Bone defect cavity filling implant
A technology for bone defects and implants, which is used in bone implants, joint implants, joint implants, etc. to achieve good biocompatibility, high degradability, and complementary advantages.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The preparation method of the bone defect cavity filling implant comprises the following steps:
[0037] S1. Add chitosan and polylactic acid composite nanofibers to absolute ethanol to obtain composite nanofiber solutions, then add calcium nitrate aqueous solution and ammonium phosphate aqueous solution respectively, and the calcium nitrate and ammonium phosphate are adsorbed on the composite nanofibers respectively On the surface, calcium nitrate reaction solution and ammonium phosphate reaction solution are obtained; since the surface of chitosan is rich in polar groups such as hydroxyl and amino groups, it has good hydrophilicity and can adsorb calcium nitrate and ammonium phosphate respectively, which is convenient for subsequent nano-hydroxyapatite Fixed-point generation of stones.
[0038] In step S1, the concentration of the calcium nitrate aqueous solution is 0.4-0.6mol / L, and the concentration of the ammonium phosphate aqueous solution is 0.22-0.38mol / L; in th...
Embodiment 1
[0045] A bone defect cavity filling implant, which is a porous cross-linked network formed by chitosan and polylactic acid composite nanofibers and nano-hydroxyapatite grown in series on the surface of the composite nanofibers by a sol-gel method structure, prepared by the following steps:
[0046] S1. Prepare chitosan and polylactic acid composite nanofibers with a diameter of about 200 nm and a mass content of chitosan of 20% by electrospinning; and cut the composite nanofibers into fibers with a length of about 2 mm.
[0047] The above-mentioned chitosan and polylactic acid composite nanofibers are added to absolute ethanol to obtain a mass content of 10% composite nanofiber solution, and then the concentration is 0.5mol / L calcium nitrate aqueous solution and the concentration is 0.3mol / L ammonium phosphate an aqueous solution, wherein the calcium nitrate and ammonium phosphate are respectively adsorbed on the surface of the composite nanofiber to obtain a calcium nitrate r...
Embodiment 2-3 and comparative example 1
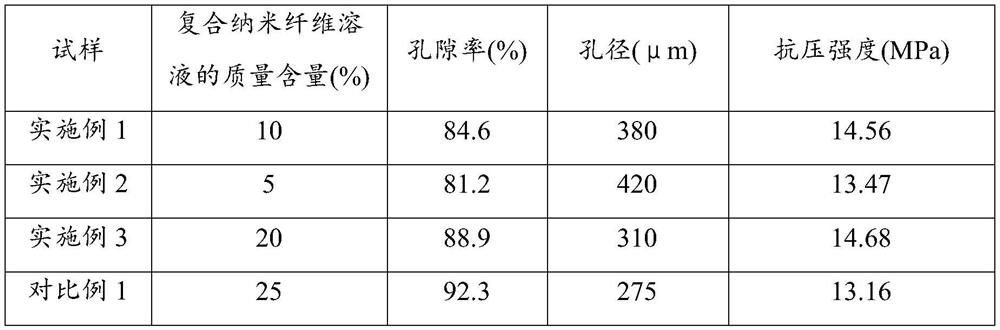
[0051] A bone defect cavity filling implant. Compared with the example, the difference is that in step S1, the mass content of the composite nanofiber solution is shown in Table 1, and the others are roughly the same as in Example 1. In This will not be repeated here.
[0052] Preparation conditions and performance parameters of table 1 embodiment 1-3 and comparative example 1
[0053]
[0054] It can be seen that when the mass content of the nanocomposite fiber solution is too high, the compressive strength decreases. This may be due to the increase of water content in the reaction system, which makes the microwave absorb heat too fast, and the reaction is uneven, resulting in uneven crosslinking structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com