Anti-ultraviolet graphene coating with hierarchical pore structure, anti-ultraviolet material and preparation method thereof
A porous graphene and graphene technology, applied in graphene, coatings, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems such as affecting graphene's UV-proof functionality, graphene content should not be too high, and use scope limitations, etc. Promote adsorption deposition, prevent excessive stacking and agglomeration, improve the effect of scattering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] A kind of preparation method of graphene anti-ultraviolet material, comprises the following steps:
[0044] S1. Add the above-mentioned porous graphene nanosheets and sodium bicarbonate into the dispersion solvent according to the mass ratio of 1:2-4, and ultrasonically disperse evenly to obtain a dispersion liquid with a graphene mass fraction of 30%-40%;
[0045] S2. Use polystyrene or polyaniline to modify the surface of the substrate to be coated, then immerse the modified substrate in the dispersion obtained in step S1, and then slowly add Dilute hydrochloric acid, after self-assembling one layer of pore diameter on the surface of the substrate is an anti-ultraviolet graphene coating with a hierarchical porous structure of 20-100nm and a thickness of 100-200nm, the substrate is taken out;
[0046] S3. Use deionized water to clean the surface of the substrate taken out in step S2, and then dry to obtain the graphene UV-resistant material. In this process, since the...
Embodiment 1
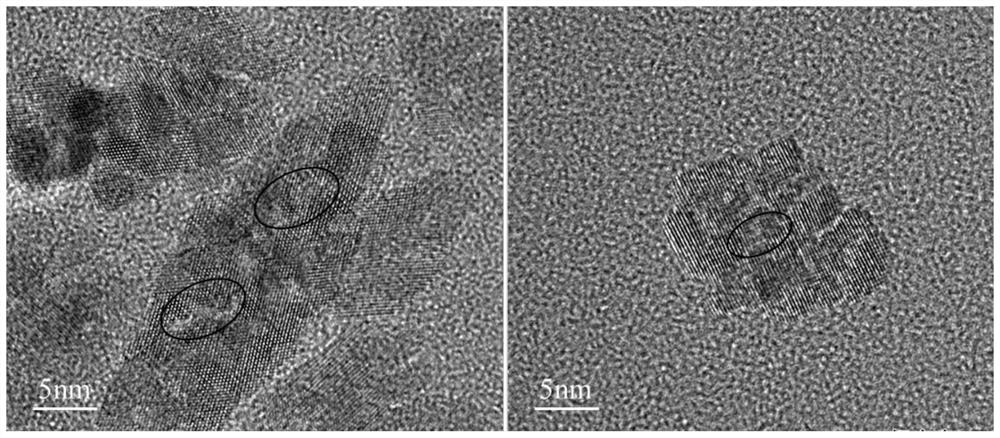
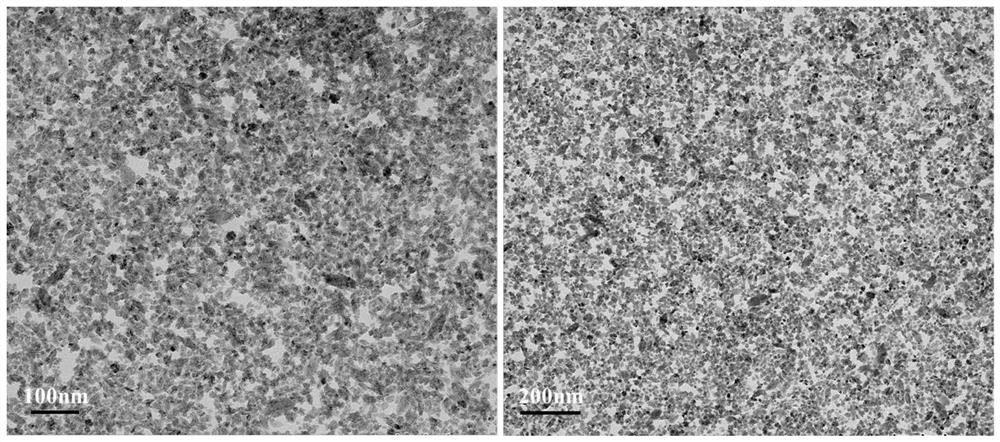
[0053] This embodiment provides a kind of anti-ultraviolet graphene coating of multi-level hole structure and the anti-ultraviolet material comprising this coating, please refer to figure 2 Shown, the anti-ultraviolet graphene coating of described hierarchical porous structure comprises aperture is 5-20nm, lateral size is the porous graphene nanoplatelet of 15-80nm, and the interlaced formation aperture between described porous graphene nanoplatelet is Anti-ultraviolet graphene coating with a hierarchical porous structure of 40-60nm and a thickness of about 120nm. It can be seen from conflict 2 that the porous graphene nanosheets in this embodiment are interlaced to form a coating with a pore diameter of about 40-60 nm, and the dispersion is relatively uniform.
[0054] In this example, the porous graphene nanosheets can be commercially available or self-made.
[0055] Homemade porous graphene nanosheets can be prepared by the following methods:
[0056] (1) Ultrasonic disp...
Embodiment 2
[0067] A graphene anti-ultraviolet material, compared with Example 1, the difference is that in step S2, the polystyrene is replaced by polyaniline. Others are substantially the same as in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0068] The average value of the ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) of this embodiment is 750, the ultraviolet light transmittance T (UVA) is 1.24%, and T (UVB) is 0.06%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com