An induction electrode and a method for degrading pollutants in an electro-magnetic coupling field
An induction electrode, magnetic coupling technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of slow dissolution rate and low electrode activity, achieve fast dissolution rate, and solve recycling and utilization. , the effect of mild reaction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
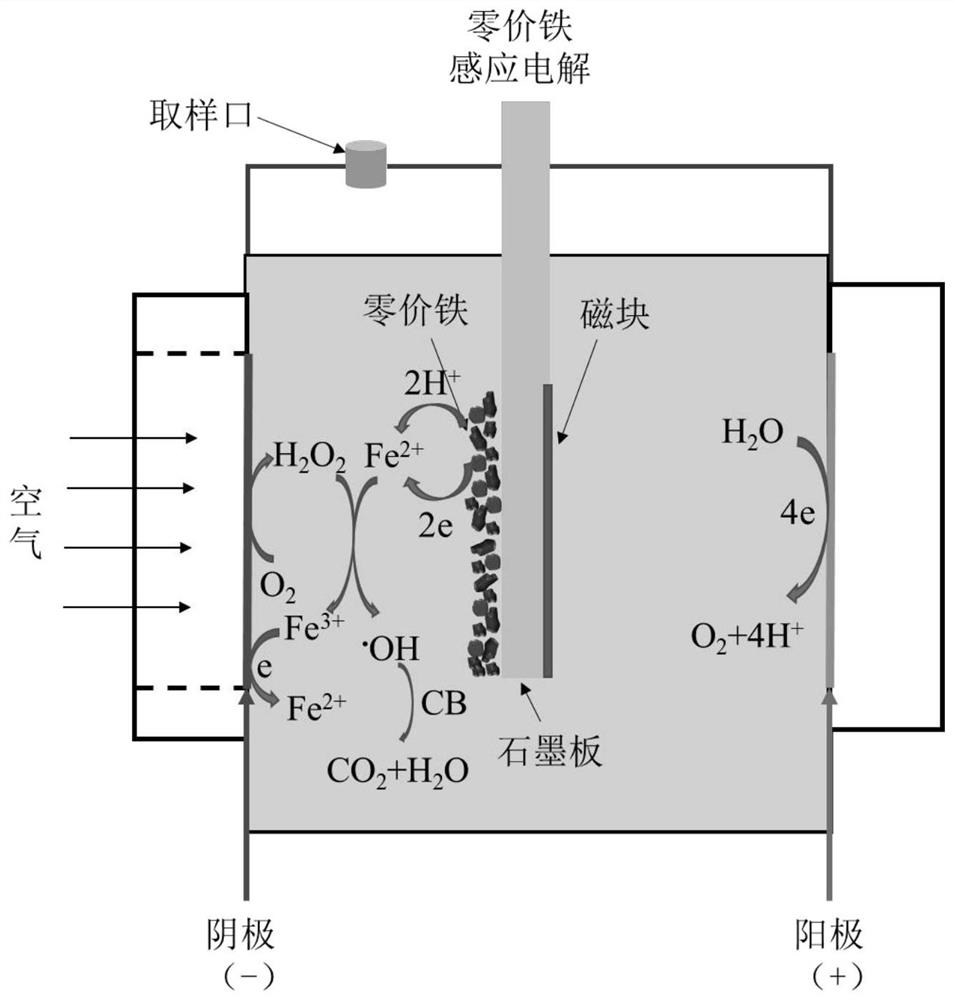
[0043] In the water treatment method of this embodiment, the anode uses a DSA electrode, and the cathode uses a carbon black-modified carbon felt electrode, wherein the catalytic layer of the cathode (the side loaded with carbon black) is in contact with the solution, and the other side is in direct contact with the air. Relying on the active diffusion of air to the cathode catalytic layer, the hydrogen peroxide can be efficiently produced in situ without the need for additional aeration devices. The arrangement of cathode and anode is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the induction electrode is placed between the cathode and the anode, and the active component is pure micron-sized zero-valent iron powder. The active component is evenly adsorbed on the graphite plate under the action of the magnetic block, and the active component is facing the cathode. .
