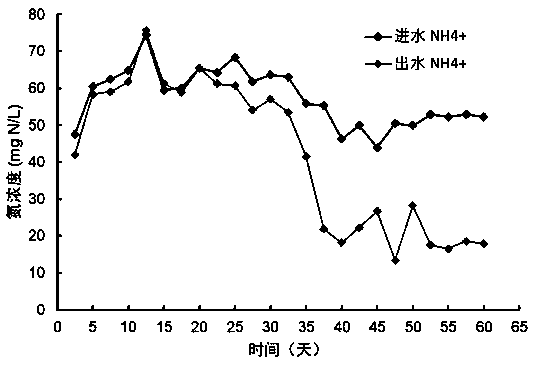
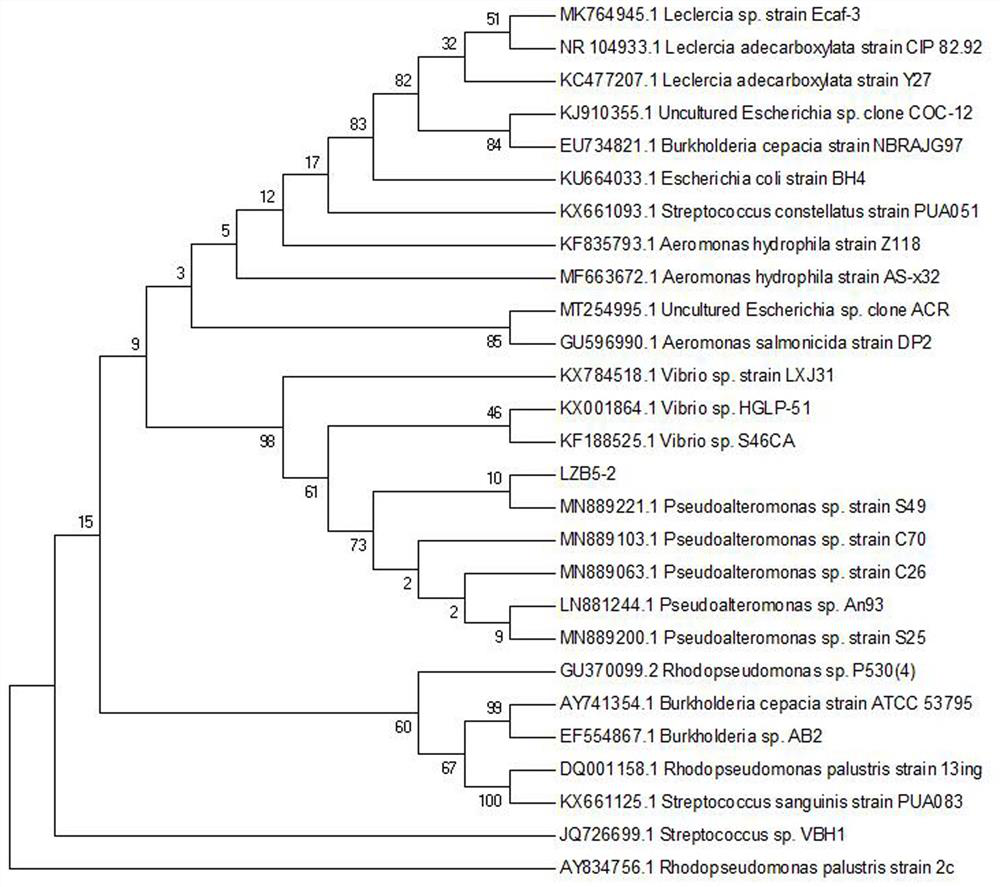
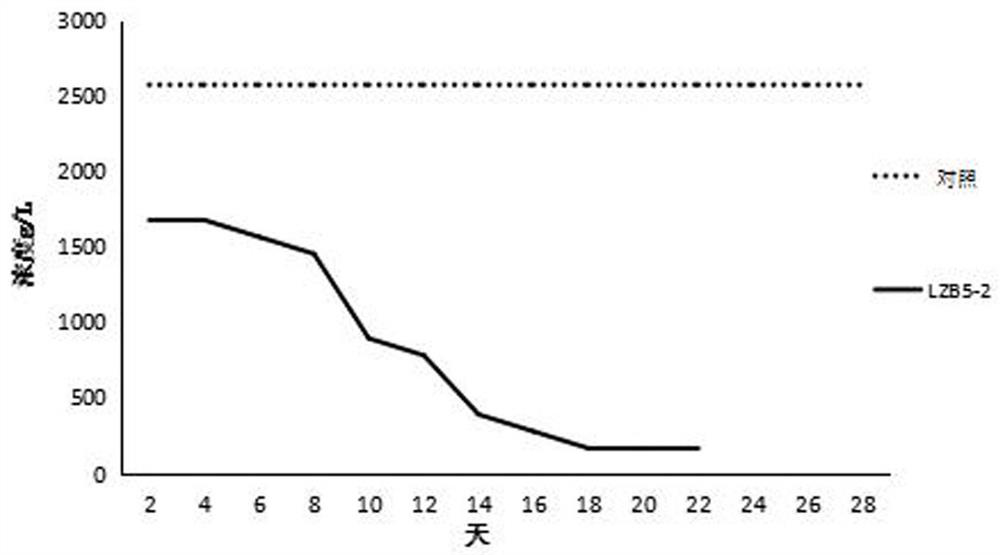
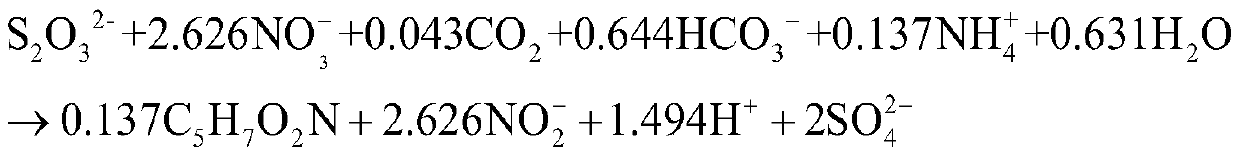Patents
Literature
113 results about "Sulphur oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial oxidation of sulfur is the oxidation of sulfur by microorganisms to produce energy. All organisms require a mechanism to obtain energy in order to build their structural components, survive, grow and reproduce. The oxidation of inorganic compounds is the strategy primarily used by chemolithotrophic microorganisms for this purpose.
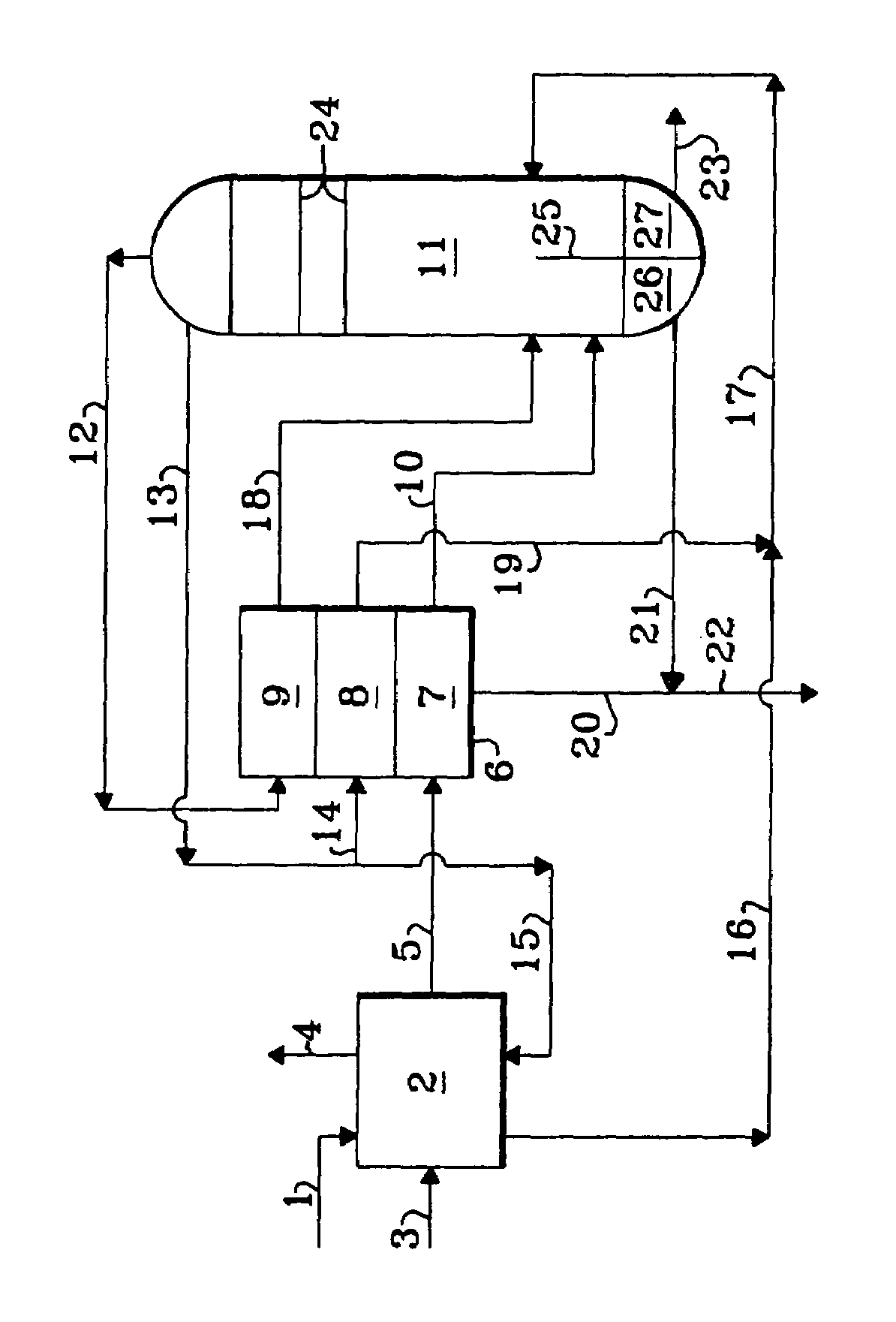
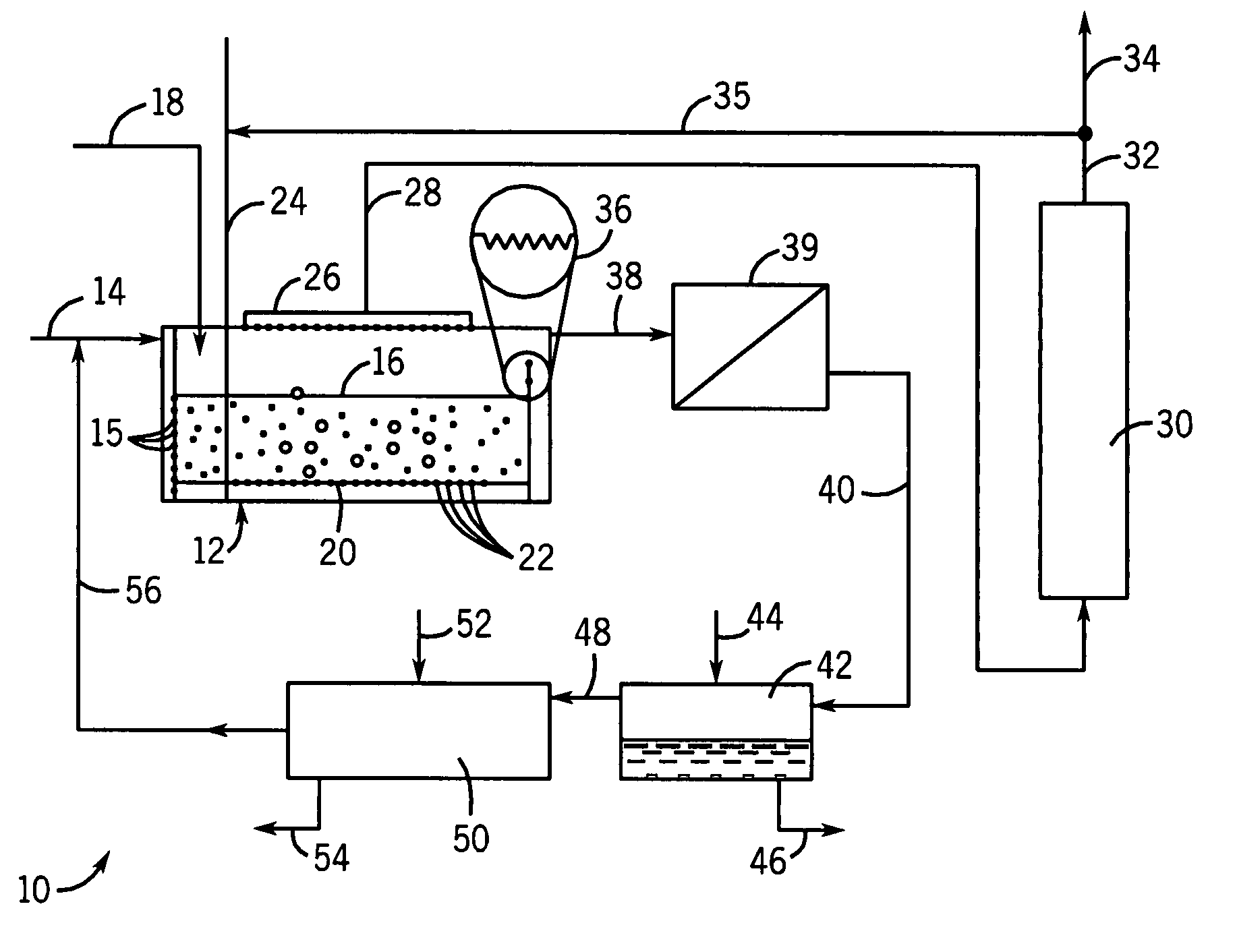
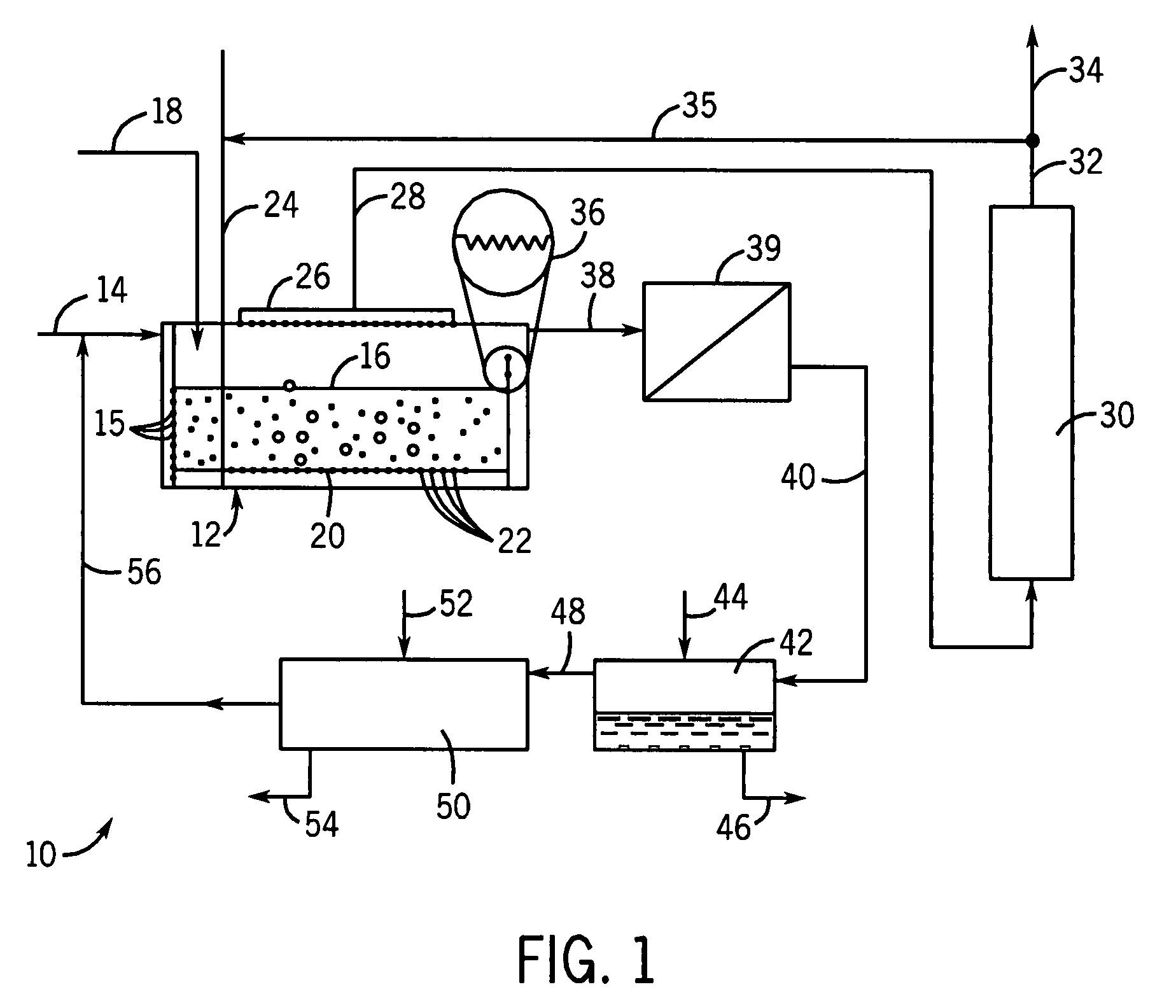
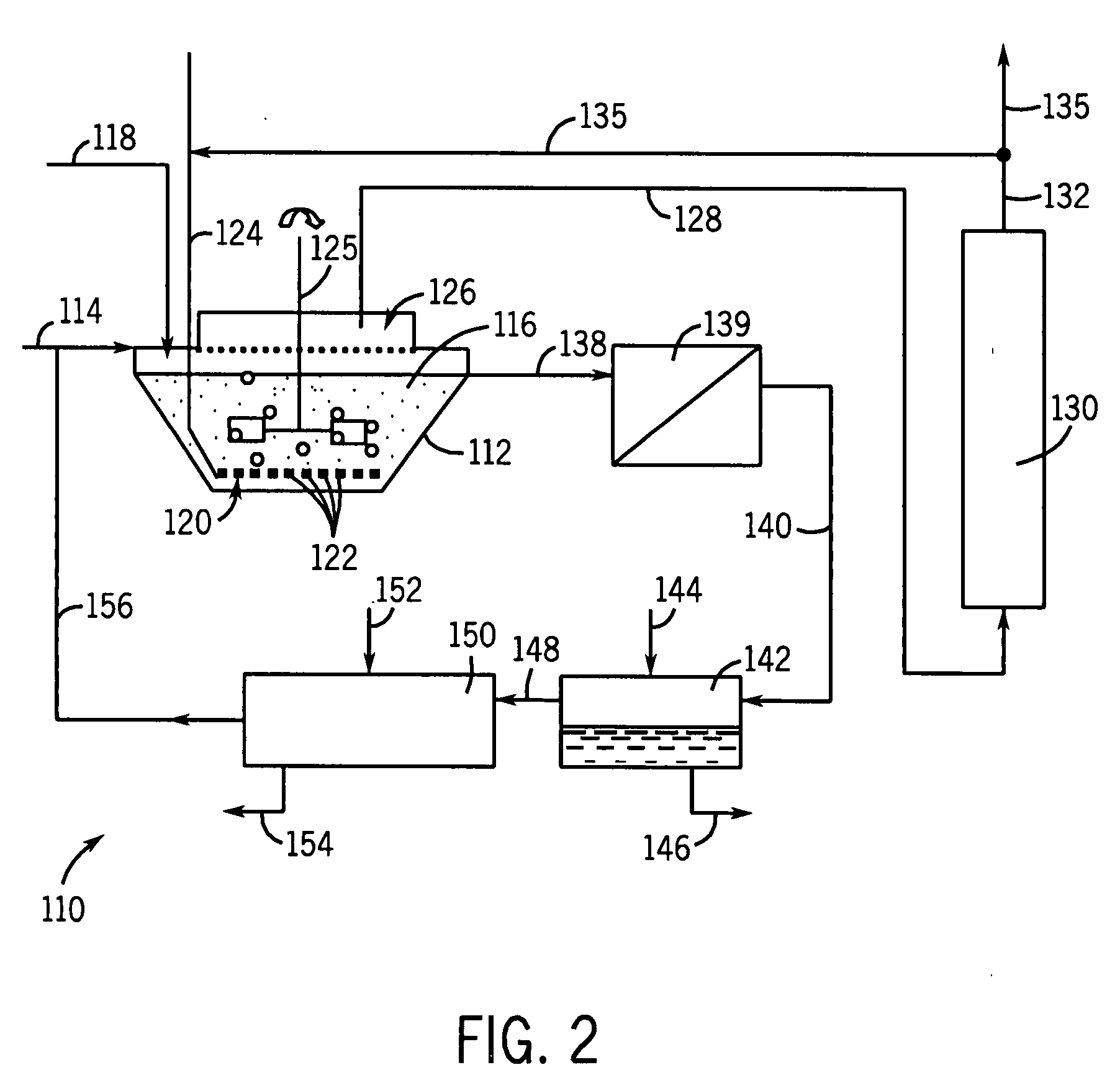
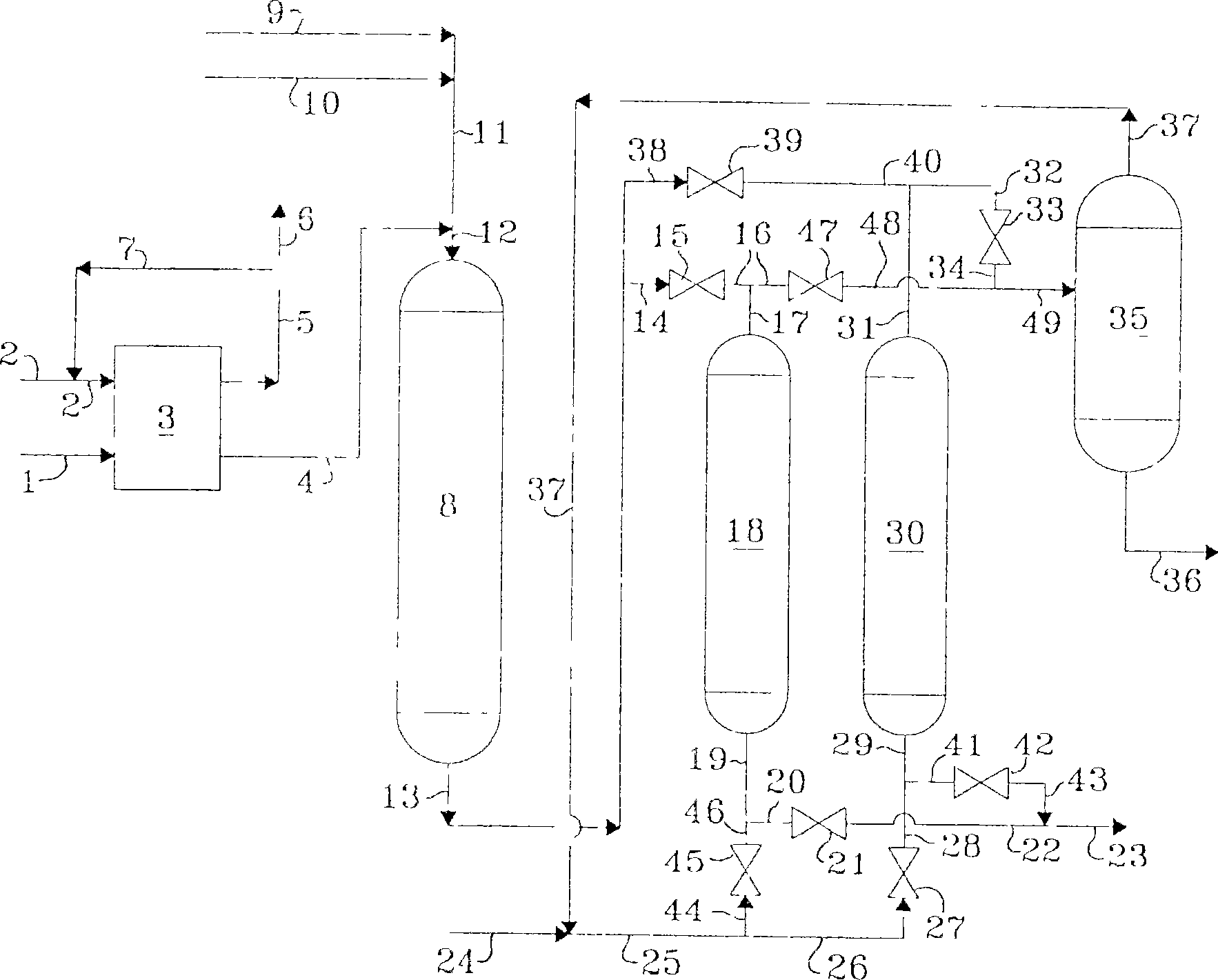
Method, device and reactor for recovery of sulfur from acidic gas
InactiveCN104138713AAffect conversion performanceImpact protectionDispersed particle separationSulfur preparation/purificationAlcoholSulfur
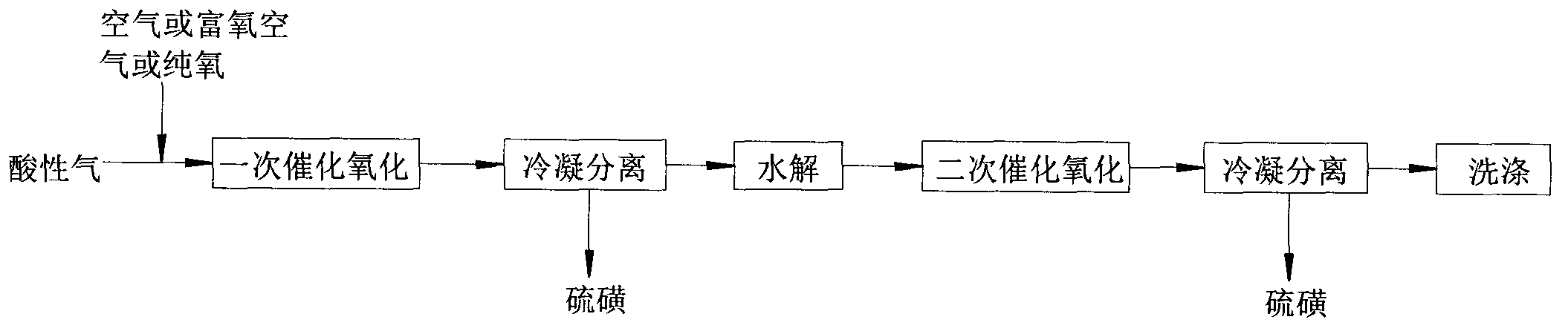
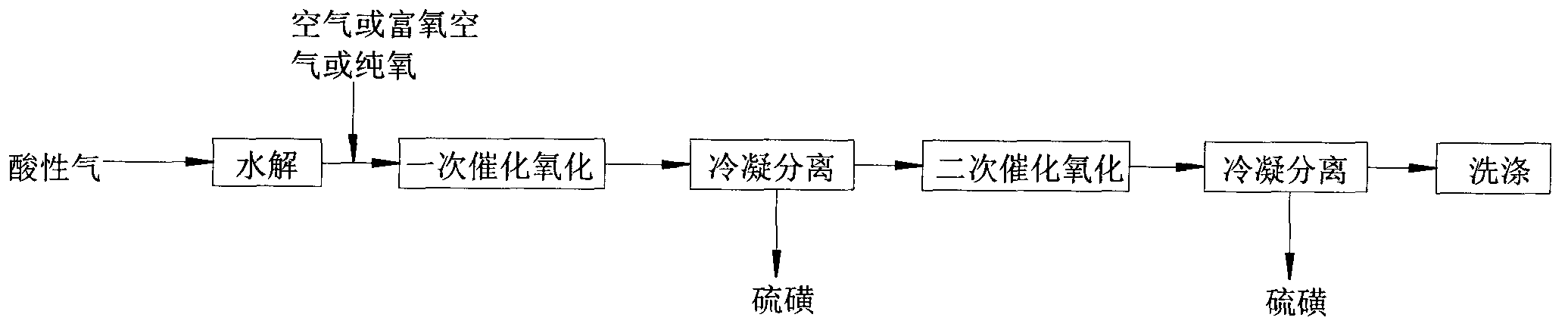
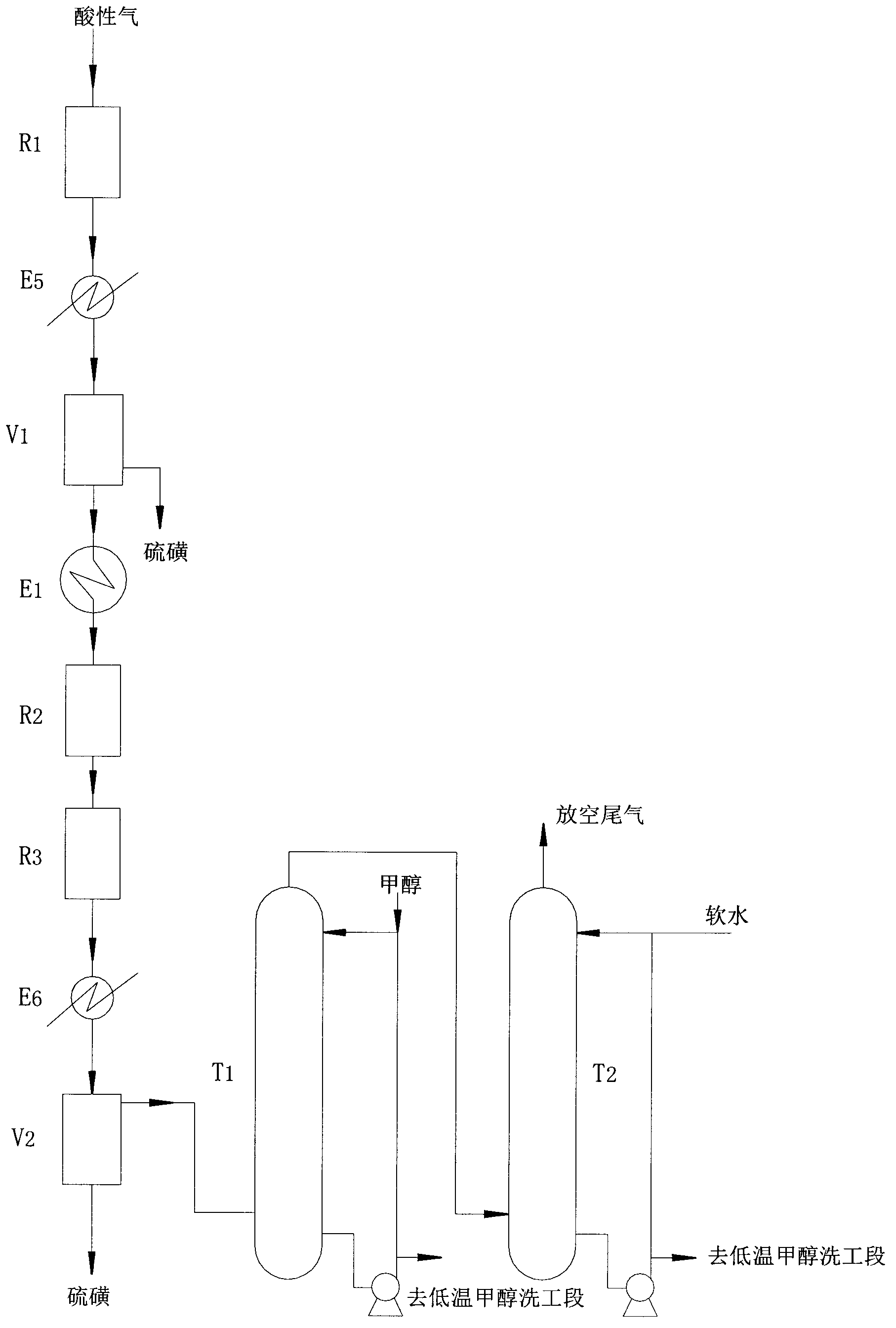
The invention discloses a method, device and reactor for recovery of sulfur from acidic gas. An inorganic sulfide in the acidic gas is catalyzed and oxidized into sulfur by catalytic oxidation reaction, then the organic sulfur in the acidic gas is hydrogenated and hydrolyzed into an inorganic sulfide through catalytic hydrolysis reaction, finally the residual inorganic sulfur in the reaction gas is oxidized into sulfur through secondary catalytic oxidation reaction, and the tail gas is washed by a methanol lotion and / or water, thus realizing complete recovery of sulfur. The invention also discloses the device and reactor for realizing the method. The method and device provided by the invention are suitable for sulfur recovery of low H2S content acidic gas. An alcohol-containing solution is utilized for washing treatment of desulfurized tail gas according to the low temperature methanol washing process, the content of sulfide in the tail gas is reduced, and the environment is protected. At the same time, the reactor involved in the invention has a simple and reasonable structure, saves land occupation of equipment, and lowers the project investment.
Owner:杭州林达化工技术工程有限公司
Compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching sulphide ore, and compounding method and application method thereof
ActiveCN103396964AIncrease resistanceImprove leaching efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical reactionEngineering
