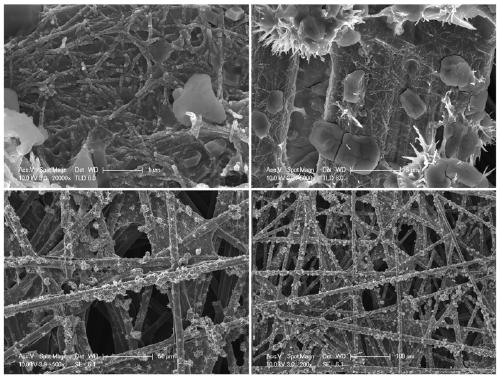
Method for preparing boron-and-nitrogen-doped cobalt-molybdenum-sulfur-oxygen compound/carbon composite material
A technology of sulfur-oxygen compounds and carbon composite materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve unseen problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
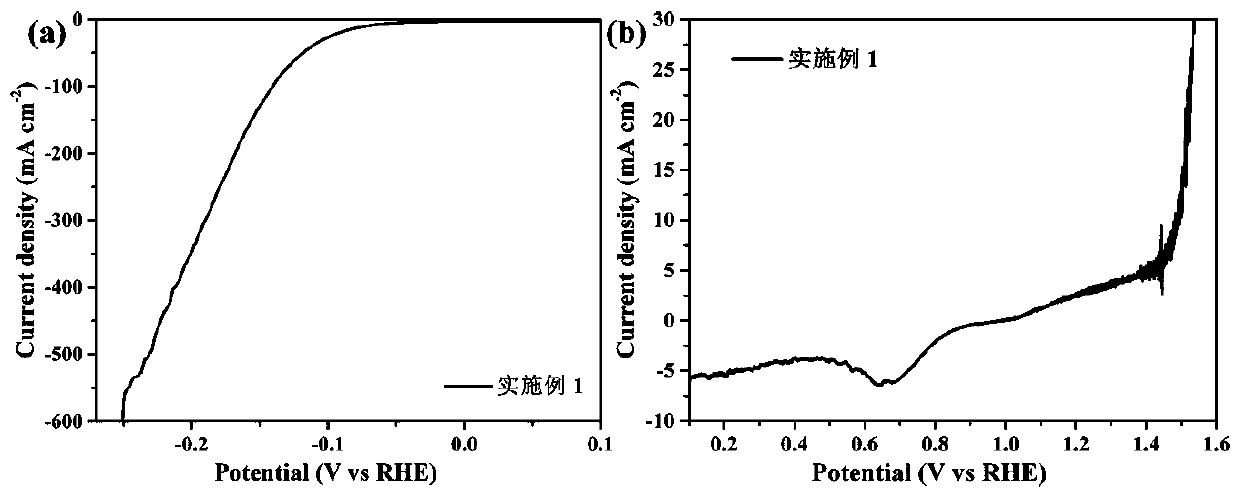
Embodiment 1
[0024] CoCl 2 ∙ 6H 2 O and urea were dissolved in 40 mL of deionized water at room temperature, in which CoCl 2The concentration of urea was 0.15 M, and the mass fraction of urea was 6.25 wt.%. After immersing the hydrophilic carbon paper in the solution, it was incubated at 90°C for 2 h. After natural cooling to room temperature, the carbon paper was taken out and rinsed with deionized water. Three times, dry and set aside. The carbon paper with basic cobalt salt arrays was placed in the air at 500 °C for 0.5 h, and then in an Ar+S atmosphere at 500 °C for 1 h, cooled naturally and taken out for use. Soak the above-mentioned carbon paper with cobalt sulfide arrays grown in 400 mM molybdenum chloride solution, which is composed of 50 mg bipyridyl, 0.1 g glucose and 3 mL N, N-dimethylformamide, soak for about 1 min, and dried on a hot table at 80°C for 10 min after taking it out. The coated substrate was placed in a tube furnace with Ar as the protective gas and boric acid ...
