Method for improving Zea mays L. straw enzymolysis efficiency by Rhodococcus biphenylivorans
A technology for Rhodococcus biphenophila and corn stalks is applied in the field of improving the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of corn stalks by using Rhodococcus biphenophila, and can solve the problems of low enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, hindering the contact between cellulase and cellulose, and difficulty in production, etc. To achieve the effect of improving hydrolysis effect and increasing accessibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for improving the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of corn stalks by using Rhodococcus biphenylophilum, comprising the steps of:
[0026] (1) Preparation of corn stalk powder
[0027] drying and crushing corn stalks to obtain corn stalk powder;
[0028] (2) Preparation of Rhodococcus biphenylphila crude enzyme solution
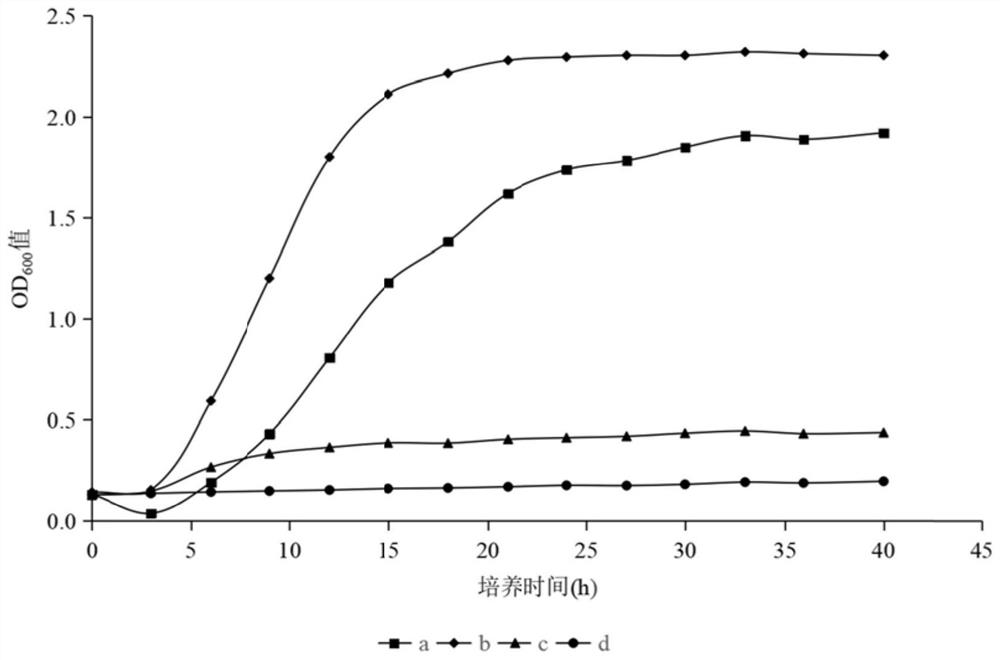
[0029] Configure LB medium with added inorganic salts, inoculate activated Rhodococcus biphenylophilus colonies, and culture in an incubator set at 28°C and 200rpm for 12h, OD 600 When the value reaches 2.5, prepare an ice box, put the bacterial liquid into a sterilized and dry 50mL centrifuge tube in a sterile operating table, use a low-temperature high-speed centrifuge to separate the bacterial cells and bacterial liquid at 4°C and 8000rpm, and obtain the supernatant As the crude enzyme solution of Rhodococcus biphenylophilus;
[0030] LB medium with inorganic salts added: 50 mL of LB medium + 50 mL of inorganic salt medium;
[0031] Where...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Calculation of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Efficiency of Corn Stalk