The invention discloses a compound bacterium community capable of efficiently leaching a sulphide ore, and a compounding method and an application method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of wet-process metallurgy. Aiming at a biological leaching mechanism of the sulphide ore and the physiological-biochemical characteristics of microorganisms, a community capable of efficiently leaching the sulphide ore is compounded by a plurality of mineral leaching microorganisms, wherein the mineral leaching microorganisms comprise marine bacteria which come from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and are capable of enduring high concentration sodium chloride, sulfur-oxidized bacteria, iron-oxidized bacteria and archaea which are from a freshwater environment, autotrophic bacteria and facultative heterotrophic bacteria. Not only can the difficult problem that the mineral leaching microorganisms from the freshwater environment are intolerance of sodium chloride be solved, but also microorganisms required by oxidation and dissolution of the sulphide ore and diversity of chemical reactions are guaranteed. The compound bacterium community can obviously increase leaching efficiency and leaching rate of the sulphide ore such as copper pyrites and can be applied in a leaching process and a dump leaching process of a stirring tank. A certain basis for popularization and application of biological metallurgy of the sulphide ore is provided by the invention.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
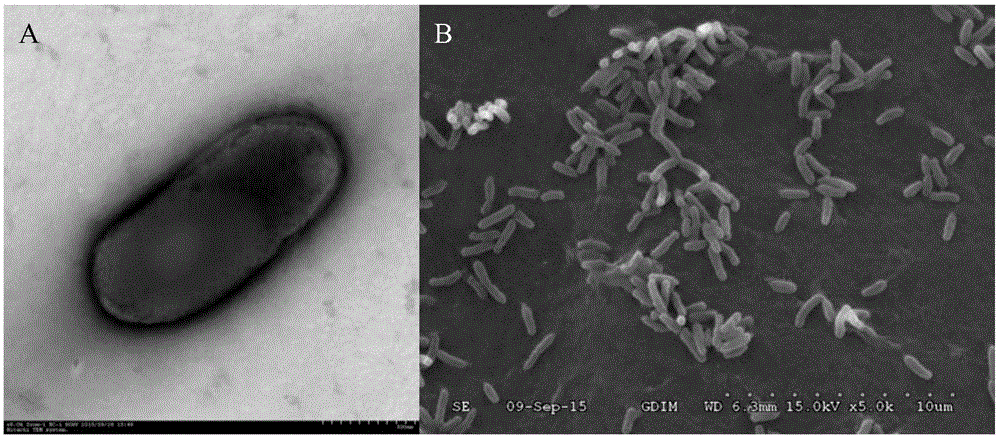
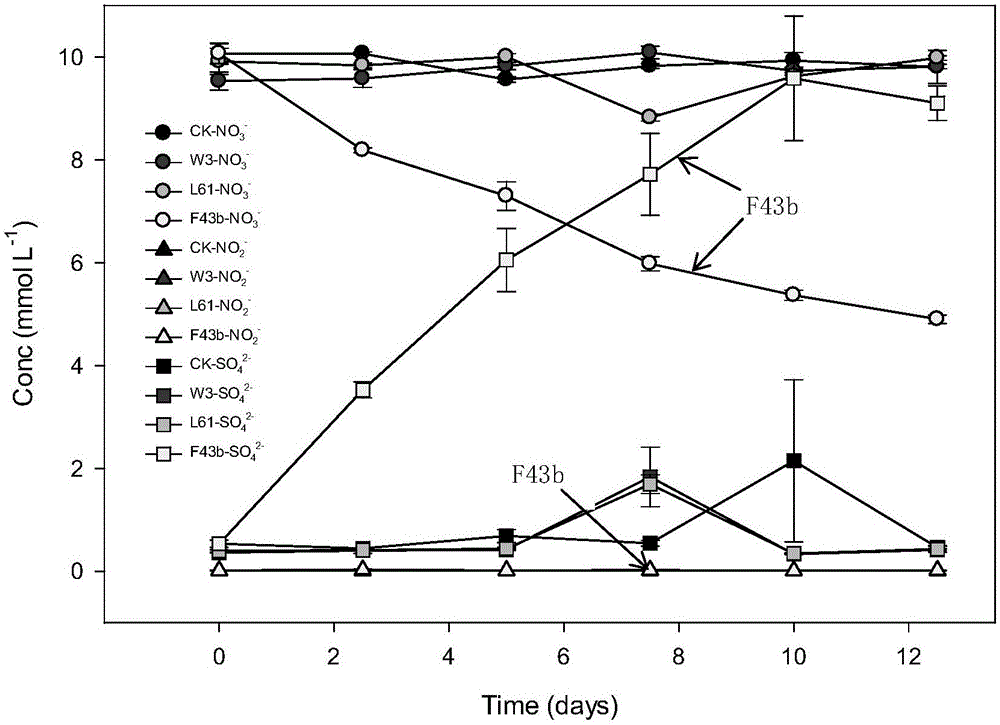
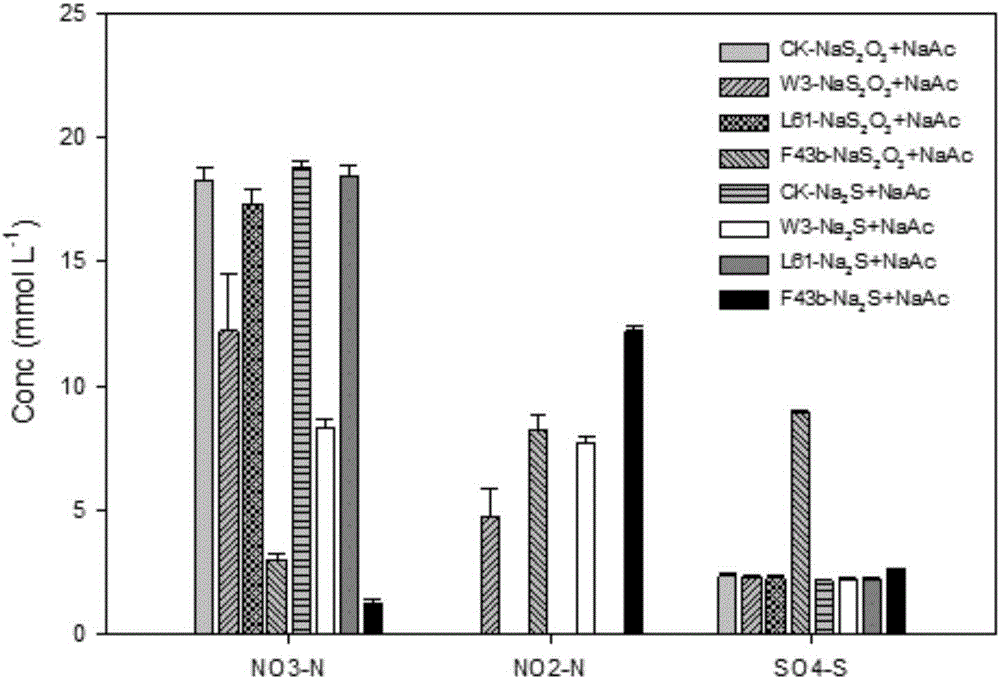
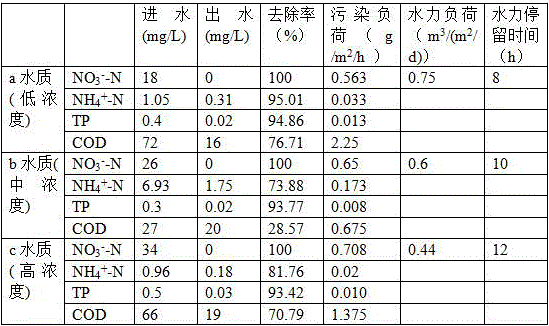
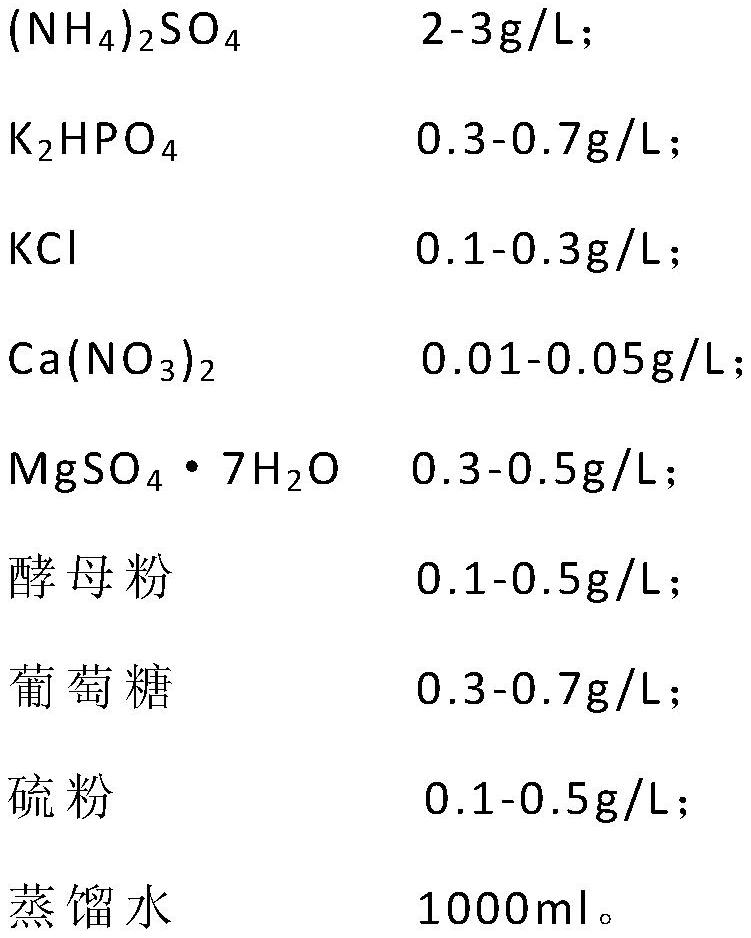
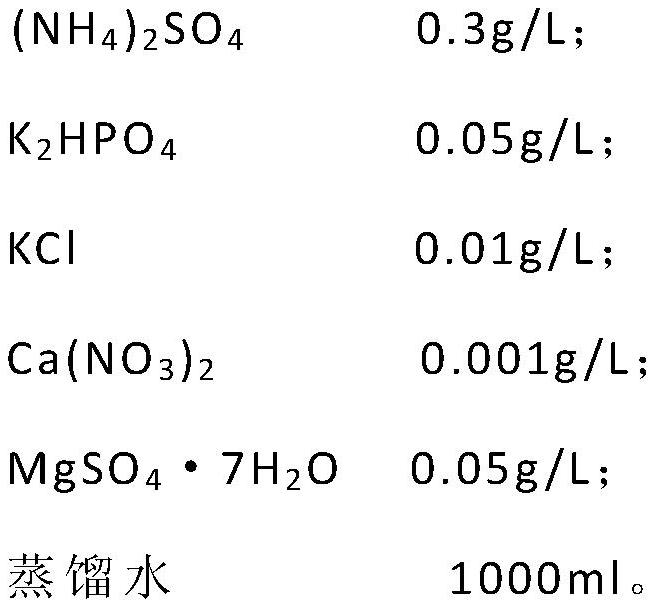
Facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and application thereof
The invention discloses a facultatively autotrophic sulfur oxidation denitrification rhizobium F43b and an application thereof. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) Wuhan University in Wuhan in China on March 30, 2016 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016158. The Rhizobium sp. F43b<T> is facultatively autotrophic rhizobium with sulfur oxidation and denitrification functions, can remove COD, nitrates and sulfides from polluted water or deposits, realizes simultaneous removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur from the polluted