[0044] Reaction conditions: solution volume: 130mL, sodium sulfate concentration: 0.05mol / L, chlorobenzene concentration: 0...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The sensing electrode of this embodiment is used in wastewater treatment, and the specific process of wastewater treatment is the same as in Example 1. Reaction conditions: solution volume: 130ml, sodium sulfate concentration: 0.05mol / L, chlorobenzene concentration: 0.1mmol / L, anode: DSA , Cathode: carbon black modified carbon felt, initial pH 7.0, zero-valent iron sensing electrode.
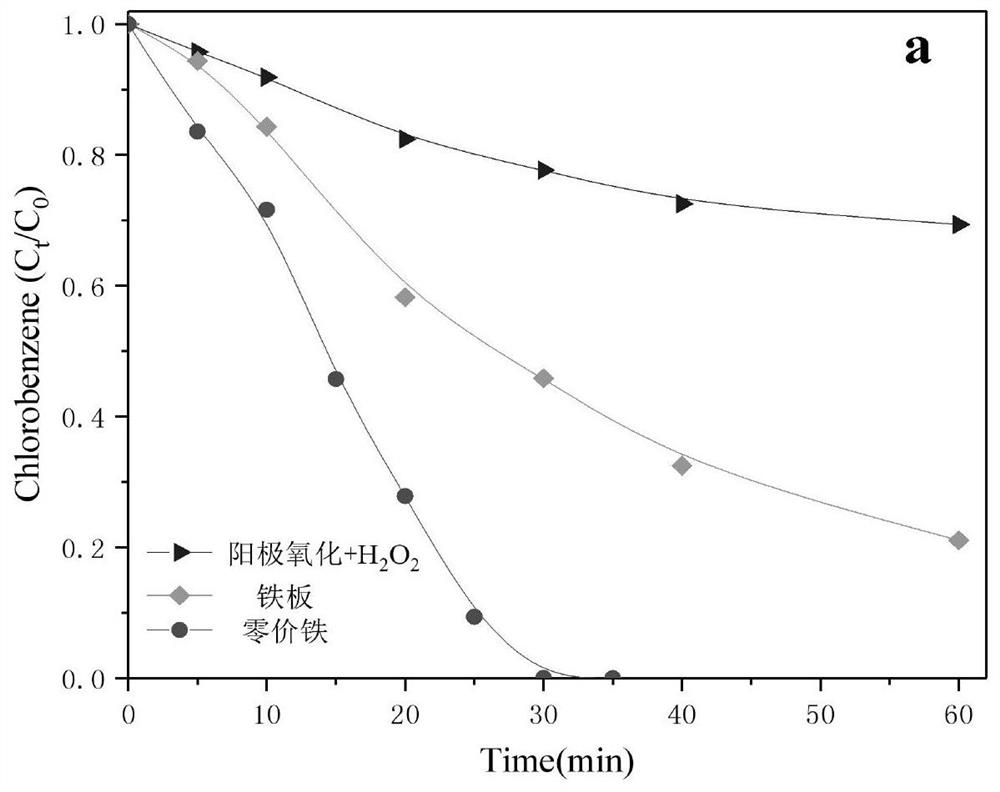
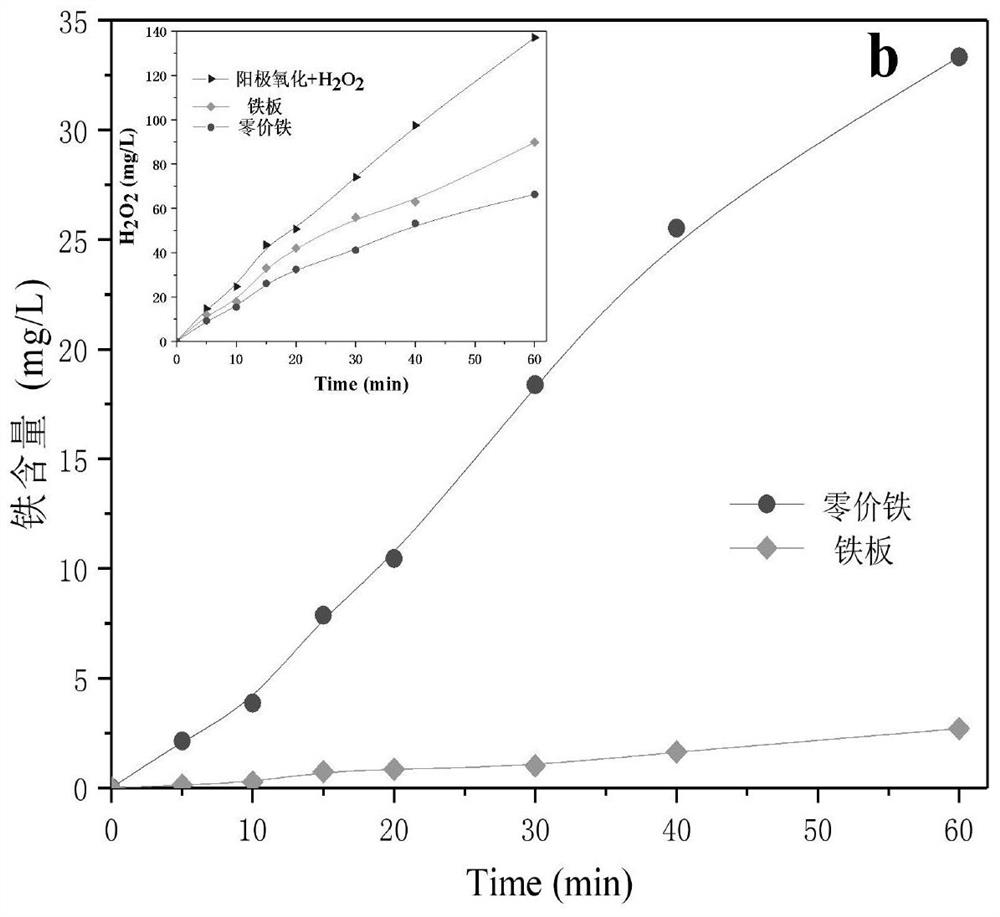
[0049] Figure 3(a) shows that when the current increases from 10mA to 30mA, the degradation rate of chlorobenzene increases with the increase of current, and when the current increases from 30mA to 40mA, the degradation performance of chlorobenzene decreases . This is because when the current is lower than 30mA, as the current increases, the production of hydrogen peroxide and the amount of iron precipitation increase (Figure 3(b)), more hydroxyl radicals are produced in the system, and the degradation rate of chlorobenzene get promoted. When the current was further increased, the hydro...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Solution volume: 130mL, sodium sulfate concentration: 0.05mol / L, chlorobenzene concentration: 0.1mmol / L, current 30mA, cathode: carbon black modified carbon felt, initial pH 7.0. Peroxygen flocculation system: The zero-valent iron sensing electrode is the anode, which is connected to the power supply. Induction electric Fenton system: the anode is a DSA electrode, and the zero-valent iron induction electrode is placed between the cathode and anode, and the power is not connected. Use zero-valent iron sensing electrodes in different reaction systems for water treatment.
[0052] Figure 4(a) shows that the degradation rate of p-chlorobenzene in the induction electro-Fenton system is slightly higher than that in the peroxygen flocculation system. When the initial pH of the solution was 7.0, the pH of the solution dropped to 4.2 after the reaction in the induction electro-Fenton system, while in the peroxygen flocculation system, the pH of the solution gradually rose to 7....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com