Microorganism-derived agricultural bacteriostatic agent and preparation method thereof
A bacteriostatic agent and microorganism technology, applied in the field of agricultural bacteriostatic agents and their preparation, can solve the problems of narrow bacteriostatic spectrum of chemical bacteriostatic agents, drug resistance of plant pathogens, incomplete degradation, etc. Good bacteriostatic effect and strong cytolytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
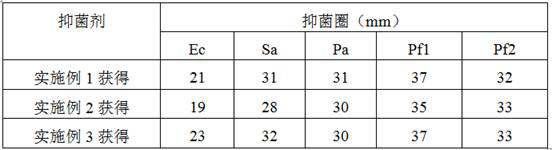
[0022] Example 1: Extraction and separation of single rhamnolipid components from fermentation broth of conventional rhamnolipid-producing bacteria
[0023] Rhamnolipids synthesized by conventional rhamnolipid-producing bacteria are mixtures of mono-rhamnolipids and di-rhamnolipids. In the embodiment, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ( Pseudomonas aeruginosa ) SG(Zhao et al. Comparative studies on the structural composition, surface / interfaceactivity and application potential of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa using hydrophobic or hydrophobic substrates. BioresourceTechnology, 2020, 295, 122269) as the starting strain.
[0024] LB medium: peptone 10g, yeast powder 5g, NaCl 10g, add deionized water to 1L, pH 7.0.
[0025] Fermentation medium: glycerol 45g, NaNO 3 3.5g, K 2 HPO 4 ∙3H 2 O 4.0g, KH 2 PO 4 3.0g, MgSO 4 ∙7H 2 O1.0g, add deionized water to 1L, pH 7.0.
[0026] Weigh the above reagents with an electronic balance to prepare the corresponding med...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: Preparation of single rhamnolipid fermentation broth
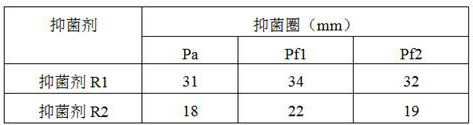
[0034] Select the rhamnolipid product as a genetically engineered bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri that is completely mono-rhamnolipid Pseudomonas stutzeri Rhl (Zhao et al. Heterologous production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipid under anaerobic conditions for microbial enhanced oil recovery. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2015, 118: 379-389) as the starting strain for the production of monorhamnolipid.
[0035]Utilize the LB medium and fermentation medium among the embodiment 1, get the slant 1 inoculation loop of bacterial strain Rh1, inoculate in the Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml LB medium, at 30 ℃, under 180 rpm / min, cultivate 6-10 hours , to OD 600 The value is 0.6~1.0, and the seed solution of strain Rhl is obtained. Then, inoculate the fermentation medium with a 3% inoculum amount (v / v), and culture it for 5 days at 37°C and 180 rpm to ferment and produce monorhamnolipids to obta...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Extracting mono-rhamnolipid from fermentation broth of mono-rhamnolipid-producing bacteria
[0038] Centrifuge the fermented liquid obtained from the above-mentioned Example 2 at 8000 g to remove insoluble matter such as bacteria, and use the chloroform / methanol (v / v, 2:1) extraction method in Example 1 to extract the single mouse in the fermented liquid Li glycolipid.
[0039] The extracted monorhamnolipid product was qualitatively verified by the thin-layer chromatography method in Example 1.
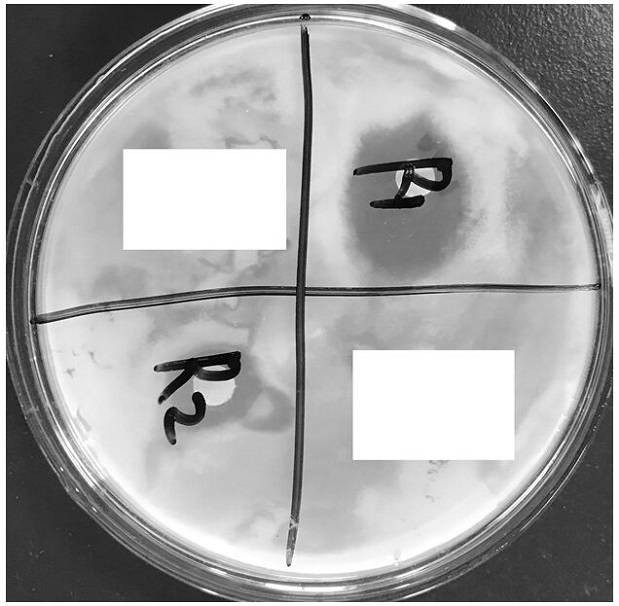
[0040] The extracted mono-rhamnolipid is used to prepare an aqueous solution, wherein the concentration of the mono-rhamnolipid is 200-2000 mg / L, which is used as a bacteriostatic agent for plant pathogenic bacteria.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com