water or deposits, and provides bacterial strains and microbial preparations for river restoration and carbon, nitrogen and sulfur wastewater treatment, and researches of the rhizobium provide theoretic guidance for river restoration and removal of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Process for the reactivation of sulfur deactivated cobalt titania catalysts; the catalyst compositions, use of the reactivated catalysts for conducting carbon monoxide hydrogenation, reactions and the products of such reactions
A process for the desulfurization, and reactivation of a sulfur deactivated catalyst constituted of cobalt composited with a titania support. The sulfur deactivated cobalt titania catalyst is first contacted with a gaseous stream of molecular oxygen at temperature sufficiently high to oxidize the sulfur component of the catalyst. The sulfur oxidized catalyst is next contacted with a liquid, preferably water, to remove the oxide, or oxides of the sulfur. The catalyst is then contacted with a reducing agent, suitably hydrogen, to restore the activity of the catalyst. During the treatment there is no substantial loss, if any, of cobalt from the catalyst.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Removal of mercury from coal via a microbial pretreatment process
A process for the removal of mercury from coal prior to combustion is disclosed. The process is based on use of microorganisms to oxidize iron, sulfur and other species binding mercury within the coal, followed by volatilization of mercury by the microorganisms. The microorganisms are from a class of iron and / or sulfur oxidizing bacteria. The process involves contacting coal with the bacteria in a batch or continuous manner. The mercury is first solubilized from the coal, followed by microbial reduction to elemental mercury, which is stripped off by sparging gas and captured by a mercury recovery unit, giving mercury-free coal. The mercury can be recovered in pure form from the sorbents via additional processing.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
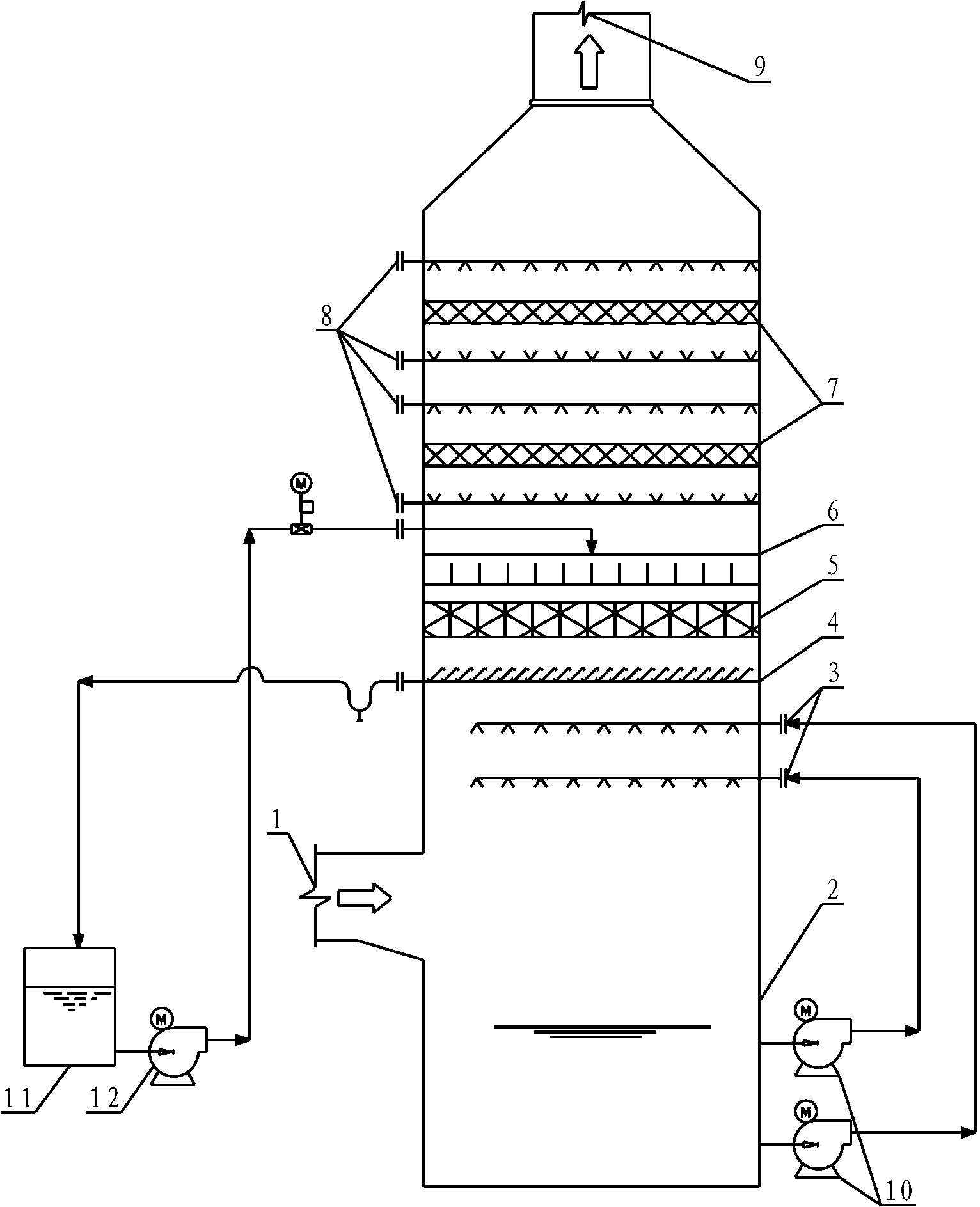
Sectional absorption ammonia desulfurization process and device
