Potato production place tracing method based on mineral elements and stable isotopes
A stable isotope and carbon stable isotope technology, applied in the field of potato origin traceability based on mineral elements and stable isotopes, can solve the problems of extensive production and processing, market fairness, brand protection and consumer rights infringement, lack of geographical identification and protection methods, etc. , to achieve the effect of wide application prospects and protection of regional potato brands with advantages of origin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028]Sample collection: During the potato harvest period, 129 samples were collected from potato production bases in four major potato-producing counties and cities in Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Xinjiang, and Sichuan provinces. The sampling location information is shown in Table 1. Three samples were randomly collected at each sampling point. After the collected potatoes are peeled, washed with deionized water, homogenized by a tissue masher, 50-100g is taken, dried in a blast oven at 60°C for 2 hours, then dried at 105°C to constant weight, fully ground, passed A 100-mesh sieve is used as an analysis sample for later use.
[0029] Table 1 Statistics of sampling locations
[0030]
Embodiment 2
[0032] Analysis of samples
[0033] Determination of mineral elements: Refer to GB 5009.268-2016 "National Food Safety Standard for the Determination of Multi-Elements in Food", accurately weigh 0.5g of potato samples (accurate to 0.001g) into a microwave digestion tube, add 10mL of concentrated nitric acid, and let stand for 1h , Tighten the cap of the tube, adopt the temperature programming method to digest the sample, cool to room temperature after the digestion, rinse the inner cap with a small amount of water, remove the acid in vacuum, dilute it to a 50mL volumetric flask with deionized water, and do a blank experiment at the same time. Sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), iron (Fe), boron (B), phosphorus (P), vanadium ( V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), selenium (Se), cadmium (Cd) a total of 18 types content of mineral elements. The external standard method was used fo...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Data analysis and model building:
[0041] The contents of 18 mineral elements in potatoes from different origins were counted separately. The variance analysis results are shown in Table 3. At the 0.05 level, the significant d values of arsenic and selenium were 0.07 and 0.0957, respectively. At the level of 0.05, the significant d values were all less than 0.05, indicating that there were significant differences in the contents of different mineral elements in potatoes in different regions.
[0042] Table 3 Statistics of variance analysis results
[0043]
[0044]
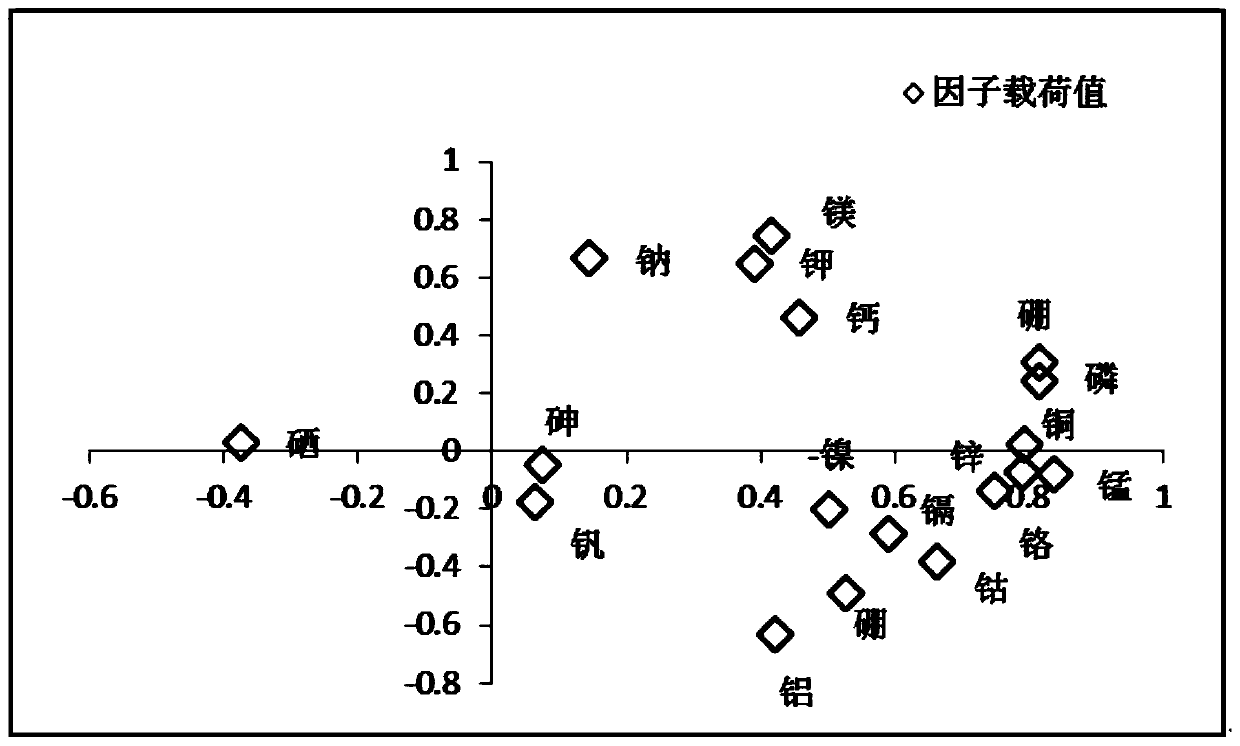
[0045] The principal component analysis was carried out on 18 kinds of potato mineral elements in different production areas. The analysis results are shown in Table 5. We selected the components with eigenvalues greater than 1 as the principal components, and extracted 5 effective principal components. The contribution rate of the first principal component is 33.747%, the contribution rate of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com