Spinning method of gel fibers
A gel fiber and spinning technology, which is applied in the field of spinning methods of gel fibers, can solve the problems of limiting the applicable system of fibrous gel, reducing water content, poor mechanical strength of gel fibers, etc., and achieving increased robustness. and application range, reducing friction, broadening the effect of compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] (1) 7.088g poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid) solution, 0.414g polyethylene glycol diacrylate (Mn=600), 1.500g acrylamide and 0.0450g 2-hydroxy- 2-Methyl-1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-acetone was mixed in a 20mL glass bottle, and vigorously magnetically stirred for 30min to completely dissolve the raw materials, and then defoamed under ultrasound for 10min. to obtain a precursor solution;
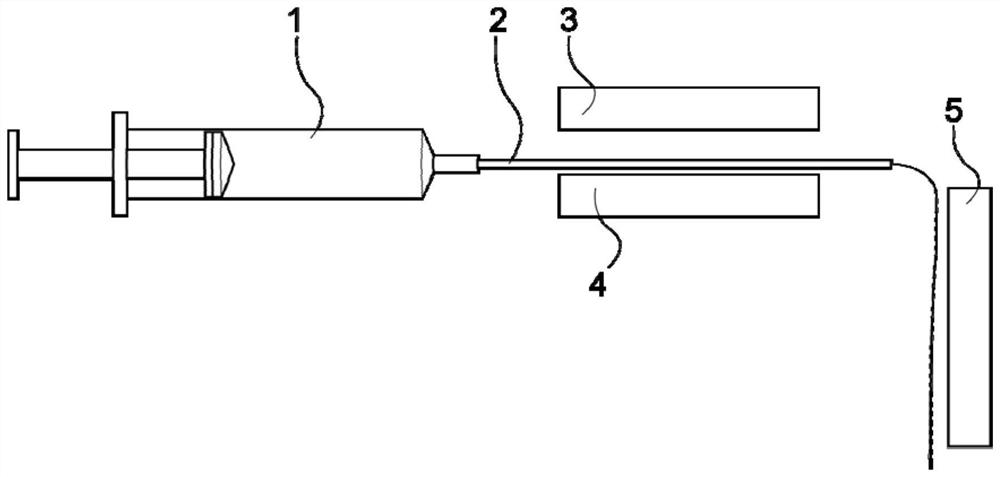
[0051] (2) First put the precursor solution into a 10mL syringe and fix it in the syringe pump 1, then turn on the syringe pump 1, adjust the flow rate to 40 μL / min, and inject the precursor solution into a polytetrafluoroethylene having a diameter of 0.86mm and a length of 30cm In the ethylene tube 2, after the precursor solution reaches the nozzle of the PTFE tube 2, turn off the syringe pump 1, turn on the first UV lamp 3, and after irradiating for 200s, turn on the syringe pump 1 again and turn on the second UV lamp 5, and wait for extrusion. After the stabilizati...
Embodiment 2
[0058] (1) 7.017g poly(N,N,N-trimethyl-2-[(2-methyl-2-acryloyl)oxy]ethylammonium chloride solution, 0.414g polyethylene glycol diacrylate ( Mn=600), 1.500 g acrylamide and 0.0450 g 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-propanone were mixed in a 20 mL glass bottle and vigorously Magnetic stirring for 30min made the raw material completely dissolved, and then ultrasonically defoamed for 10min to obtain the precursor solution;
[0059] (2) First put the precursor solution into a 10mL syringe and fix it in the syringe pump 1, then turn on the syringe pump 1, adjust the flow rate to 40 μL / min, and inject the precursor solution into a polytetrafluoroethylene having a diameter of 0.86mm and a length of 30cm In the ethylene tube 2, after the precursor solution reaches the nozzle of the PTFE tube 2, turn off the syringe pump 1, turn on the first UV lamp 3, and after irradiating for 200s, turn on the syringe pump 1 again and turn on the second UV lamp 5, and wait for extrus...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) 7.088g poly(2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid) solution, 0.414g polyethylene glycol diacrylate (Mn=600), 1.500g acrylamide and 0.0450g 2-hydroxy- 2-Methyl-1-[4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-acetone was mixed in a 20mL glass bottle, and vigorously magnetically stirred for 30min to completely dissolve the raw materials, and then defoamed under ultrasound for 10min. to obtain a precursor solution;
[0066] (2) First, the precursor solution was loaded into a 10 mL syringe and fixed in the syringe pump 1, then the syringe pump 1 was turned on, the flow rate was adjusted to 220 μL / min, and the precursor solution was injected into a polytetrafluoroethylene having a diameter of 2.5 mm and a length of 30 cm. In the ethylene tube 2, after the precursor solution reaches the nozzle of the PTFE tube 2, turn off the syringe pump 1, turn on the first UV lamp 3, and after irradiating for 250s, turn on the syringe pump 1 again and turn on the second UV lamp 5, and wait for extr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com