ActiveCN102698584AAvoid easy cloggingLong runUsing liquid separation agentParticulatesPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a sectional absorption ammonia desulfurization process and device. Desulfurization, oxidation and crystallization can be realized in a same absorption tower, and different structures and different absorbents are adopted in different absorption section layers, so that crystallization, absorption, dust removal and oxidation can be respectively performed in the corresponding sections; sulfur-containing smoke gas can enter from an inlet at the middle part of the absorption tower, sequentially upwards flow back and pass through a spraying layer, a packing layer and a defogging and washing layer, sulfur dioxide in the smoke gas can be removed, and the smoke gas can leave the absorption tower for exhaust after dust removal and defogging; the process flow is complex, the blockage is difficult to occur and long-period operation of equipment can be ensured; and the sulfur dioxide can be effectively removed, and ammonia sulfate dust particles generated during the desulfurization process can be simultaneously effectively removed.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ELECTRIC POWER ENVIRONMENTAL
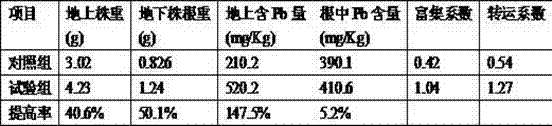
Compound photosynthetic bacteria preparation for enhancing phytoremediation for heavy metal pollution of soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104707864AIncrease nutritionActivation activityContaminated soil reclamationPlant growthChemistry
The invention provides a compound photosynthetic bacteria preparation for enhancing the phytoremediation for heavy metal pollution of soil and a preparation method thereof. The high concentration compound photosynthetic bacteria preparation of thiocapsa roseopersicina and rhodopseudomonas capsulata is adopted through the step that thiocapsa roseopersicina cultures in purple sulfur photosynthetic bacteria and rhodopseudomonas capsulate cultures in purple non-sulfur photosynthetic bacteria are subjected to such culture steps as seed activation, seed culture and anaerobic fermentor irradiation culture. The compound photosynthetic bacteria preparation is used for enhancing the phytoremediation for heavy metal pollution of soil, thiocapsa roseopersicina as sulfur-oxidizing bacteria can be used for oxidizing relatively stable sulfides with heavy metals, thereby promoting sulfur cycle of soil, reducing the PH value of soil and improving the activity of heavy metals; the thiocapsa roseopersicina and rhodopseudomonas capsulata as bacterial manure can promote the conversion of soil substances, improve the soil structure and soil fertility, promote plant growth and improve the biomass of plants enriched with heavy metals, thereby enhancing the efficiency of phytoremediation for heavy metals in soil.
