Method for detecting target nucleic acid based on cationic conjugated polymer and nuclease-assisted cyclic amplification
A nuclease and nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as low content, difficulty in detecting sequence similarity of miRNA family members, and difficult miRNA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Embodiment 1, the establishment of the method for detecting miRNA or DNA using azo-PPE(+)
[0073] 1. Establishment of a method for detecting target DNA using azo-PPE(+) and DNA exonuclease III (Exo III)
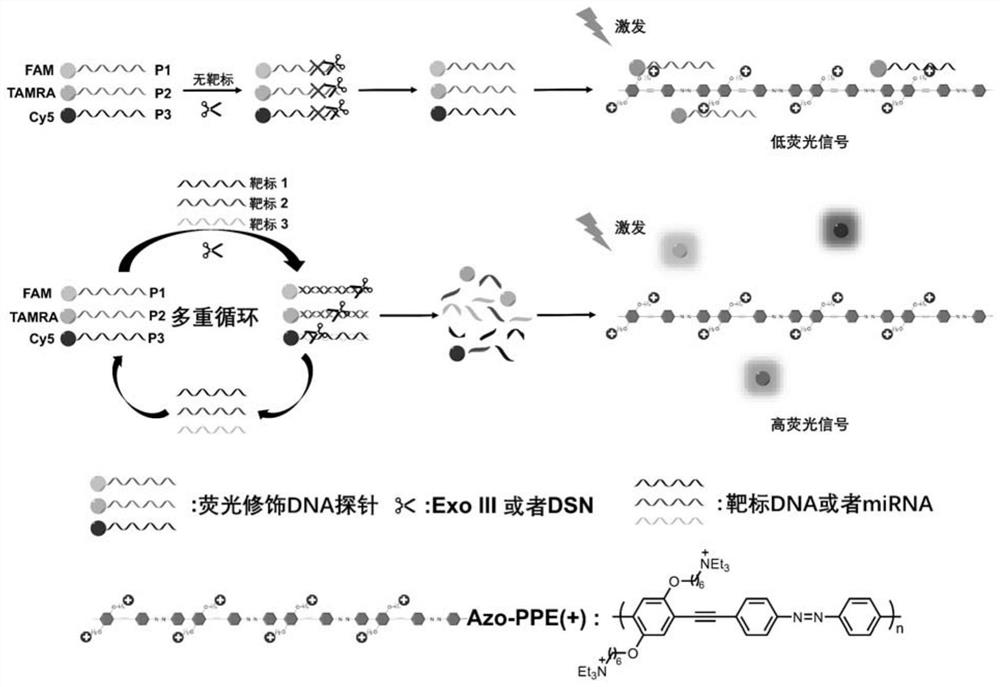
[0074]The inventors of the present invention have established a method for detecting target DNA using azo-PPE(+) and Exo III through a large number of experiments. Digestion by Exo III into oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide fragments (Exo III can remove a single nucleotide from the 3' blunt end or cohesive end of dsDNA, respectively, followed by release of ssDNA, which does not require a specific recognition site ), as a result, the electrostatic interaction becomes weaker, resulting in the fluorescence of the probe being unable to be quenched, thereby forming a "turn on" phenomenon of the fluorescent signal; when the target DNA does not exist, the probe cannot form a double-stranded structure because it cannot Cut into oligonucleotide fragments by Exo III, the str...
