Indigestible branched glucan and processing method thereof
A processing method and indigestible technology, which are applied in the field of indigestible branched glucan and its processing, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting the individual needs of consumers in terms of quality and quality, gaps in product performance, and complex reaction processes, and achieve continuous Green production, improved bioavailability and controllable reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]For the process of obtaining α-glucosidase, see the literature Microbial Starch-Converting Enzymes: Recent Insights and Perspectives, Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2018, 17(5): 1238-1260, including enzyme gene mining, engineering bacteria construction, Fermentation and enzyme production and other steps.
[0032]Specifically, the α-glucosidase gene derived from microorganisms such as Aspergillus niger, Acremonium cladosporium, Paecilomyces or Paecilomyces spp. is connected to the expression vector pET-15b(+) to obtain a recombinant plasmid. Transform the recombinant plasmid into E.coil competent cells by chemical transformation method and add 1mL of LB medium, and culture for 1-1.5h in a shaker at 37°C and 200r / min; take the above 100-200μL bacterial solution, Spread on an LB plate containing ampicillin (Amp), and then incubate in a 37°C incubator for 12 hours. A single colony that was successfully transformed was picked on the LB plate, and then put into ...
Embodiment 2
[0034]Weigh 10g corn starch to prepare 10% starch milk with mass percentage concentration, place it in a boiling water bath and heat it until it is completely gelatinized; when the temperature drops to 60℃, add 200U / g starch α-amylase and heat it for 0.5h, then add The α-glucosidase of 100 U / g starch continues to react for 1 h; the enzyme is inactivated by heating, centrifuged, and the obtained supernatant is dried to obtain a branched glucan product. In this process, the DE value after α-amylase hydrolyzes the starch chain is 7.3.
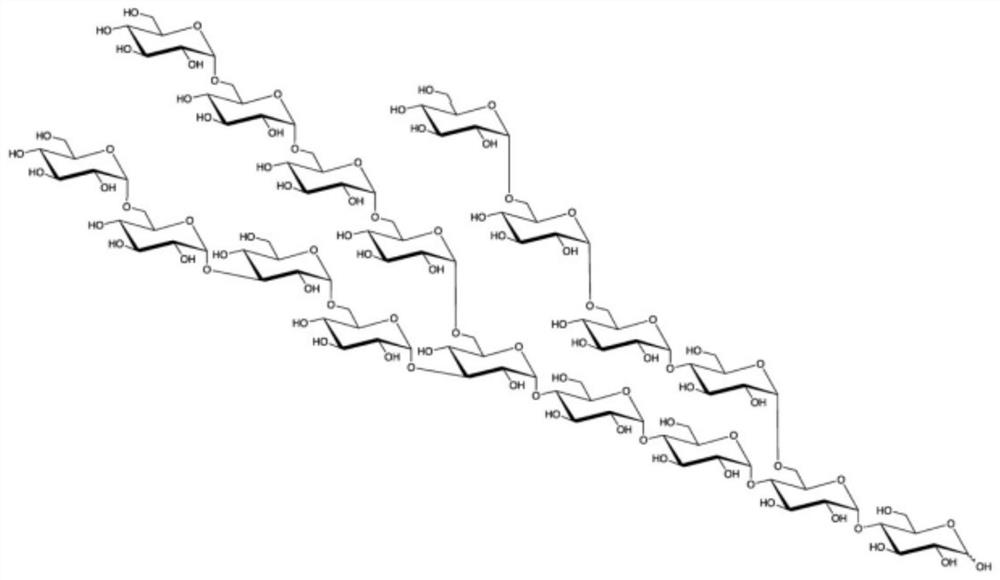
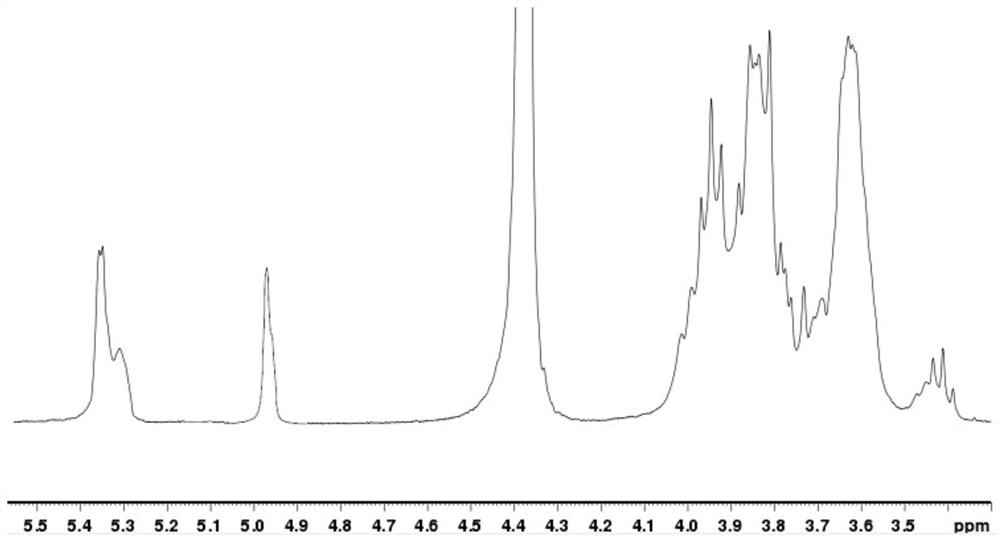
[0035]After analysis and determination, the average molecular weight of the prepared branched glucan is 4800g / mol, the content of α-1,3 bonds is 8.2%, the content of α-1,6 bonds is 49%, and the proportion of indigestible nutrient fragments reaches 80%. .figure 1 withfigure 2 Respectively, the structure diagram and NMR chart of the prepared indigestible branched glucan.
Embodiment 3
[0037]Weigh 40g wheat starch to prepare a starch milk with a mass percentage concentration of 40%, place it in a boiling water bath and heat it until it is completely gelatinized; when the temperature drops to 30℃, add 100U / g starch α-amylase and keep it warm for 1h, then add 20U / g starch α-glucosidase continues to react for 12 hours; heat inactivation of the enzyme, centrifugal separation, and the obtained supernatant is dried to obtain a branched glucan product. In this process, the DE value after α-amylase hydrolyzes the starch chain is 5.5.
[0038]After analysis and determination, it can be seen that the prepared branched glucan has an average molecular weight of 6100 g / mol, an α-1,3 bond content of 7.5%, a α-1,6 bond content of 60%, and a proportion of indigestible nutrient fragments of 83%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com