Method for rapidly propagating bait microalgae biomass by utilizing polyculture
A bait microalgae and culture medium technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of slow cell growth, long generation time, inability to effectively improve the growth of commonly used bait microalgae, etc. The effect of improving nutritional value, reducing production costs and increasing the speed of reproduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: the cultivation effect comparison of different organic carbon sources of bait microalgae
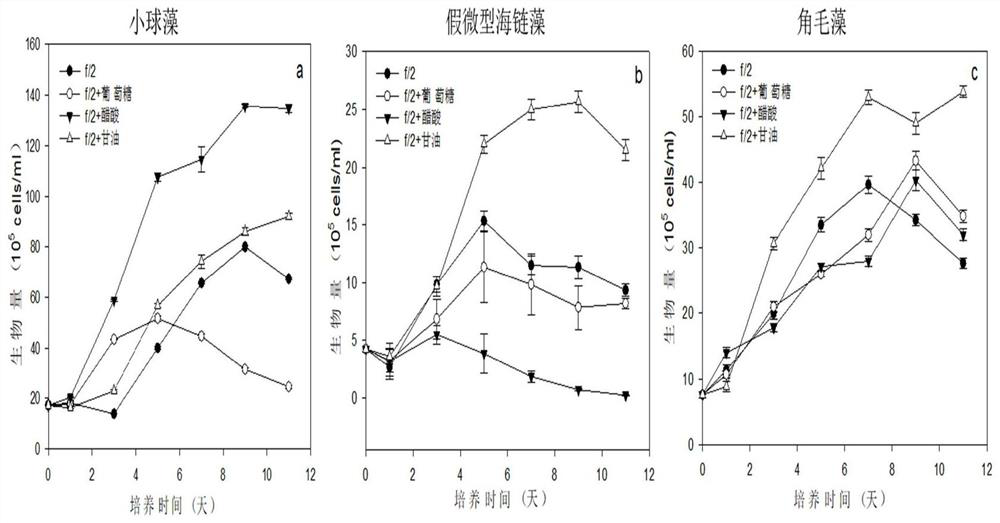
[0020] Three commonly used bait microalgae Chlorella, Thalassiosira pseudonana, and Chaetoceros were placed in f / 2 medium, and the light intensity was 80 μmol.m -2 .s -1 , under the condition of temperature 25°C, the liquid mixed nutrient culture in the triangular flask was carried out ( figure 1 ), and f / 2 medium were added with a concentration of 2.0g.L -1 The organic carbon sources glucose, acetic acid and glycerol. The group distribution ratio of f / 2 medium is as follows (mg.L -1 ): Sodium Nitrate 75, Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Monohydrate 5, Sodium Silicate Nonahydrate 30, Ferric Chloride Hexahydrate 3.15, Disodium EDTA Dihydrate 4.36, Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate 0.0098, Sodium Molybdate Dihydrate 0.0063, zinc sulfate heptahydrate 0.022, cobalt chloride hexahydrate 0.01, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 0.18, vitamin B 1 0.1, vitamin H 0.0005, vitamin B 1...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Optimal screening of different carbon source concentrations under mixed nutrition conditions
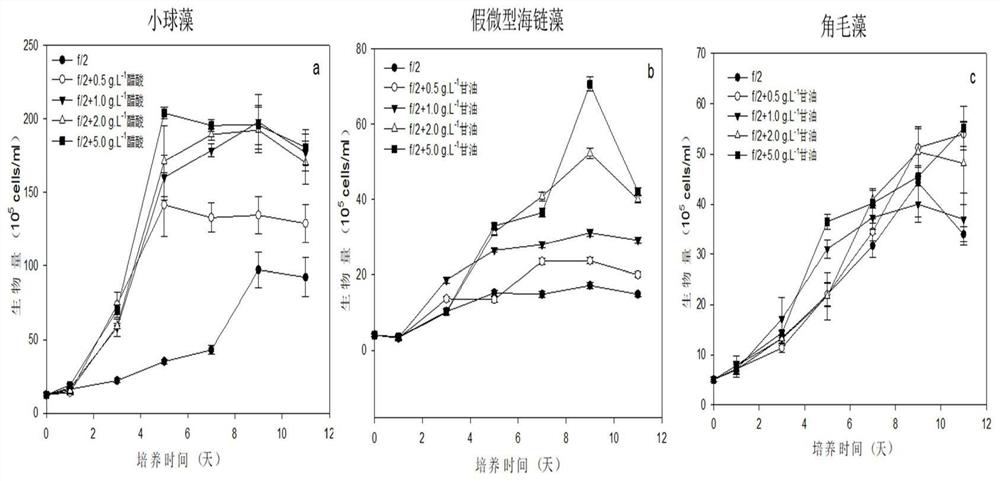
[0023] according to figure 1 The experimental program, three bait microalgae Chlorella, Thalassiosira pseudonana, Chaetoceros under the same light intensity (80μmol.m -2 .s -1 ) and temperature conditions (25°C); add organic carbon sources acetic acid, glycerol, and glycerol to f / 2 normal medium, respectively. The concentrations of the three organic carbon sources are set to 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0g.L respectively -1 , after cultivating respectively 11 days under the same conditions as in Example 1, the result is as follows image 3 shown. The results showed that Chlorella in the concentration of acetic acid 5.0g.L -1 The growth effect is good, and the biomass is 141.7×10 5 cells / ml, better than the value of f / 2 normal medium 84×10 5 cells / ml; Thalassiosira pseudonana in the organic carbon source glycerol concentration 5.0g.L -1 The lower growth is good, the biom...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3: Algae cell biochemical components and main fatty acid changes under optimal organic carbon source and concentration of bait microalgae
[0025] With reference to the conditions described in Example 1 and Example 2, 3 strains of bait microalgae Chlorella, Thalassiosira pseudonana, and Chaetoceros were respectively added with an optimal organic carbon source concentration of 5.0g.L -1 Acetic acid, 5.0g.L -1 Glycerin and 5.0g.L -1 Glycerol was cultured in f / 2 normal medium for 11 days, and then the content of oil, sugar, protein components and main fatty acids of algae cells were determined respectively. The result is as Figure 4 As shown, the polysaccharide and lipid components of the three bait algae under the condition of organic carbon source were all better than those under the corresponding normal medium condition.
[0026] Most importantly, under the dominant organic carbon source and concentration of Thalassiosira pseudonana, the component contents o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com