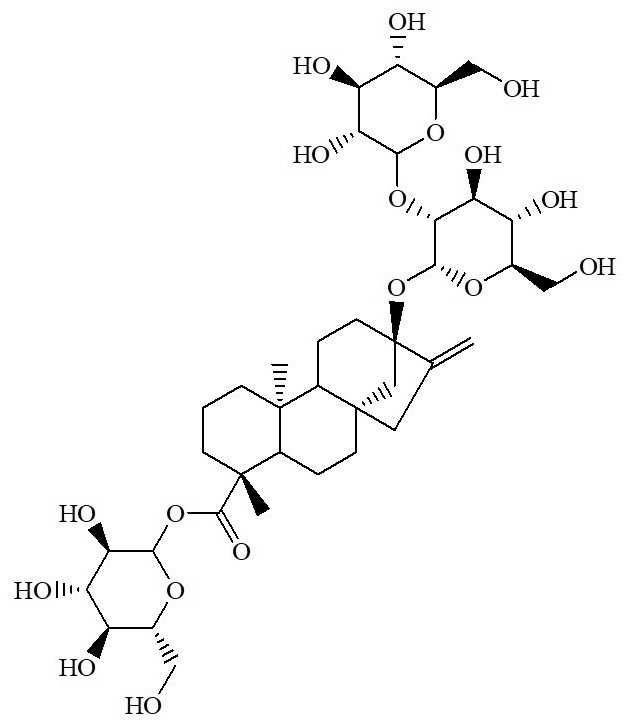
A compound pickling corrosion inhibitor of stevioside and zinc acetate
A technology of stevioside and zinc acetate, which is applied in the fields of natural source plant-type corrosion inhibitors and compound applications with Zn2+, and can solve problems such as poor water solubility, complicated process, and secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Use a 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to prepare a test solution with a molar ratio of stevioside and zinc acetate of 3:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3, of which stevioside is 1:1. and zinc acetate are both 1 mmol / L.
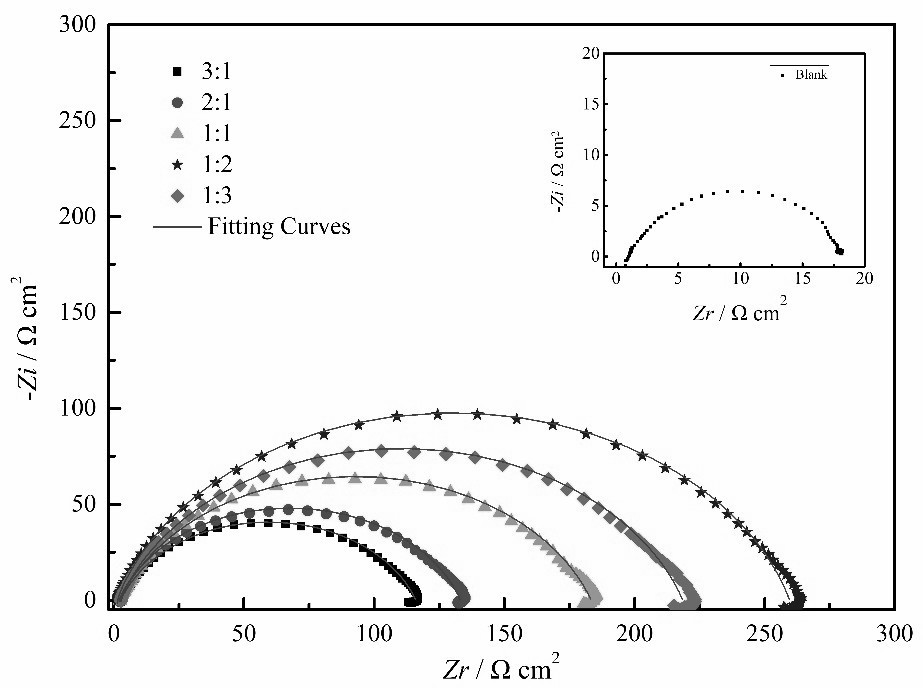
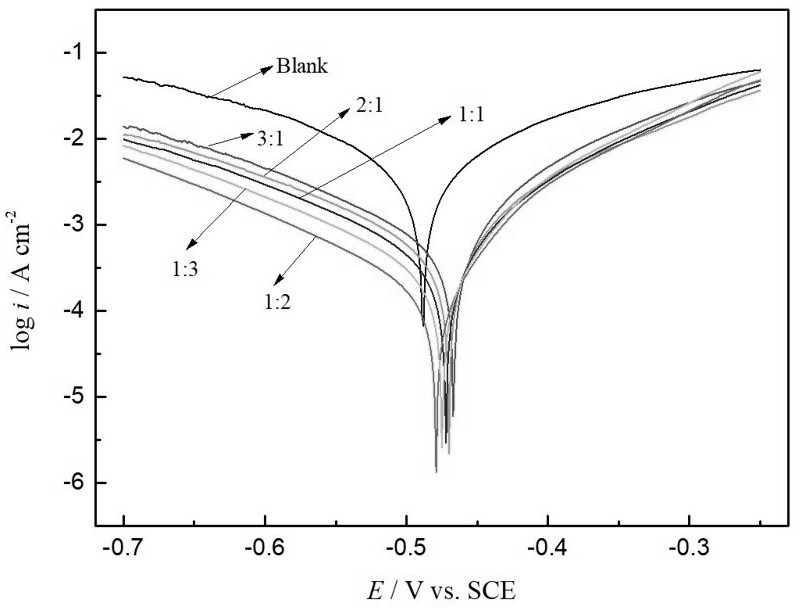
[0024] (2) At room temperature, the epoxy resin is encapsulated and the exposed area at one end is 0.5 cm 2 A C1020 carbon steel rod was used as the working electrode, a saturated calomel electrode was used as the reference electrode, and a platinum sheet electrode with a size of 1.0 cm × 1.0 cm was used as the auxiliary electrode. The C1020 carbon steel working electrode was measured by a traditional three-electrode system using CHI760e electrochemical workstation Tafel polarization curves and AC impedances of different amounts of stevioside and zinc acetate added to hydrochloric acid solution.
[0025] figure 2 It is the Nyquist impedance spectrum of the C1020 carbon steel working electrode obtained in Example 1 with different amounts of stevioside...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Use 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution to prepare 1 mmol / L stevioside and 2 mmol / L zinc acetate solution to be tested.
[0029] (2) Under the condition of 25 °C, the C1020 carbon steel sheet was fixed on the mounter, completely immersed in the experimental solution, and rotated at 75 rpm for 24 h, and the weight of the test piece before and after the experiment was recorded. According to the formula: v = (w 1 −w 2 ) / (s×t) to calculate the corrosion efficiency, where w 1 and w 2 (mg) is the weight loss of the sample before and after soaking, s (cm -2 ) is the area of the steel sample, t(h) is the soaking time; n w = (v 0 −v) / v 0 Calculate the corrosion inhibition efficiency, where v and v 0 Corrosion rates without inhibitor and with inhibitor, respectively.
[0030] The corrosion inhibition efficiency of the compound corrosion inhibitor of the above example 2 is as follows:
[0031] Table 1 Example 2
[0032]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com