Owner:北京聚益成广科技有限公司
Denitration catalyst with sulfur oxidation preventive characteristic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102872858AFine powderLarge specific surface areaDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystFlue gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts, and particularly relates to a denitration catalyst with a sulfur oxidation preventive characteristic and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises, by mass, 1% of V2O, 5-10% of WO3, 1-2% of BaO and the balance being TiO2. The preparation method of the denitration catalyst includes three steps of preparation of impregnation liquid, loading of active components and roasting. As the denitration catalyst is modified by BaO, the modified denitration catalyst has good pore structure, obvious change of the acid center position is avoided, oxidation of SO2 on the surface of the catalyst is suppressed, and NO removal rate is higher than 95%. The denitration catalyst with the sulfur oxidation preventive characteristic and the preparation method thereof are adaptable to the characteristic of high sulfur content of domestic coals, the service life of the catalyst is prolonged effectively, and flue gas denitration cost is lowered.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +2
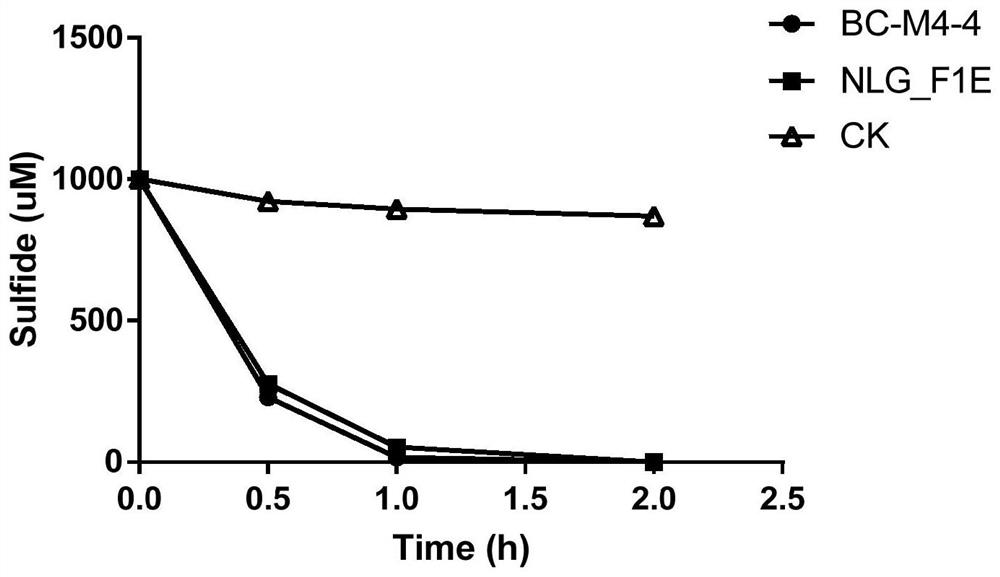
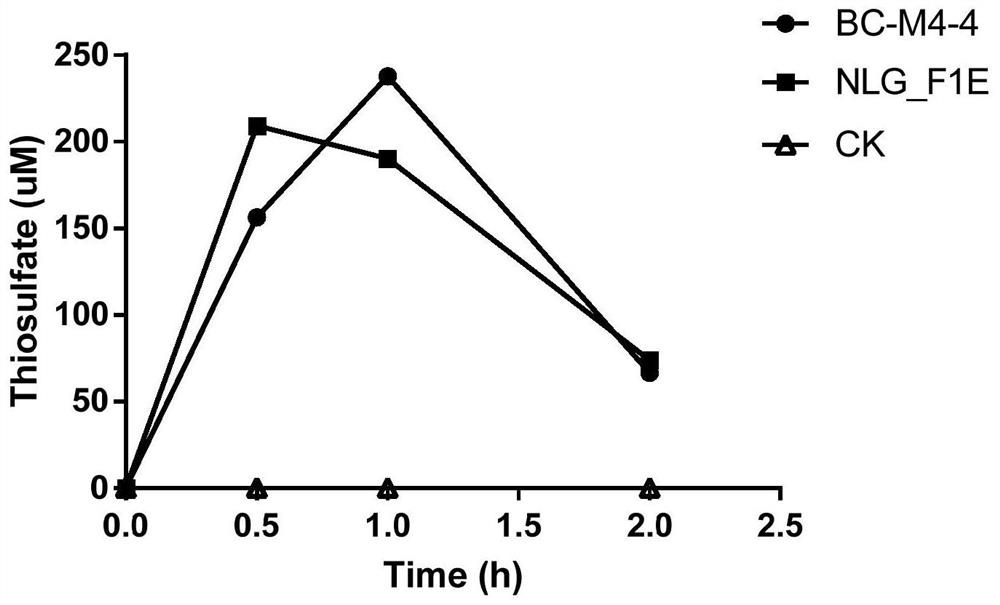
Sulfur-oxidizing bacterium and method for removing sulfide by using sulfur-oxidizing bacterium
ActiveCN103667096AImprove desulfurization efficiencyHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThermithiobacillus tepidariusSulfate
The invention discloses a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium and a method for removing sulfide by using the sulfur-oxidizing bacterium and belongs to the technical field of biological and environmental protection. The invention discloses the bacterium classified and named Themithiobacillustepidarius JUN-2, and the preservation number is CCTCCNO:M2013217. The bacterium has very high oxidizing efficiency for sulfur compounds, and a byproduct named elemental sulfur with high additional value is efficiently generated. The invention further relates to a method for removing the sulfur compounds in sulfur-containing waste liquid by applying the the sulfur compounds in sulfur-containing waste liquid in a gas lifting type inner circulation continuous operation aerobic reaction device; the hydraulic retention time (HRT) is 10 hours; the yield of the elemental sulfur is 0.1-gL<-1>h<-1>; the generation ratio of the elemental sulfur is about 60 percent; the oxygenation efficiency of thiosulfate is greater than 98 percent. The gas lifting type inner circulation continuous operation aerobic reaction device behaves well, and has a potential to removal of the sulfides in the sulfur-containing waste liquid on large scale.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrate nitrogen removal method and device for said method
InactiveCN102295352AInhibitionWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesNitrate saltsNitrate nitrogen
Nitrate nitrogen removal method and apparatus for said method. The present invention provides a method for removing nitrate nitrogen in wastewater using sulfur oxidizing bacteria in the presence of a denitrification material containing sulfur and calcium-based components. The method for removing nitrate nitrogen according to the present invention comprises: in a drainage treatment tank having a filling layer of denitrification material, allowing the drainage containing nitrate nitrogen to pass through the filling layer of the denitrification material, and making at least a part of the treated drainage through the filling layer Circulation to the inlet side of the fill layer or to the middle layer of the fill layer. In addition, the nitrate nitrogen removal device of the present invention has a circulation pump for circulating at least a part of the wastewater passing through the packed bed in the drainage treatment tank to the inlet side of the packed bed or to the intermediate layer. As the denitrification material, there are materials containing calcium carbonate and sulfur, and iron oxide may be mixed therein.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
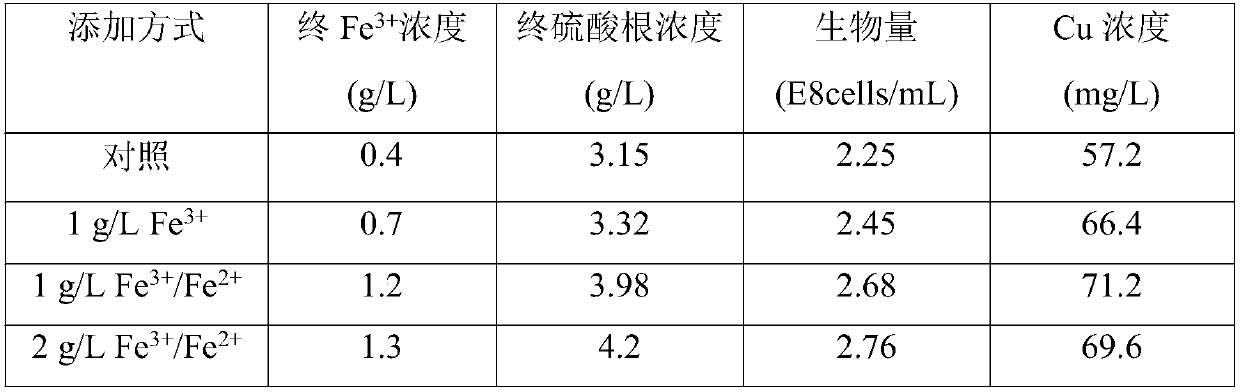
Method for enhancing leaching of copper pyrites based on microbial growth and chemical regulation and control
ActiveCN107794368AWeaken the passivation effectImprove the bioleaching processProcess efficiency improvementPotassiumCommunity structure
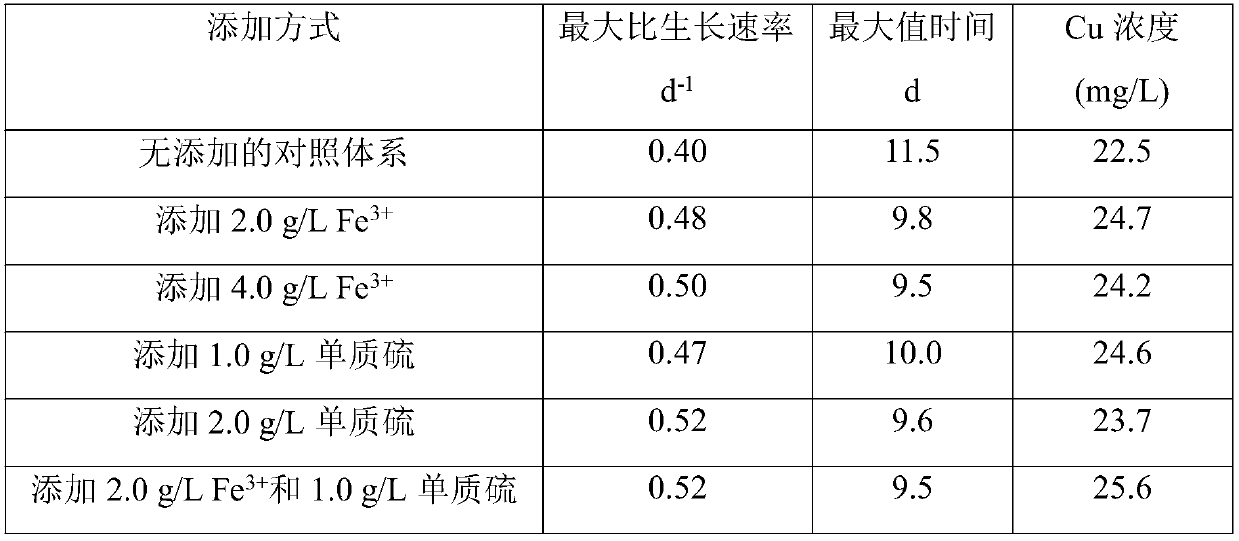
The invention discloses a method for enhancing leaching of copper pyrites based on microbial growth and chemical regulation and control and belongs to the biology technical field. The method comprisesthe steps that purely cultured iron oxide bacterial and sulfur oxide bacterial cells are inoculated into a copper pyrite composite culture medium, bioleaching of the copper pyrites is conducted, a proper quantity of ferrous and ferric ions are supplemented in the medium term of leaching, ferrooxidant deficiency caused by generation of jarosite is avoided by supplementing, and energy substrates are supplemented for iron oxide bacterial cells; at the same time, the constant pH value is adjusted, a proper amount of elemental sulfur is supplemented, the acidity is enhanced while the sulfur metabolism is improved, and generation of the jarosite is restrained; the iron oxide bacterial and sulfur oxide bacterial cells collected in the pure culturing process are added gradually by a proper proportion, the microbial growth is improved in the microbial leaching process, the microbial community structure and the metabolic activity of iron and sulfur are optimized, and thus the leaching microenvironment is improved. The method is easy to operate, low in requirement for equipment and suitable for being applied and popularized on a large scale in the similar biological leaching process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
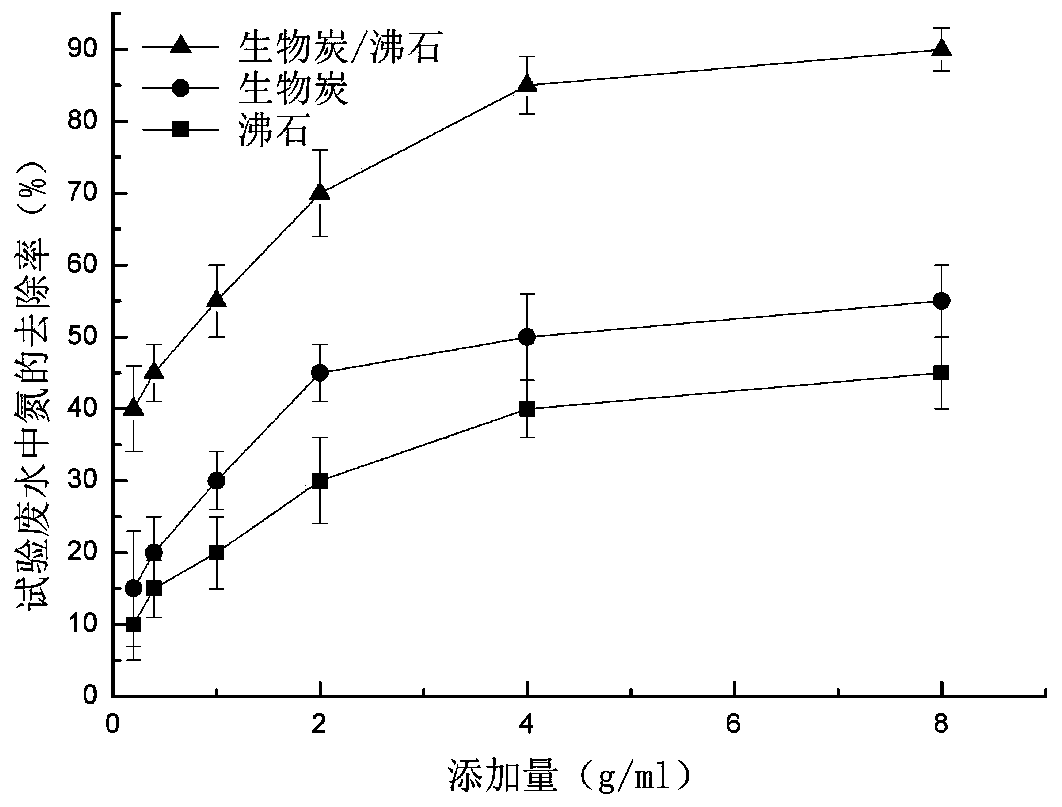
Biochar/zeolite composite adsorbent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110773123AImprove adsorption capacityDemonstration effect is goodOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentAdsorption effect
The invention discloses a biochar / zeolite composite adsorbent material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: 1) drying and dehydrating a biomass raw material to 1% or below; 2) crushing the dried raw material into granules of 1 mm or below; 3) performing thermal cracking treatment; 4) performing alkali liquor zeolitization treatment; and 5) performingcleaning. By use of the method, ash components in biochar are subjected to hot alkali liquor treatment to obtain Y-type zeolite, the Y-type zeolite and a bonding effect with biochar to form a super adsorbent material, and the material has significant effects on heavy metals, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, antibiotics and the like in sewage.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Trickling filtration technique and device for effectively removing nitrate nitrogen in high-nitrogen low-carbon environment
InactiveCN106745718AMitigate the problemRelieve stressClimate change adaptationTreatment involving filtrationTrickling filterTreatments water
The invention discloses a trickling filtration technique and device for effectively removing nitrate nitrogen in a high-nitrogen low-carbon environment. The trickling filtration technique comprises the following steps: sewage is firstly lifted to the top of a trickling filter to implement uniform water distribution, wherein the treatment water temperature is not lower than 8 DEG C, the height of the filter layer is 1.2-1.5m, and the filter layer is filled with a sulfur-limestone mixed filler; and in an anoxic state, the sewage passes through the filter layer, and finally submerges the effluent at the bottom of the filter material. According to the characteristics of higher nitrate nitrogen content and lower carbon-nitrogen ratio in the sewage, the trickling filtration technique is improved, the filler is improved, the parameters are adjusted, and the trickling filter is improved; the water is uniformly distributed on the top of the filter tank, penetrates through the special denitrification filter layer, and submerges the effluent at the bottom of the filter material; and in the anoxic state, sulfur autotrophic nitrobacteria are utilized to oxidize the sulfur into sulfates and reduce the nitrate nitrogen into nitrogen, thereby finally achieving the goal of efficiently removing nitrate nitrogen and greatly relieving the environmental pressure.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Process for the desulfurization of hydrocarbonacecus oil
InactiveCN1852966AHigh recovery rateReduce sulfur contentRefining with oxygen compoundsTreatment with plural serial refining stagesPtru catalystHydrodesulfurization
A process for the desulfurization of hydrocarbonaceous oil wherein the hydrocarbonaceous oil is contacted with a hydrodesulfurization catalyst in a hydrodesulfurization reaction zone (3) to reduce the sulfur level to a relatively low level then contacting the resulting hydrocarbonaceous stream from the hydrodesulfurization zone with an oxidizing agent (8) to convert the residual, low level of sulfur compounds into sulfur-oxidated compounds. The resulting hydrocarbonaceous oil stream containing the sulfur-oxidated compounds is separated after decomposing any residual oxidizing agent by contacting the stream with an adsorbent material (18, 30) to adsorb the sulfur-oxidated compounds to produce a hydrocarbonaceous oil stream having a reduced concentration of sulfur-oxidated compounds. The spent adsorbent (18, 30) is regenerated and subsequently returned to adsorbent service.
