referred to as MR-11.25%, MR-12.5%, MR-13.75%, wherein sodium lactate concentration is 20mmol / L, with 0.1M HCI solution and 0.1M NaOH solution The initial pH value of the chromium solution was adjusted to 7 for the experiment, the reaction system was 40mL, and the reaction was carried out in a 100mL vial, and the entire reaction process was carried out in an anaerobic box;
[0040] Step 3): start timing after feeding, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com