Embodiment 2
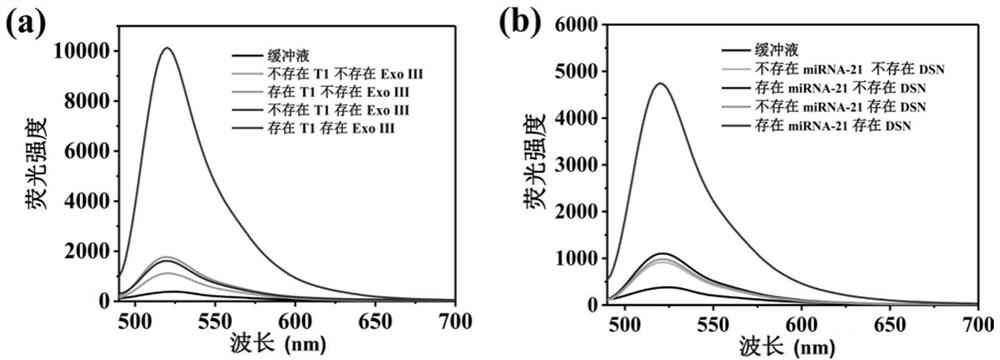
[0096] The feasibility analysis of the method that embodiment 2, embodiment 1 establish
[0097] In this example, P1 was selected as the model probe, and the feasibility of detecting the target DNA T1 and the target miRNA-21 by the biosensor was explored according to the method established in Example 1.
[0098] 1. Obtain the fluorescence emission spectrum of the DNA detection system under different conditions according to the method established in step 1 of Example 1
[0099] Condition 1: Reaction system 1 is 100 uL, consisting of reaction buffer 1.
[0100] Condition 2: Reaction system 1 is 100 uL, consisting of probe P1 and reaction buffer 1; in reaction system 1, the concentration of probe P1 is 100 nM. In system 1, the concentration of azo-PPE(+) was 3.6 μM.
[0101] Condition 3: Reaction system 1 is 100 uL, consisting of probe P1, reaction buffer 1 and target DNA T1; in reaction system 1, the concentrations of probe P1 and target DNA T1 are both 100 nM. In system 1, t...
Embodiment 3
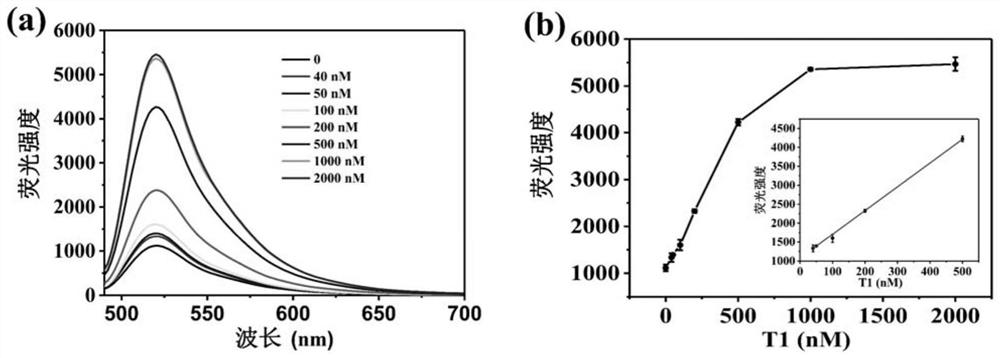
[0113] Embodiment 3, sensitivity analysis
[0114] 1. Sensitivity analysis of DNA detection
[0115] According to the method established in step 1 of Example 1, the fluorescence emission spectra of the DNA detection system were obtained under different reaction systems.
[0116] Reaction system 1-1: Reaction system 1-1 is 100 uL, consisting of probe P1, reaction buffer 1 and Exo III (about 5 U); in reaction system 1-1, the concentration of probe P1 is 100 nM.
[0117] Reaction system 1-2: Reaction system 1-2 is 100uL, consisting of probe P1, reaction buffer 1, Exo III (about 5U) and target DNA T1; in reaction system 1-2, the concentration of probe P1 is 100nM , the concentration of target DNA T1 was 40 nM.
[0118] Reaction system 1-3: Reaction system 1-3 is 100uL, composed of probe P1, reaction buffer 1, Exo III (about 5U) and target DNA T1; in reaction system 1-3, the concentration of probe P1 is 100nM , the concentration of target DNA T1 was 50 nM.
[0119] Reaction sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com