Owner:UOP LLC
Complex microbial agent for efficiently converting heavy metal chromium in soil as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113265362AGood synergyImprove adaptabilityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationThiobacillus ferrooxidansMicrobial agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil remediation, and particularly relates to a complex microbial agent for efficiently converting heavy metal chromium in soil as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The complex microbial agent is obtained by mixing and carrying out enrichment culture on the following two florae: a flora A consisting of bacillus, pediococcus acidilactici, clostridium coriolis, actinobacillus succinogenes and bacillus aceticus; a flora B consisting of acidophilic iron bacteria, thiobacillus ferrooxidans, acid-thiobacillus thiooxidans, sulfur-oxidizing acid-thiobacillus thiooxidans, sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans. After the complex microbial agent is used for treating the chromium-contaminated soil, the chromium removal rate can reach 91% or above. The complex microbial agent is formed by culturing and mixing a plurality of strains, and the strains have a good synergistic effect and do not generate antagonism; after compounding, the adaptability to heavy metals can be improved, so that the survival and removal effects of the soil in heavy metal contaminated soil are improved. The microbial agent is simple in preparation and application method, short in culture period and treatment period and low in cost, prevents secondary pollution, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +2
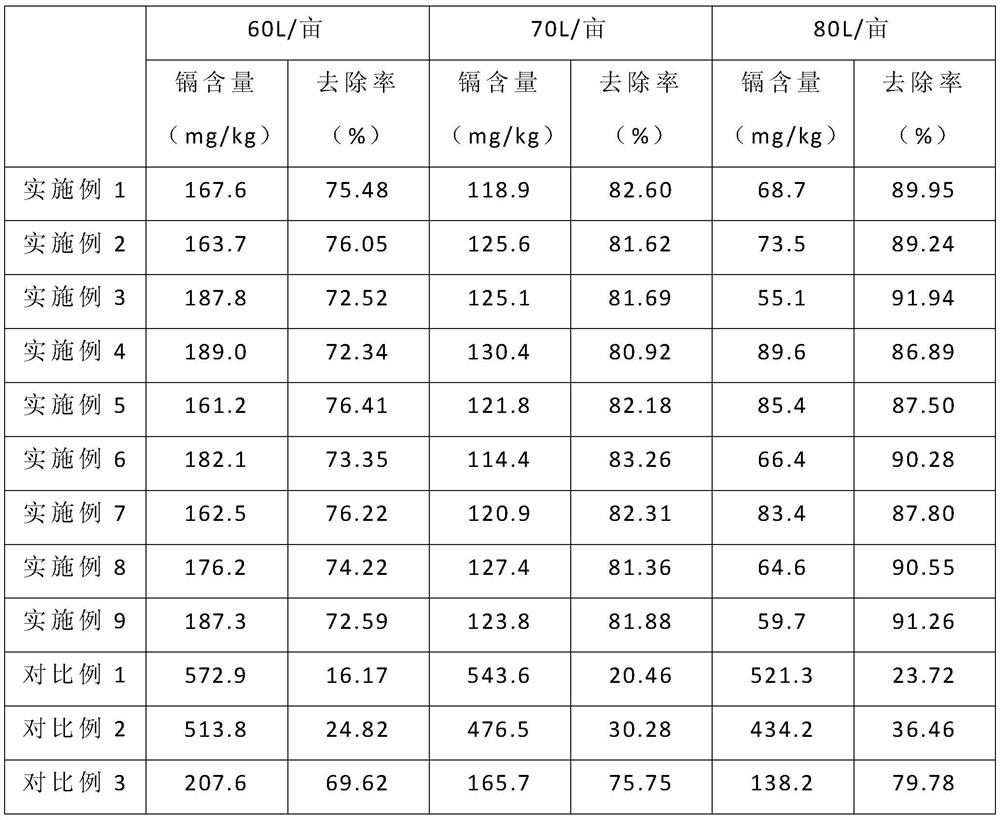
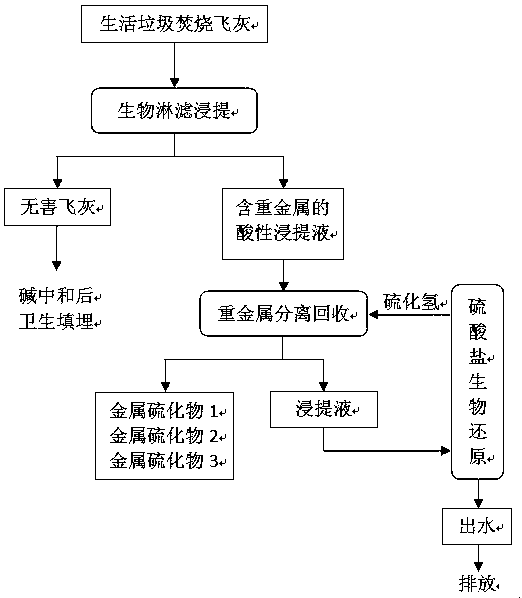
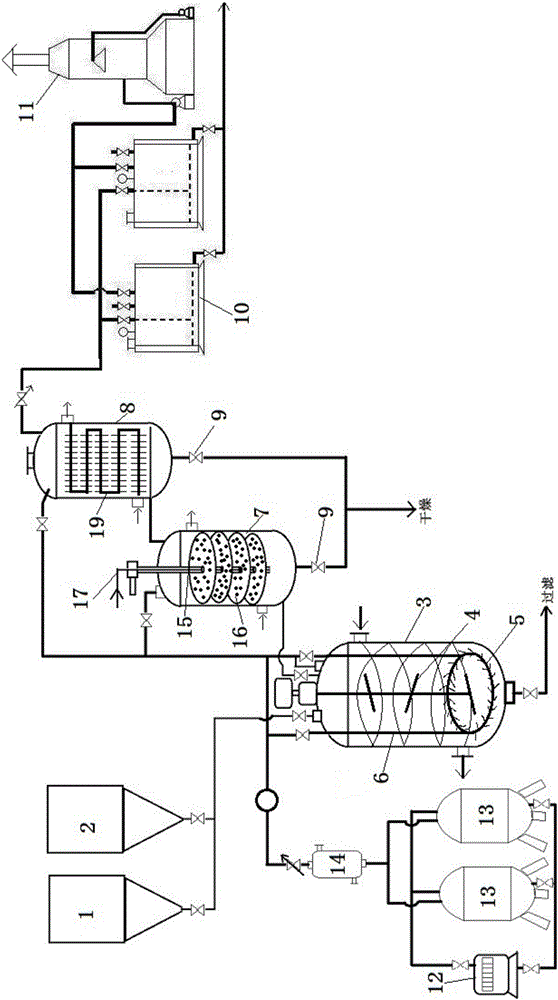
Garbage incineration fly ash hazard-free treatment and heavy metal recycling method
ActiveCN107716519AHarmlessReduce heavy metal contentSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingPersulfateSulfide
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment engineering and particularly relates to a method for separating and recycling heavy metal from garbage incineration fly ash and conducting hazard-free treatment on the fly ash. The method comprises the steps that after the household garbage incineration fly ash is diluted through an acidic sulphur oxidation bacteria culture medium solution, sulphur balls are added, so that acidic leach liquor containing the heavy metal is obtained; after a proper amount of alkali is added for pH adjustment, hydrogen sulfide gas is introduced into theacidic leach liquor; the hydrogen sulfide gas reacts with the heavy metal, so that sulfide precipitation is formed; and after solid-liquid separation is completed, recycling is conducted in the form of the sulfide precipitation, so that the pure heavy metal is obtained. The treatment process is implemented at the normal temperature and normal pressure; energy consumption is low; the process is simple; the large-scale engineering potential is achieved; a biological leaching energy source substance, namely sulphur, is recycled to be reused, so that the post-acidification problem of the treated fly ash is solved; the heavy metal entering the leach liquor is subjected to reduction and precipitation conducted through sulfate, so that the heavy metal is separated or recycled or removed effectively; and the sulfate and pH problems are solved at the same time.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for comprehensive utilization of copper tailing sludge and tailing obtained after copper smelting beneficiation
ActiveCN106086433AAchieve the effect of turning waste into treasureLow costSilicaProcess efficiency improvementSludgeSulfide minerals
The invention provides a method for comprehensive utilization of copper tailing sludge and tailing obtained after copper smelting beneficiation. The method comprises the steps that valuable metal in the sludge or the tailing obtained after copper smelting beneficiation in a dissolved mode with nitric acid with oxidizability, sulfur in sulfide minerals such as copper sulphide is oxidized into sulfuric acid, and nitrate is generated by other metal and left in acid liquor; filtering is conducted, filtrate is treated independently, and thus relevant metal such as silver, gold, platinum, rhodium, nickel and molybdenum are separated out; and then filter residues are prepared into a high-added-value product, namely fumed silica, the content of SiO2 in the prepared product is higher than 99.9%, the specific surface area measured through a multi-point BET method is 350-500 m<2> / g, and the effect of recycling waste is achieved. Meanwhile, the invention provides a production device for the method. Parts of the production device are all common parts in a chemical plant, cost is low, and large-scale industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV +1
Biological sewage denitrification method based on sulfur autotrophic short-cut denitrification, and reaction device
PendingCN111960532AAddress toxicitySolve the speed problemWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaSulfite salt
The invention discloses a biological sewage denitrification method based on sulfur autotrophic short-cut denitrification. The biological sewage denitrification method comprises the following steps: introducing a thiosulfate solution into a gas stripping type up-flow reactor from the bottom; deposing the thiosulfate into elemental sulfur and sulfite under the action of sulfur oxidizing bacteria domesticated in an anaerobic environment in the reactor; introducing sewage containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrate into the gas stripping type up-flow reactor from the bottom; and making the elemental sulfur and sulfite be respectively subjected to short-cut denitrification reaction with nitrate, wherein the generated nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen generate nitrogen under the action of anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria. According to the invention, by selecting a new sulfur source, the problem of toxicity of hydrogen sulfide or low elemental sulfur reaction rate in a sulfur autotrophicdenitrification process is solved; and by means of sulfur autotrophic short-cut denitrification, stable nitrite nitrogen is provided for anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and autotrophic nitrogen removal treatment based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation is achieved.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST
