Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker for resistance identification of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease in watermelon and application of molecular marker
A green mottled flower and molecular marker technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/testing, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems affecting the high-throughput screening and identification of watermelon resistance to cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease, etc. To achieve the effect of improving resistance and overcoming the long cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1. Resistance identification of watermelon wild germplasm 'P.I.595203' and cultivar 'M1511-3' to cucumber green mottle mosaic virus disease:
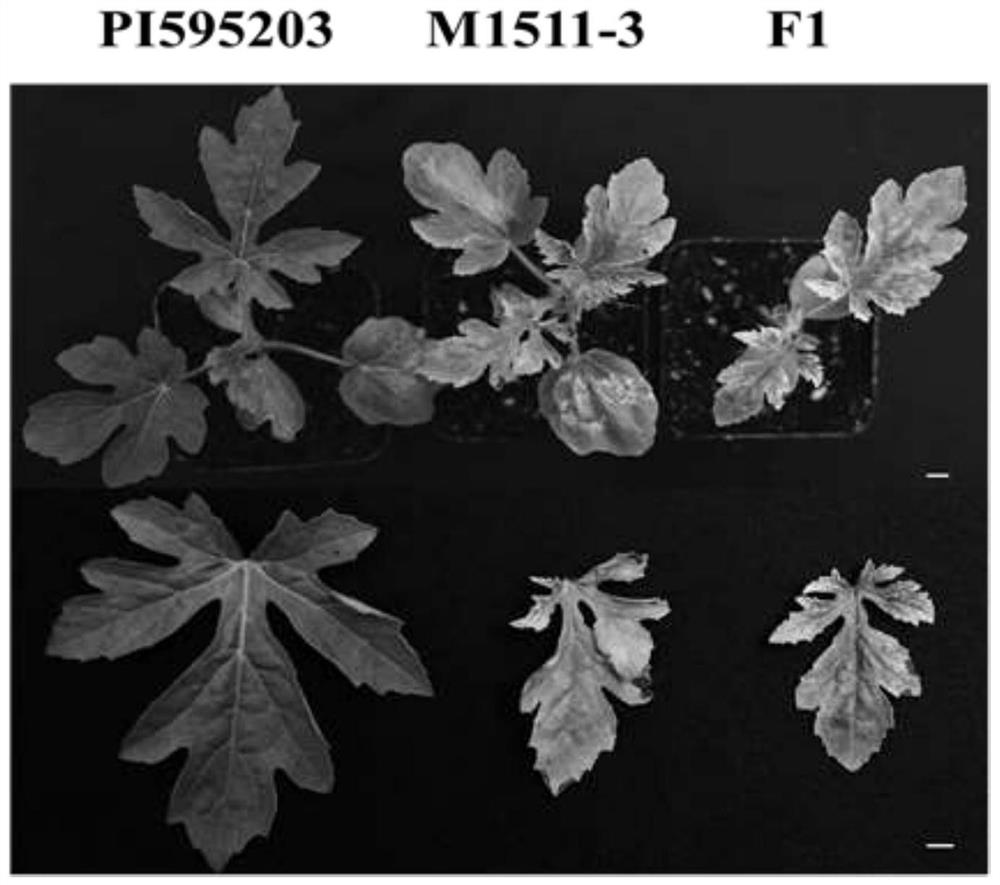
[0076] Select watermelon materials --- 'P.I.595203', 'M1511-3', 'P.I.595203' and 'M1511-3' hybrid F1 offspring from the laboratory germplasm resource bank, inoculate with cucumber green mottle virus, and use the plant phenotype symptoms Determine resistance; if figure 1 .
[0077] details as follows:
[0078] 1. Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus inoculation:
[0079]Carry out inoculation at the stage of one leaf and one heart leaf of watermelon seedling, take by weighing the fresh diseased leaf 2g that has been infected with cucumber green mottle mosaic virus, put into the mortar of high temperature sterilization, according to 1:10 (W / V, namely, 1g: 10ml) was added into a corresponding volume of 0.02mol / LPBS buffer solution (pH7.2) and ground into a slurry, which was used as virus juice for artificial friction inocula...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Embodiment 2, genetic analysis and gene mapping of resistance to cucumber green mottled mosaic virus disease:
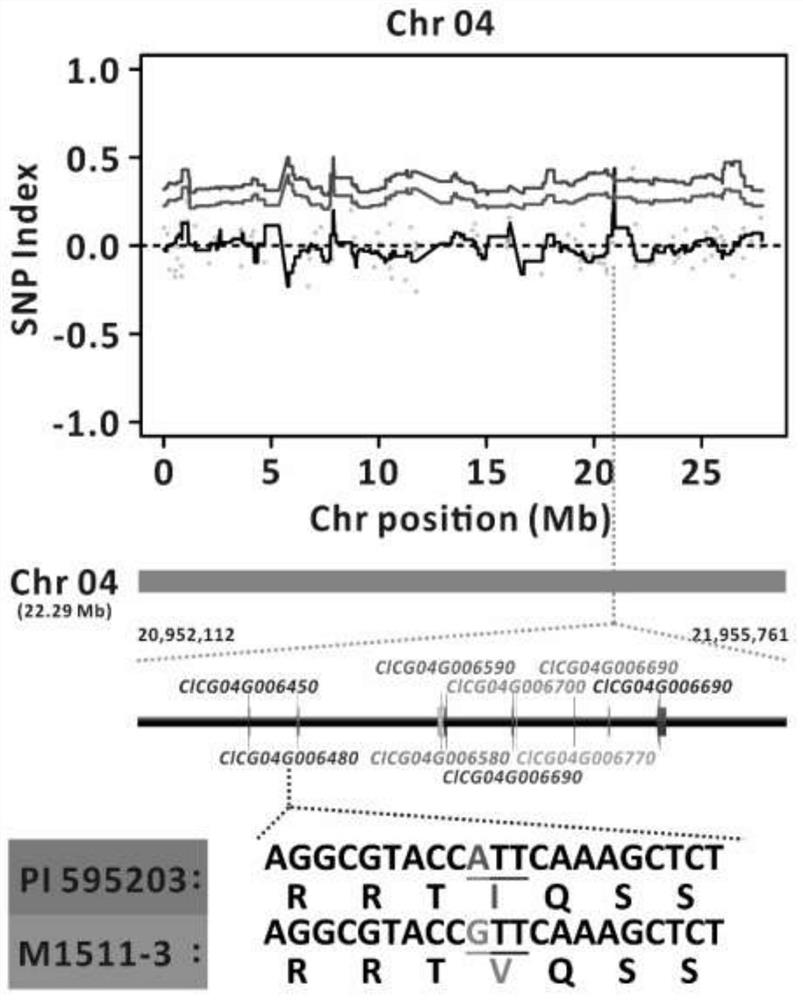
[0091] Selected melon materials from the germplasm resource bank of the laboratory --- 'P.I.595203', 'M1511-3', 'P.I.595203' and 'M1511-3' hybrid F1 offspring and F2 population obtained by selfing of F1, cucumber green mottled Mosaic virus inoculation, use plant phenotype symptoms to determine resistance, and carry out genetic analysis of disease resistance. Then based on the BSA method for disease resistance gene mapping, such as figure 2 .
