Nuclear facility post-accident hydrogen absorption material preparation process
A technology for hydrogen-absorbing materials and nuclear facilities, applied in metal material coating technology, liquid chemical plating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of unseen mature applications in the nuclear field, and achieve excellent hydrogen-absorbing performance and compact structure , Improve the effect of stability and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
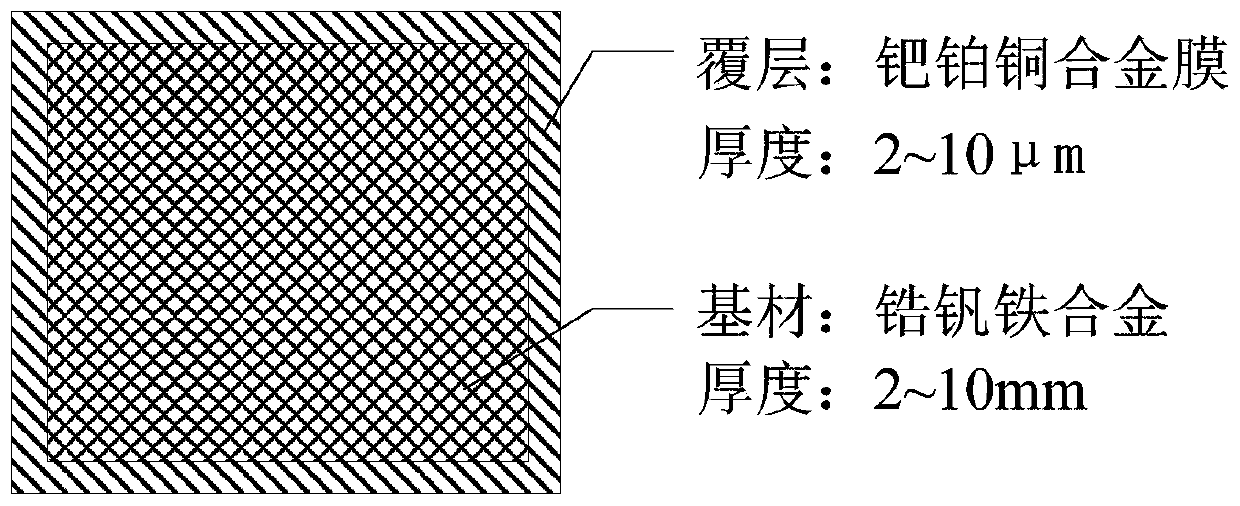
[0018] When preparing the ferro-zirconium vanadium alloy, the alloy is melted in a vacuum induction furnace at a melting temperature of about 1900°C, and the alloy ingot obtained by melting is heat-treated for 160 hours at 900°C under the protection of an argon atmosphere. The ferro-zirconium-vanadium alloy after heat treatment is cut into blocks, and its size is (10mm) (length) × (10mm) (width) × (2mm) (height). After the surface of the alloy is cleaned and polished, a palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is coated on the surface of the zirconium-vanadium-iron alloy by electroless plating, and the thickness of the palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is 2 μm. Then, the hydrogen-absorbing material is cleaned and dried before activation. The activation process is: at 500°C, vacuumize the hydrogen-absorbing material for 10 minutes, and the vacuum degree required for vacuuming is 10 -2 Pa. The cost is obtained after the hydrogen absorbing material is activated.
example 2
[0020] When preparing ferro-zirconium vanadium alloy, the alloy is smelted in a vacuum induction furnace at a melting temperature of about 2000°C, and the alloy ingot obtained by melting is heat-treated for 120 hours at 1000°C under nitrogen atmosphere protection conditions. The ferro-zirconium-vanadium alloy after heat treatment is cut into blocks, and its size is (150mm) (length) × (150mm) (width) × (3.5mm) (height). After the alloy surface is cleaned and polished, a palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is coated on the surface of the zirconium-vanadium-iron alloy by electroless plating, and the thickness of the palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is 5 μm. Then, the hydrogen-absorbing material is cleaned and dried before activation. The activation process is: at 450°C, vacuumize the hydrogen-absorbing material for 30 minutes, and the vacuum degree of vacuuming is required to be 10 -2 Pa. The cost is obtained after the hydrogen absorbing material is activated.
example 3
[0022] When preparing ferro-zirconium vanadium alloy, the alloy is smelted in a vacuum induction furnace at a melting temperature of about 2200°C, and the alloy ingot obtained by melting is heat-treated for 70 hours at 1100°C under nitrogen atmosphere protection conditions. The ferro-zirconium vanadium alloy after the heat treatment is cut into blocks, and its size is (200mm) (length) × (200mm) (width) × (10mm) (height). After the surface of the alloy is cleaned and polished, a palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is coated on the surface of the zirconium-vanadium-iron alloy by electroless plating, and the thickness of the palladium-platinum-copper alloy film is 10 μm. Then, the hydrogen-absorbing material is cleaned and dried before activation. The activation process is: at 400°C, vacuumize the hydrogen-absorbing material for 60 minutes, and the vacuum degree of vacuuming is required to be 10 -1 Pa. The cost is obtained after the hydrogen absorbing material is activated.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com