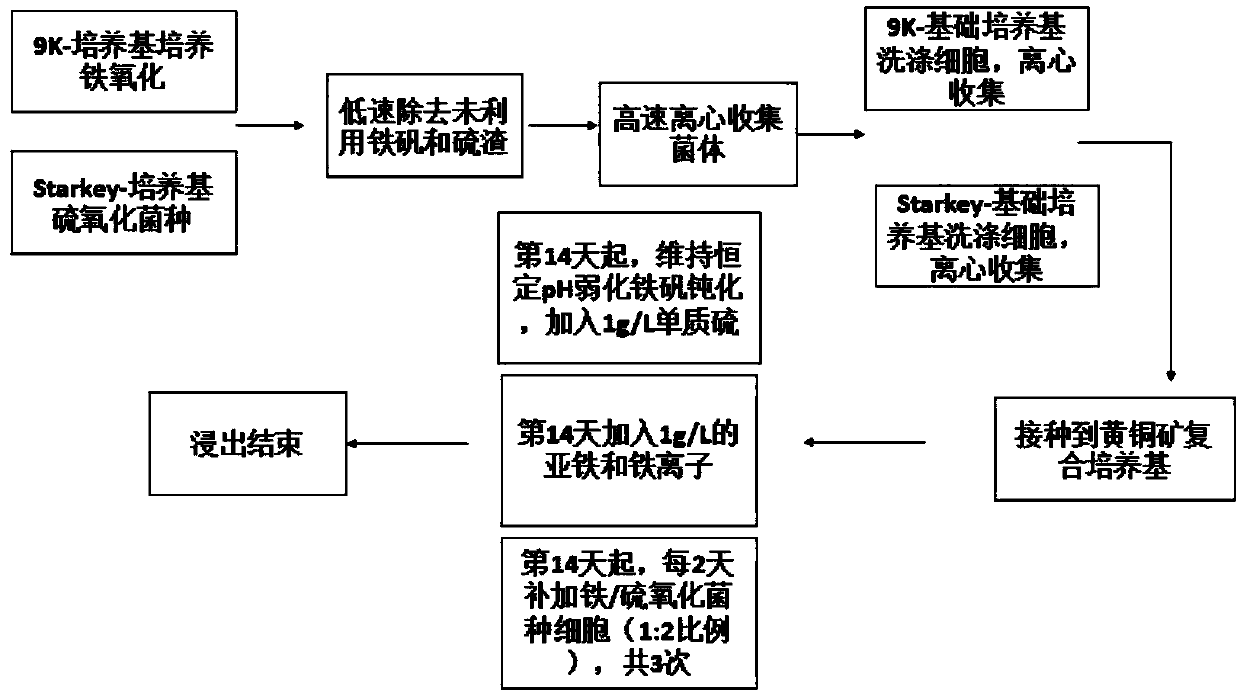
Complex method for improving efficiency of chalcopyrite leaching conducted through sulfur oxidation cultures
ActiveCN107858507AIncrease cell concentrationImprove leaching efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiobacillus ferrooxidansCell seeding
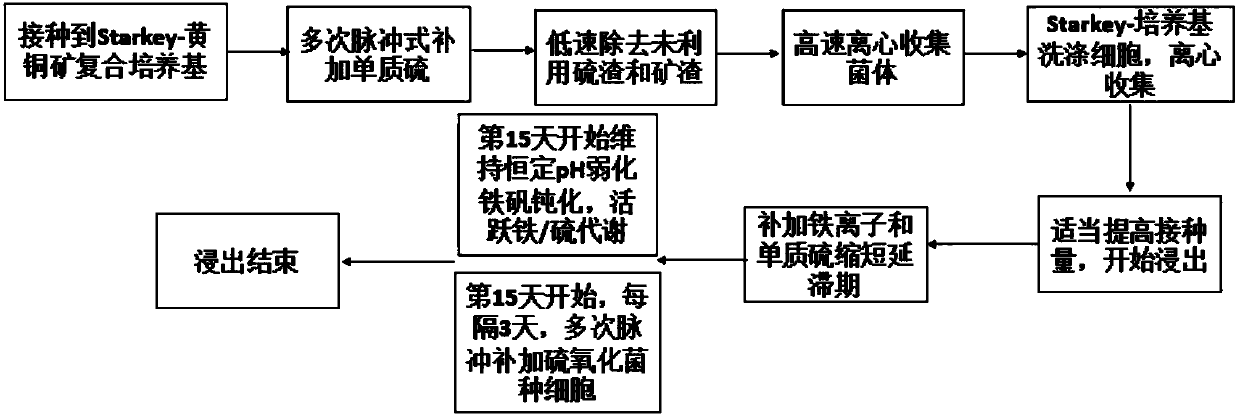
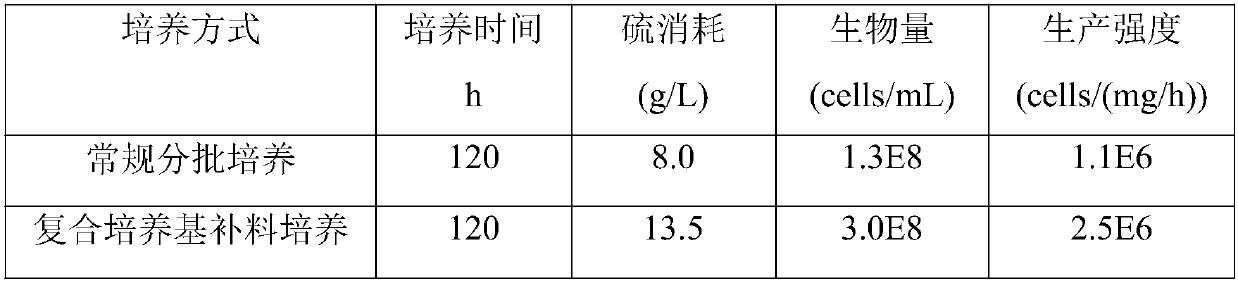
The invention discloses a complex method for improving efficiency of chalcopyrite leaching conducted through sulfur oxidation cultures and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the steps that on the basis of a Starkey-chalcopyrite composite culture medium, an external-source energy substrate, namely elemental sulfur, is supplemented in a pulsed manner at the middle and later culture stages, and high-density culture of thiobacillus thiooxidans is achieved; a proper amount of elemental sulfur and iron ions are added while cell inoculation is conducted, start of a leaching biochemical reaction cycle is accelerated, the lag phase is shortened, and the inoculum size is increased; and at the later leaching stage, the low constant pH is maintained, jarosite stress is inhibited, sulfur oxidation culture cells are added as supplementation, iron metabolism is promoted while sulfur metabolism is improved, and furthermore, the leaching microenvironment is improved. By means of the method, the sulfur oxidation cultures can be cultured more efficiently, the leaching lag phase is shortened, and active biochemical reaction state of the leaching microenvironment is maintained better, and thus the leaching rate is increased; and in addition, the method is easy to operate and implement and suitable for being applied and popularized in similar bioleaching processes on a large scale.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
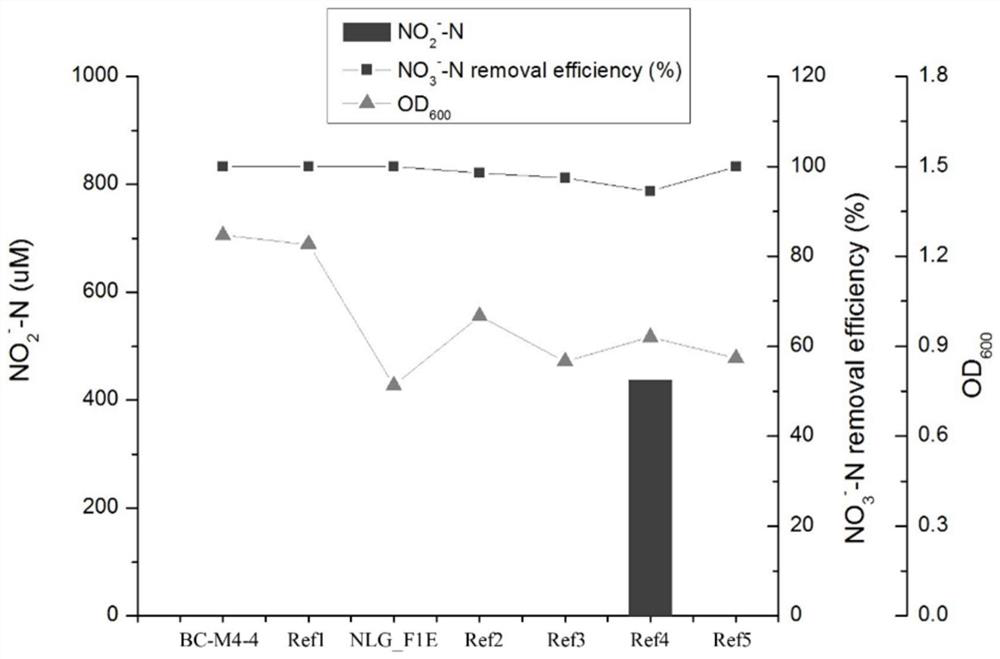
Halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof
ActiveCN112551692AImprove recovery rateGrow fastWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHalomonas salinaNitration
The invention discloses halomonas with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions and application thereof , and belongs to the technical field of microorganism application. The invention provides two strains of halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 with aerobic denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation functions, and the preservation numbers of the halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and the MCCC 1A13718 are as follows: GDMCC No:60985 and GDMCC No:60984. The halomonas sp. MCCC 1A17488 and MCCC 1A13718 can be applied to nitrogen and sulfur removal, can be suitable for biological nitrogen removal treatment of various nitrogen-containing wastewater, has efficient denitrification and heterotrophic sulfur oxidation capacity under aerobic and anoxic conditions, can rapidly and efficiently remove nitrate, nitrite, ammonia nitrogen, sulfide and the like, and has good application prospects in the biological nitrogen and sulfur removal of sewage, sludge, sedimentsor culture water bodies.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MINIST OF NATURAL RESOURCES +1
Preparation method and application of netted carrier-based sulfur-oxidizing bacteria immobilized fixed bioactive filler
ActiveCN104108800ANot easy to fall offNot easy to loseSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentStart timePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a netted carrier-based sulfur-oxidizing bacteria immobilized fixed bioactive filler, and belongs to the water treatment field. The fixed bioactive filler comprises an occlusion body and a carrier; the carrier is a netted fixed carrier prepared by adding a hydrophilic material polyvinyl alcohol to main materials comprising polyethylene and polypropylene, and carrying out hot melting or sheet hot pressing; the netted structure of the carrier allows the occlusion body to penetrate through meshes and the carrier to form a riveting structure in order to increase the integral stability; an occlusion liquid is obtained by mixing a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium concentrate with a polyvinyl alcohol solution; and the occlusion liquid is uniformly coated on the netted carrier, and is subjected to two stage crosslinking by boric acid to form the occlusion body, and the occlusion body is combined with the netted carrier to obtain the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria immobilized bioactive filler. The bioactive filler prepared in the invention can effectively solve the problems of low sulfur-oxidizing bacterium adhesion ability, low film forming ability and the like, improves the processing capacity of the reactor, and shortens the starting time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of treating a sulphide mineral
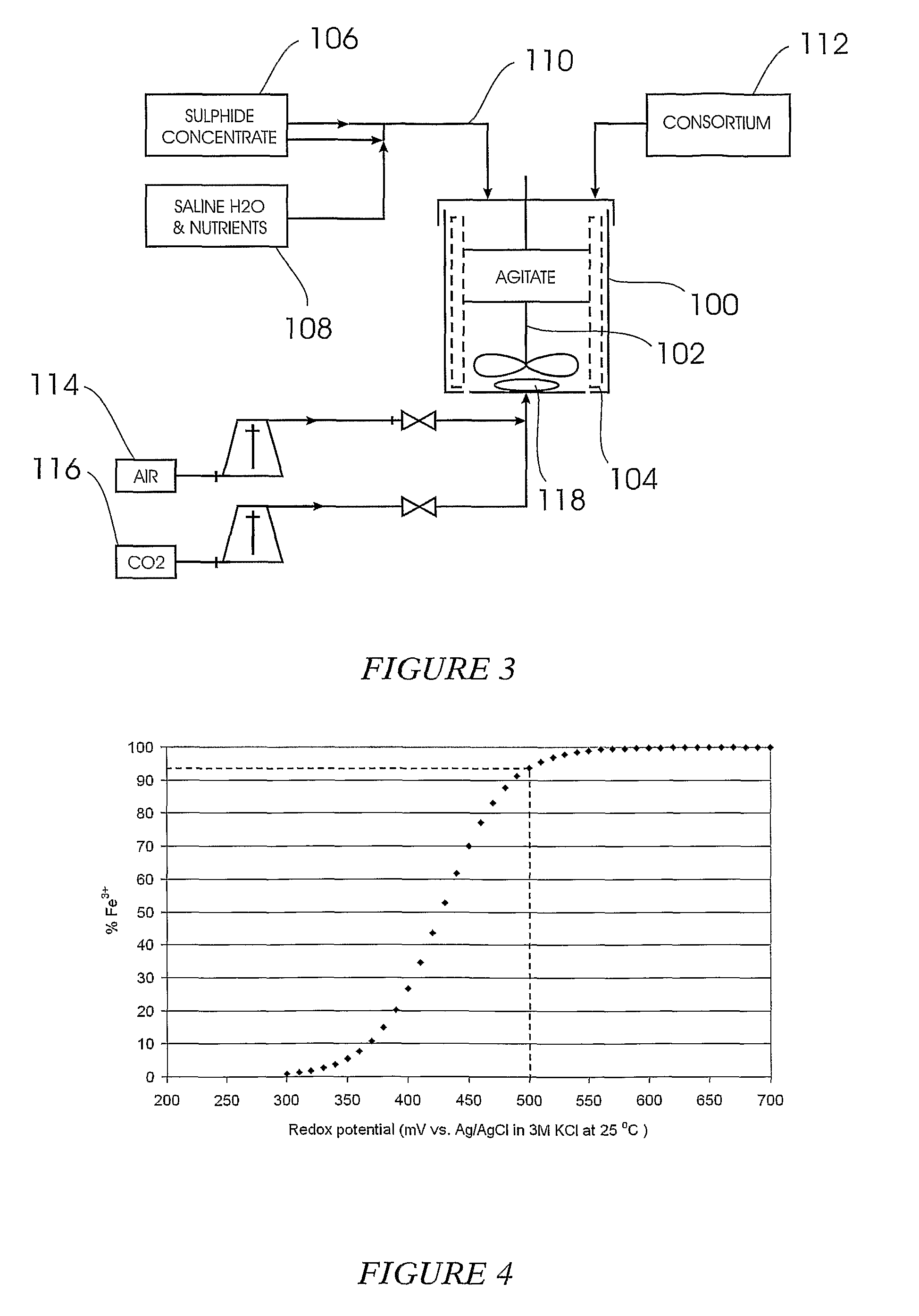
ActiveUS8597933B2Speed up the processImprove bioleaching efficiencyBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismSulfide minerals
A copper bioleaching process which makes use of a consortium which contains Leptospirillum ferriphilum and a sulphur oxidising microorganism which is halophilic or halotolerant.
