Ultra-large-mode-field low-numerical-aperture metal coating gain optical fiber and manufacturing method thereof
A numerical aperture and metal coating technology, which is applied in cladding optical fiber, multi-layer core/clad optical fiber, glass optical fiber, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient thermal tolerance temperature of optical fiber, unstable optical fiber mode, and low numerical aperture of the fiber core. To achieve the effect of ensuring single-mode operation with large core diameter, reducing the numerical aperture of the fiber core, and increasing the heat conduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
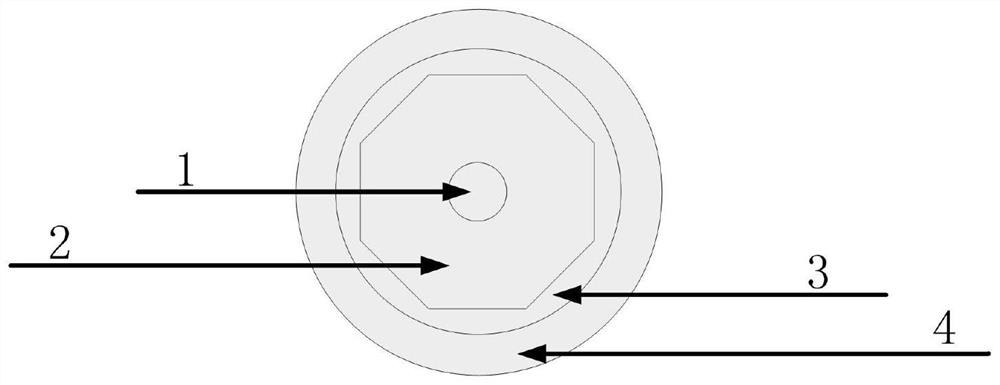
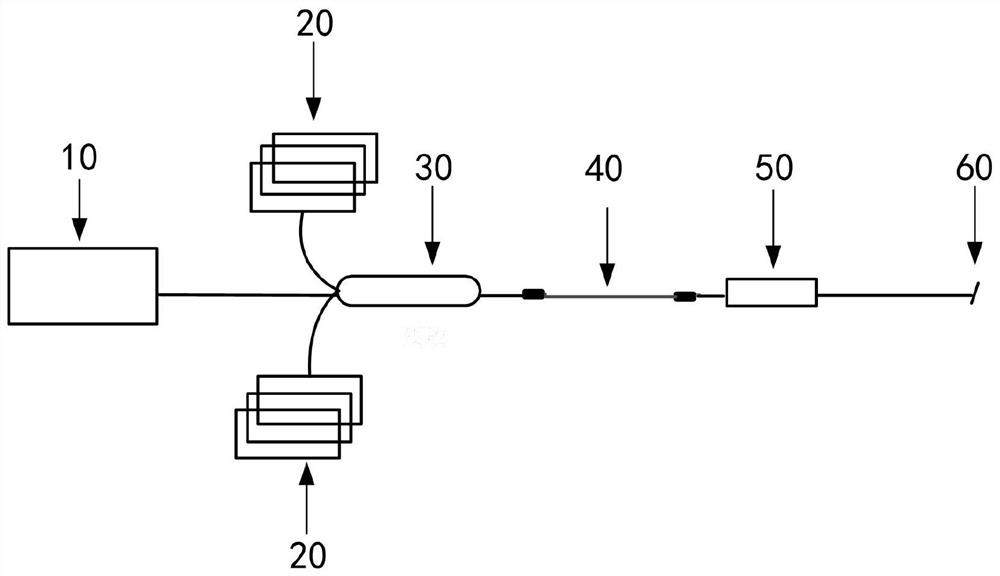
[0039] figure 1 Shown is a cross-sectional view of an ultra-large mode field low numerical aperture single-mode metal-coated gain fiber. The diameter of the core 1 of the gain fiber is 40 μm, the diameter of the cladding 2 is 400 μm, and the thickness of the third cladding 3 is 20 μm. The temperature is 640°C, the temperature difference between the silver-aluminum alloy and the bare fiber is reduced to 10°C, the stress is released, and the silver-aluminum alloy is effectively coated on the bare fiber, the thickness of the coating layer is 65 μm, and the numerical aperture of the fiber core is 0.02 , the cladding absorption coefficient @915nm is 1dB / m. Using the gain fiber to build as figure 2 The high-power narrow-linewidth fiber laser shown, wherein the length of the gain fiber is 4m, and the gain fiber is not bent.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The diameter of the core 1 of the gain fiber is 30 μm, the diameter of the cladding 2 is 300 μm, and the thickness of the third cladding 3 is 60 μm. The temperature is 850°C, reduce the temperature difference between the silver-aluminum alloy and the bare fiber to 10°C, release the stress, and effectively coat the silver-aluminum alloy on the bare fiber, the thickness of the coating layer is 20μm, and the numerical aperture of the fiber core is 0.008 , the cladding absorption coefficient @915nm is 0.4dB / m. Using the gain fiber to build as figure 2 The high-power narrow-linewidth fiber laser shown, wherein the length of the gain fiber is 2m, and the gain fiber is not bent.
Embodiment 3
[0043] figure 1 Shown is a cross-sectional view of an ultra-large mode field low numerical aperture single-mode metal-coated gain fiber. The diameter of the core 1 of the gain fiber is 100 μm, the diameter of the cladding 2 is 1000 μm, and the thickness of the third cladding 3 is 100 μm. The temperature is 950°C, the temperature difference between the silver-aluminum alloy and the bare fiber is reduced to 10°C, the stress is released, and the silver-aluminum alloy is effectively coated on the bare fiber, the thickness of the coating layer is 200μm, and the numerical aperture of the fiber core is 0.03 , the cladding absorption coefficient @915nm is 2dB / m. Using the gain fiber to build as figure 2 In the high-power narrow-linewidth fiber laser shown, the length of the gain fiber is 9m, and the gain fiber is not bent.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com