[0044] The corn stalk powder pretreated by Rhodococcus biphenylphila in Example 1 and the corn stalk powder pretreated by sterile water in the comparative example were subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis treatment with cellulase, and a control group without cellulase was set. The concentration of reducing sugar was measured every 3 hours, and the curve of reducing sugar content was drawn. The result was that the concentration of reducing sugar hydrolyzed by cellulase reached the highest after 3 hours of enzyme treatment, and basically no reducing sugar was produced in the control group, indicating that there was basically no dissolution of straw components. , after pretreatment of straw raw materials with Rhodococcus biphenylophilus, the hydrolysis effect of cellulase is significantly higher than that of corn straw pretreated with sterile water. In order to compare the effects of different treatments on cellulo...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Observation of pretreated straw by scanning electron microscope
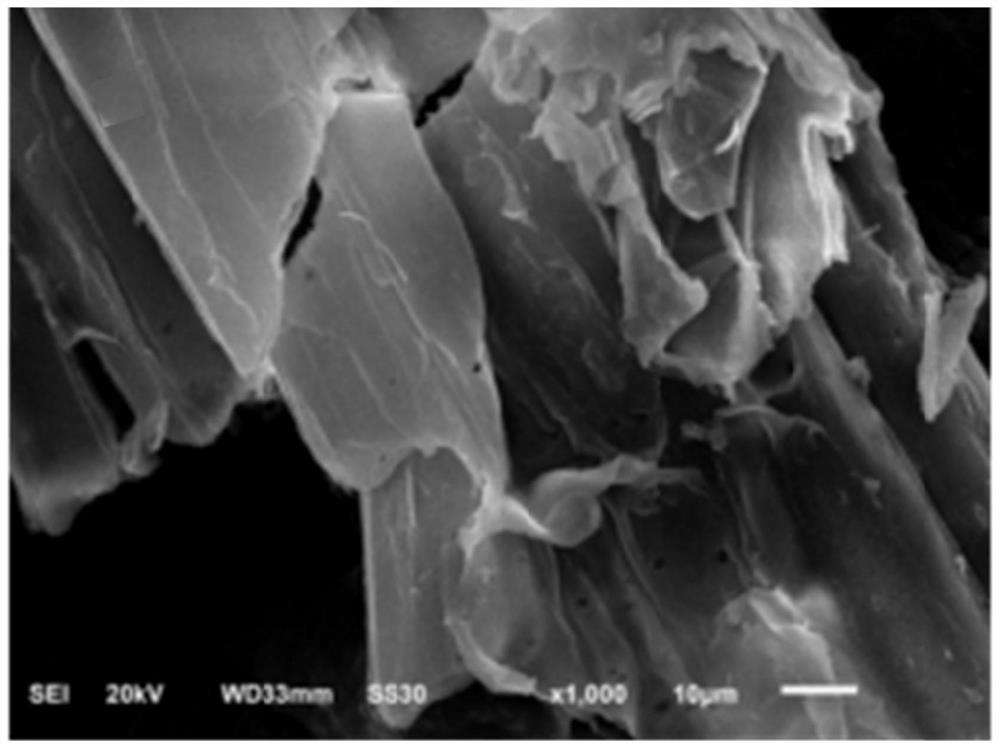
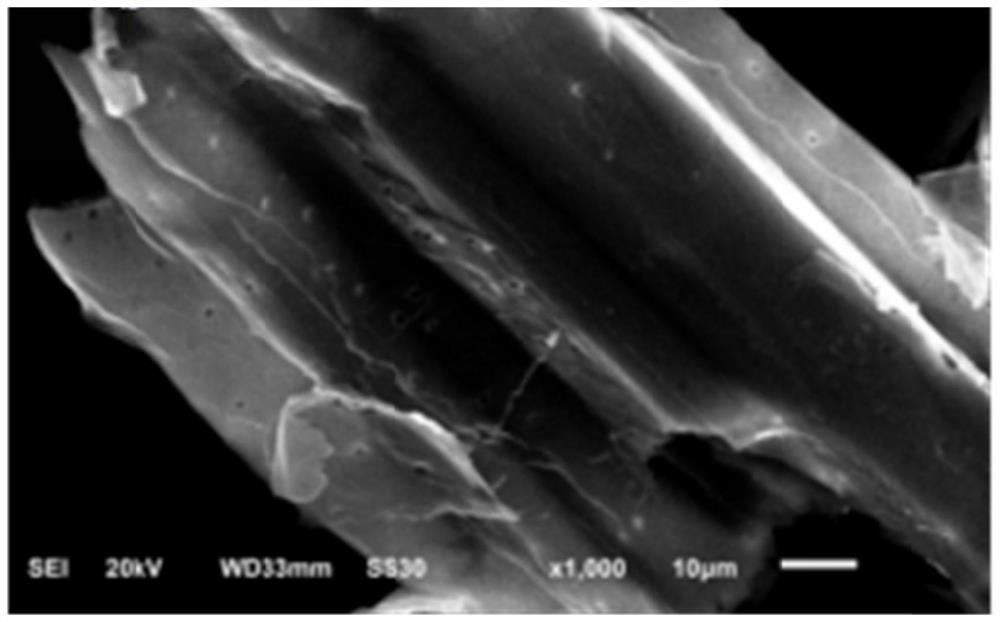
[0050] The corn stalk powder after the pretreatment of the step (3) of Example 1 and the corn stalk powder after the pretreatment of the step (3) of the comparative example were respectively used scanning electron microscopy to observe the surface structure of the corn stalk material, and the microscopic structure of the corn stalk after different pretreatments was compared. Structural changes.
[0051] The results are shown in Figure 2, the corn stalks pretreated by Rhodococcus biphenylophilus had obvious structural changes, and the comparative corn stalk materials ( Figure 2A and Figure 2C) The surface structure is more complete, with obvious lamellar structure attached to the surface of corn stalks. Observation of the section shows that the broken section is neat and basically without delamination, the holes are evenly distributed and the edges are smooth. However, on the surface of corn stover mat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com