Owner:CONSOL NOMINEES
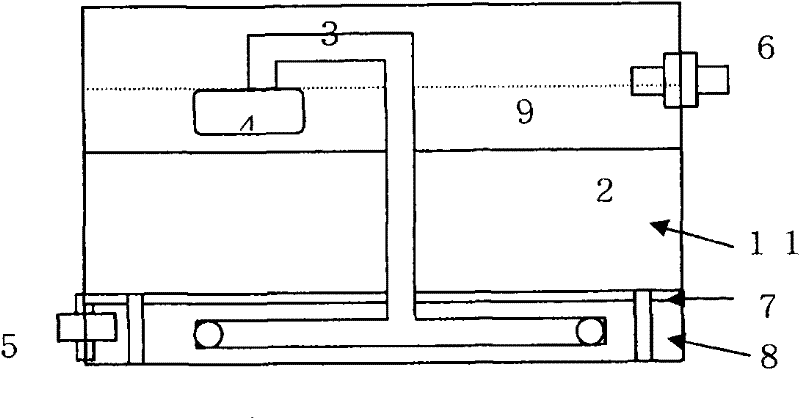
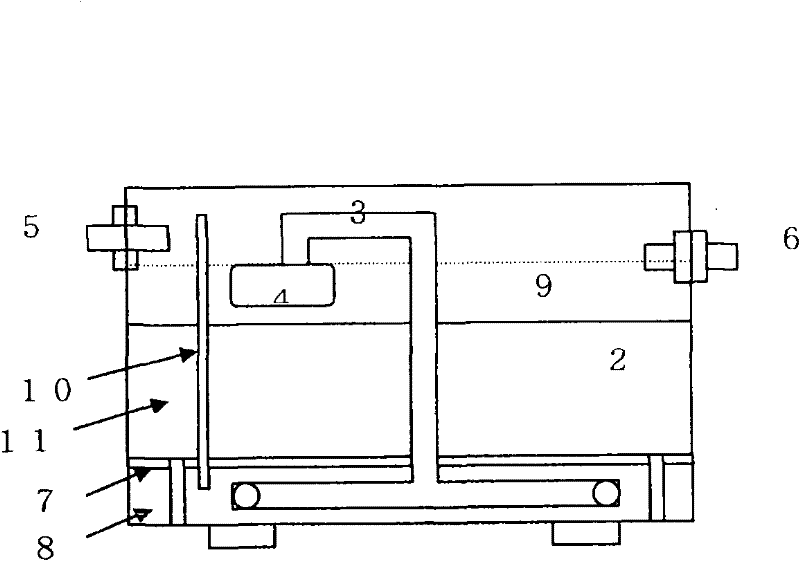
Method for promoting biological column leaching of poor chalcocite
ActiveCN110863117AImprove leaching efficiencyRich reservesProcess efficiency improvementIron sulphurEnvironmental chemistry
The invention discloses a method for promoting biological column leaching of poor chalcocite, particularly discloses a method for synergistically promoting biological column leaching of the poor chalcocite based on foreign intervention of compound sulfur oxidizing bacteria and the pyrite, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. 9K-chalcocite composite medium is used as a leaching solution, by adding a certain proportion of the pyrite and introducing a foreign compound sulfur oxidizing bacteria, various biochemical reactions in the leaching process are controlled, iron and sulfurmetabolism are promoted in the leaching process, and formation of an iron / sulfur passivation film is reduced; and the biological effect in the leaching process is strengthened by adding the compound sulfur oxidizing bacteria in batches, so as to make the copper ions leaching rate increase by 33.9%. The method is easy and convenient to operate, economical and reasonable, and is suitable for large-scale application of similar bioleaching processes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for synchronously removing volatile organic chemcials (VOCs), sulfides and ammonia in waste gas and recycling sulfur by chemical biological coupling method
ActiveCN110639358ANo secondary pollutionReduced electron donorDispersed particle separationSulfur preparation/purificationElectron donorNitration
The invention discloses a process for synchronously removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sulfides and ammonia in waste gas and recycling sulfur by a chemical biological coupling method, and belongs to the field of waste gas treatment. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, introducing waste gas into an absorption tower containing a slightly alkaline solution to absorb hydrogensulfide, ammonia and a part of soluble VOCs, discharging gas subjected to removal of most of hydrogen sulfide and ammonia and a part of soluble VOCs, introducing the liquid subjected to absorption into a micro-oxygen bioreactor, separately converting the hydrogen sulfide and the ammonia into elemental sulfur and nitrogen by utilizing sulfur oxidation, ammonia oxidation, sulfur autotrophic denitrification and short-path denitrification coupling processes (sulfur oxidation bacteria, ammonia oxidation bacteria, denitrification bacteria and sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacteria), and then, introducing the obtained gas into another bioreactor to remove residual hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and VOCs. The process is reasonable, pollutant removal is not limited by concentration, the alkaline absorption solution can be recycled, repeated addition of alkali solutions is not needed, addition of a carbon source is not needed, and secondary pollution is not generated. The sulfur oxidation, ammonia oxidation, sulfur autotrophic denitrification and short-distance denitrification coupling processes (sulfur oxidation bacteria, ammonia oxidation bacteria, denitrification bacteria and sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacteria) are utilized, so that electron donors required in a denitrification process can be reduced, and operation cost is saved. Meanwhile, pollutants are converted into available elemental sulfur for recycling, so that waste recycling is realized, and the process is an ideal process for synchronously removing VOCs, sulfides and ammonia from waste gas.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Halophilic alkalophilic biological desulfurizing treatment process and treatment device
ActiveCN110240961APlay a role in stabilizing the systemWeaken chemical oxidationGaseous fuelsDispersed particle separationMicroorganismGeneration rate
The invention relates to a halophilic alkalophilic biological desulfurizing treatment process and a treatment device. The device comprises a biological purification tower, a deep adsorption tower, a biological regeneration tower and a sulfur collection tower. The process comprises the following steps of: absorbing H2S in biogas through an absorption liquid containing sulfur oxidizing microorganisms, and then stirring a liquid phase in an anaerobic environment to strengthen the absorption of HS<-> by the sulfur oxidizing microorganisms; and under the condition of oxygen enrichment, oxidizing the HS<-> by the sulfur oxidizing microorganisms to generate elemental sulfur, and recovering the elemental sulfur. According to the invention, by adding the anaerobic strengthening treatment step in the biological desulfurizing process, the absorption of the HS<-> by the sulfur oxidizing microorganisms and the selection of HS<-> oxidation paths are strengthened, the chemical oxidation process existing in the biogas biological desulfurizing process is effectively weakened, the formation of S2O3<2->and SO4<2-> in the treatment process is greatly reduced, the generation rate of the elemental sulfur is increased, the requirement on liquid alkali for adjusting pH is reduced, and the treatment process has good economic benefits and application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Culture method of sludge with synchronous sulfur autotrophic denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation functions
ActiveCN110950428AReduce outputQuick buildWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesActivated sludgeNutrient solution
The invention discloses a culture method of sludge with synchronous sulfur autotrophic denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation functions. The method comprises sludge inoculation pretreatment and two stages. In a first stage, pretreated sludge is inoculated into a culture device, the culture device is filled with an initial artificially synthesized nutrient solution, the culture device is put into a constant-temperature water bath oscillator, and a reaction period is set. In a second stage, the concentrations of NO3<-> ions, Na2S2O3.5H2O and CH3COONa.3H2O in the artificially synthesizednutrient solution are increased, the concentration of NO2<-> ions at the end of the first stage is maintained, the concentration of other nutrients is not changed, and a continuous reaction is carried out in the culture device. The culture method has the technical effects that activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant is used as inoculated sludge, anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria and sulfur oxidation bacteria are enriched in a single mixed system at the same time, and a symbiotic system is constructed in a short time.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Sulfur oxidizing bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN113151120ANo secondary pollutionAvoid secondary pollutionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of environmental treatment, and in particular relates to sulfur oxidizing bacteria and application thereof. The sulfur oxidizing bacteria are Pseudoalteromonas sp. LZB5-2, and have been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 29, 2021; the preservation address is Beijing, China; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.21762; and the classification name is Pseudoalteromonas sp. According to the invention, sludge, sewage waste and the like which cannot be directly utilized are comprehensively utilized by utilizing microorganisms; and the invention can also be applied to aquatic product culture.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Online desulfurizing agent for aluminum oxide production and using method thereof
PendingCN112678857AImprove desulfurization effectReduce desulfurization costAluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide purificationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationSodium aluminateAluminium oxides
The invention discloses an online desulfurizing agent for aluminum oxide production and a using method thereof. The online desulfurizing agent is calcium nitrate or calcium nitrate slurry. The using method of the online desulfurizing agent is characterized in that: calcium nitrate or calcium nitrate slurry is added in a pre-desilicication stage, a raw ore pulp preparation stage or a circulating mother liquor stage on the basis of an aluminum oxide production process; low-valence sulfur in the calcium nitrate or calcium nitrate slurry is oxidized into intermediate-valence sulfur and high-valence sulfur, so that the sulfur in a sodium aluminate solution is promoted to be discharged out of a system along with red mud; and therefore, the influence of the sulfur on key links such as dissolution, sedimentation, decomposition and evaporation in the aluminum oxide production process, equipment corrosion and product quality is eliminated. The agent can be deeply combined with a production line, and can facilitate online desulfurization.
Owner:贵州华锦铝业有限公司
A/O coupled sulfur autotrophic denitrification enhanced low carbon-nitrogen ratio sewage denitrification and dephosphorization device and method
ActiveCN111777179AImprove denitrification abilityReduce consumptionWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSulphur reducing bacteriaPhosphate
The invention discloses an A / O coupled sulfur autotrophic denitrification enhanced low carbon-nitrogen ratio sewage denitrification and dephosphorization device, and a method, and belongs to the fieldof biological sewage treatment. The method comprises steps: raw water, a reflux solution of a sulfur autotrophic denitrification filter tank and reflux sludge of a secondary sedimentation tank are introduced into an anaerobic tank of an A / O process together, easily degradable organic matters are absorbed by phosphorus-accumulating bacteria in the anaerobic tank to synthesize PHAs, the PHAs are stored in the body, and phosphate is released; and the easily degradable organic matters are used by sulfur reducing bacteria to reduce sulfate into polysulfide, the polysulfide is transferred into sulfur oxidizing bacteria, and meanwhile, a phosphorus release effect is realized by sulfur oxidizing bacteria; mixed liquid of the anaerobic tank is introduced into an aerobic zone of the A / O process, the concentration of dissolved oxygen is controlled, ammonia nitrogen is completely converted into nitrate, and meanwhile, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria are adopted to absorb a large amount of phosphorus; a supernatant of a secondary sedimentation tank is introduced into a sulfur autotrophic denitrification filter tank, and deep denitrification is carried out throughthe sulfur autotrophic denitrification effect. According to the method, the requirement of the A / O process on the carbon-nitrogen ratio of inlet water is reduced, and synchronous nitrogen and phosphorus removal of low-carbon-nitrogen-ratio sewage can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com