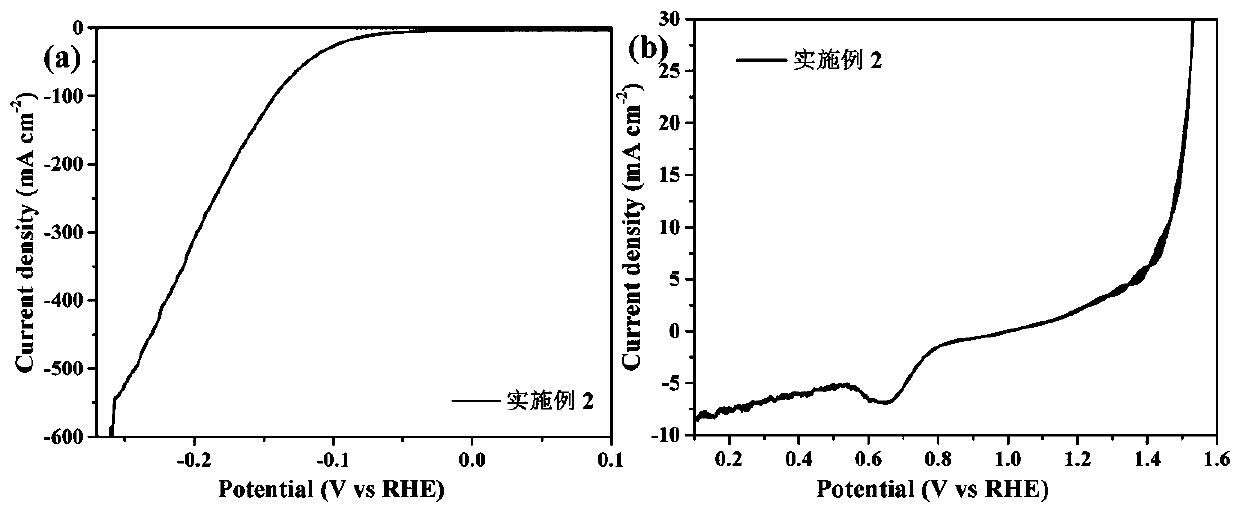
Embodiment 2
[0027] CoCl 2 ∙ 6H 2 O and urea were dissolved in 40 mL of deionized water at room temperature, in which CoCl 2 The concentration of urea was 0.15 M, and the mass fraction of urea was 6.25 wt.%. After immersing the hydrophilic carbon paper in the solution, it was incubated at 90°C for 2 h. After natural cooling to room temperature, the carbon paper was taken out and rinsed with deionized water. Three times, dry and set aside. The carbon paper with basic cobalt salt arrays was placed in the air at 500 °C for 0.5 h, and then in an Ar+S atmosphere at 500 °C for 1 h, cooled naturally and taken out for use. Soak the above-mentioned carbon paper with cobalt sulfide arrays grown in 400 mM molybdenum chloride solution, which is composed of 50 mg o-phenanthroline, 0.1 g glucose and 3 mL N, N-dimethylformamide, soak After about 1 min, take it out and dry it on a hot table at 80°C for 10 min. Put the coated substrate into a tube furnace, use Ar as the protective gas, and use a solid ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] CoCl 2 ∙ 6H 2 O and urea were dissolved in 40 mL of deionized water at room temperature, in which CoCl 2 The concentration of urea was 0.15 M, and the mass fraction of urea was 6.25 wt.%. After immersing the hydrophilic carbon paper in the solution, it was incubated at 90°C for 2 h. After natural cooling to room temperature, the carbon paper was taken out and rinsed with deionized water. Three times, dry and set aside. The carbon paper with basic cobalt salt arrays was placed in the air at 500 °C for 0.5 h, and then in an Ar+S atmosphere at 500 °C for 1 h, cooled naturally and taken out for use. Soak the above-mentioned carbon paper grown with cobalt sulfide arrays in 400 mM molybdenum chloride solution, which is composed of 50 mg o-phenanthroline, 0.05 g glucose and 3 mL N, N-dimethylformamide, soak After about 1 min, take it out and dry it on a hot table at 80°C for 10 min. Put the coated substrate into a tube furnace, use Ar as the protective gas, and use a solid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com