Preparation method of Vitrimer material based on carboxyl-containing polysaccharide and dynamic ester bond
A carboxyl polysaccharide and ester bond technology, applied in the field of Vitrimer material preparation, can solve environmental pollution, resource waste and other problems, and achieve high economic efficiency, reduced usage, and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Dissolve 0.500g of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) (DS=1.2) and 0.600g of glycerol in 5mL of distilled water while stirring at 60°C, and add bisphenol A diglycidyl ether to it after the solution is clear and transparent (DGEBA) 0.390g and continue to stir rapidly at 60°C for 30min to form a homogeneous emulsion. Then add 0.064 g of 1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (TBD) therein and continue stirring until the mixture is uniform. Then the homogeneous emulsion was scraped into a polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and the mold was placed in a constant temperature oven at 60°C for 4h. Afterwards, the temperature was raised to 120° C. for 3 hours to obtain a white material film, that is, a Vitrimer material.
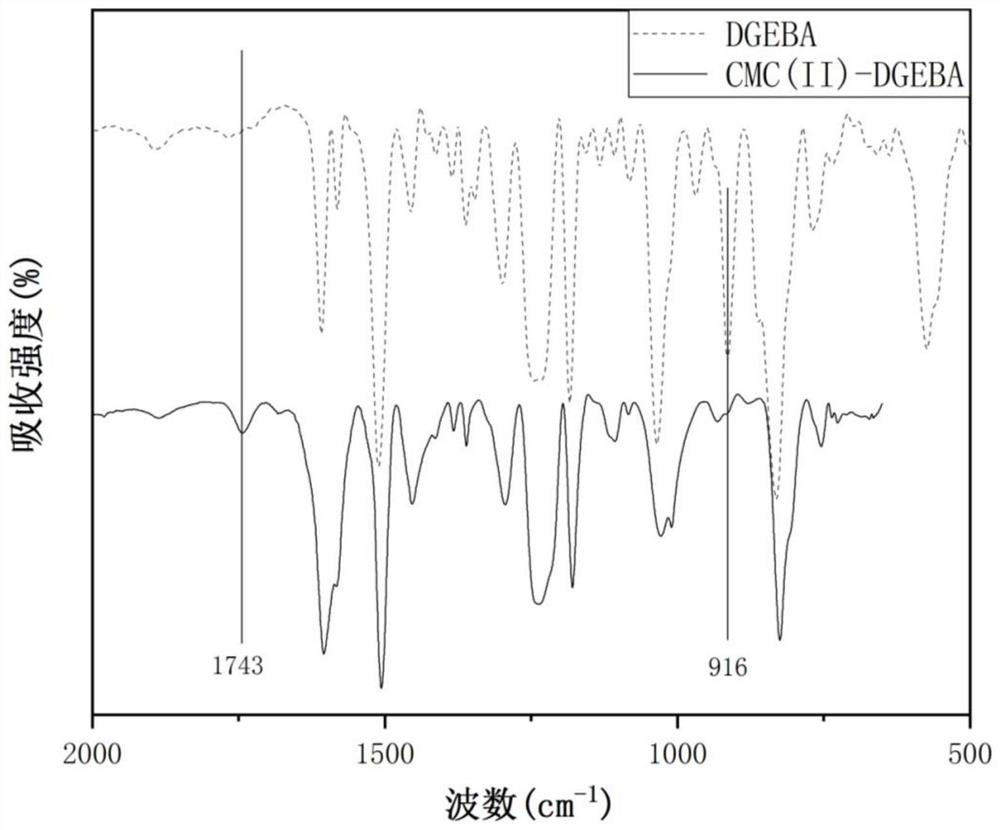
[0032] Described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, figure 1 It is the infrared spectrum comparison chart of the Vitrimer material (CMC-DGEBA) prepared in Example 1 and bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA), and the peak position of the epoxy group is at 916cm -1...
Embodiment 2
[0034]Dissolve 0.500g of succinylated cellulose and 0.200g of sorbitol in 5mL of distilled water and 2mL of ethanol mixed solvent while stirring at 50°C. After the solution is clear and transparent, add 0.390g of bisphenol F diglycidyl ether and add Continue rapid stirring for 30 min at 60°C to form a homogeneous emulsion. Then add DBU 0.032g therein and continue to stir until the mixture is uniform. Then the homogeneous emulsion was scraped into a polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and the mold was placed in a constant temperature oven at 70°C for 2h. Afterwards, the temperature was raised to 135° C. for 2 hours to obtain a white material film, that is, a Vitrimer material.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Dissolve 0.500g of cellulose acetate phthalate and 0.200g of isosorbide in 5mL of distilled water and 2mL of methanol mixed solvent while stirring at 65°C, and add ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether to the solution after it is clear and transparent 0.390g and continued rapid stirring at 65°C for 30min to form a homogeneous emulsion. Then add DMAP 0.064g therein and continue to stir until the mixture is uniform. Then the homogeneous emulsion was scraped into a polytetrafluoroethylene mold, and the mold was placed in a constant temperature oven at 65°C for 3.5h. Afterwards, the temperature was raised to 120° C. for 2.5 hours to obtain a yellow material film, that is, a Vitrimer material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com