[0092] Genetic analysis of resistance: the cucumber green mottled mosaic virus inoculation method in Example 1 was used to inoculate 304 individual plants of the F2 population, and the resistance was determined according to the phenotype, and the F2 population was resistant to the cucumber green mottled mosaic virus disease Sexual segregation occurred, including 33 disease-resistant plants and 271 susceptible plants, ...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Embodiment 3, the development and verification of marking CGMMVR with KASP
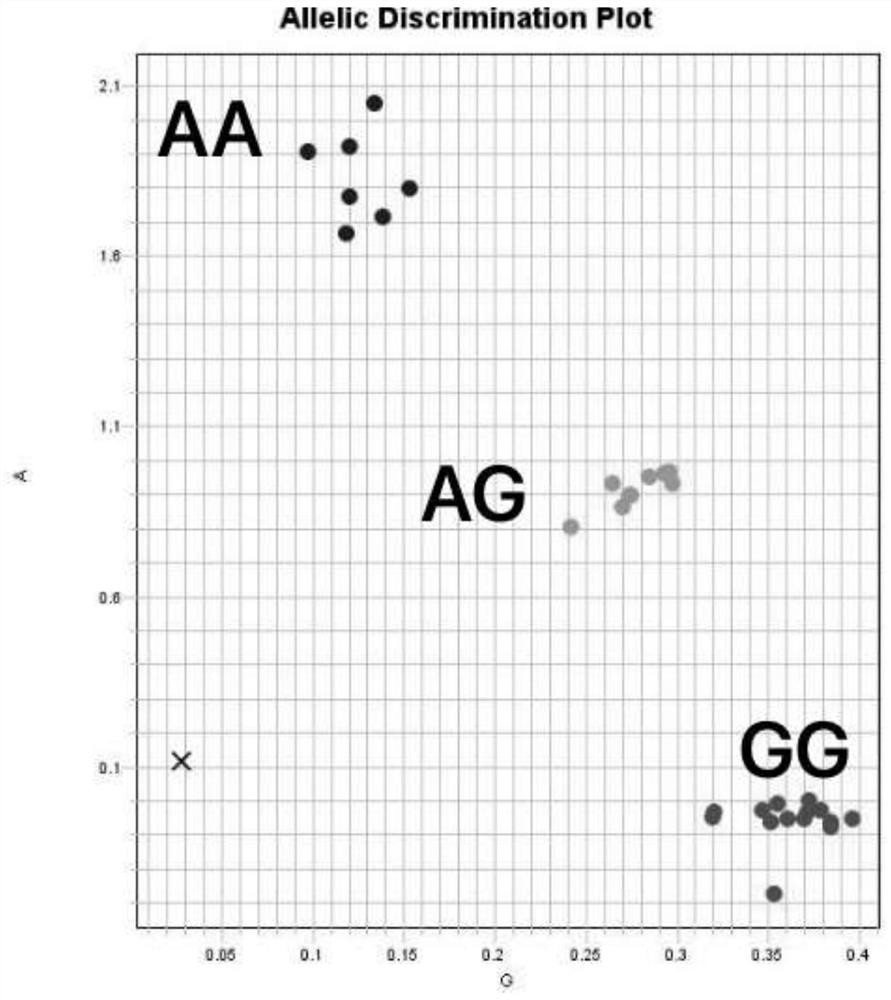
[0103] Watermelon materials --- 'P.I.595203', 'M1511-3', 'P.I.595203' and 'M1511-3' hybrid F1 offspring, F2 population obtained by F1 self-crossing and other 184 accessions were selected from the laboratory germplasm resource bank For watermelon germplasm, the SNPs were first transformed into KASP markers, and the genotype and genetic segregation rules were identified by amplifying the KASP marker CGMMVR with primers.
[0104] details as follows:
[0105] 1. KASP marks the development of CGMMVR:
[0106] 1. SNP information extraction:
[0107] According to the gene mapping results in Example 2, the SNP information closely linked with the disease resistance gene was extracted.
[0108] 2. Extract DNA
[0109] The genomic DNA of the hybrid F1 offspring of 'P.I.595203', 'M1511-3', 'P.I.595203' and 'M1511-3' was extracted, and the method was the same as in Example 2.
[0110] 3. PCR amplificat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com