Method for producing ethylene glycol and glycolic acid by using escherichia coli and genetically engineered bacteria
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of production of ethylene glycol and glycolic acid, can solve the problems of poor growth and achieve the effects of low production cost, simple process route, good application value and economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] Step 4, preparation of Escherichia coli electroshock competent cells and electrotransformation of homologous recombination fragments;
[0034] Step 5, identifying the Escherichia coli △aldA recombinant by PCR.
[0035] Obtaining the genetically engineered strain (taking aldA as an example) of gene overexpression is divided into the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, linearization of the high-level expression vector pDK6;
[0037] Step 2, obtaining the aldA gene fragment;
[0038] Step 3, constructing an overexpression plasmid by homologous recombination;
[0039] Step 4, transformation into Escherichia coli DH5α;
[0040] Step 5, identifying pDK6-aldA transformants by PCR;
[0041] Step 6, extracting the plasmid pDK6-aldA;
[0042] Step 7. Preparation of electroporated cells and electroporation of pDK6-aldA to target Escherichia coli;
[0043] Step 8: Identify pDK6-aldA transformants by PCR.
Embodiment 1
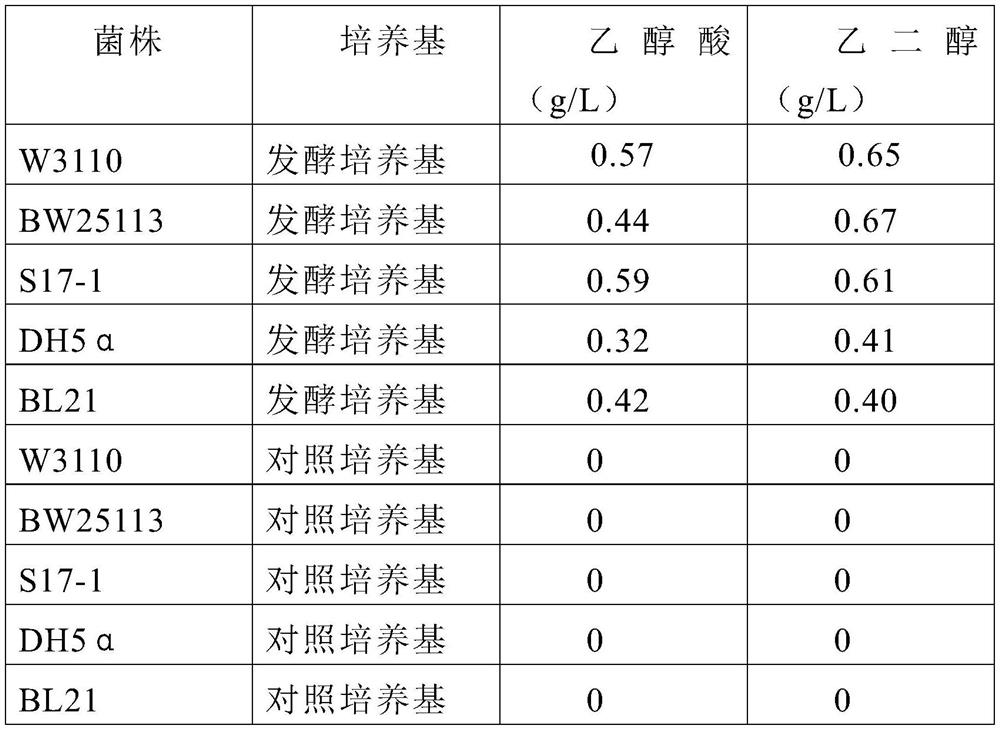
[0045] Production of ethylene glycol and / or glycolic acid by Escherichia coli fermentation using xylose as carbon source.
[0046] Escherichia coli used were wild type strains W3110, BW25113, S17-1, DH5α, BL21.
[0047] Escherichia coli was inoculated into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed culture medium, and the shaker cabinet was rotated at 200 rpm and kept at a constant temperature of 37°C for seed cultivation.
[0048] The components of the seed medium are: peptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5g / L, sodium chloride 5g / L.
[0049] The composition of the fermentation medium is: xylonic acid 15g / L, corn steep liquor 50g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2g / L, calcium chloride 1g / L, magnesium sulfate 4g / L.
[0050] The composition of the control medium was: xylose 15g / L, corn steep liquor 50g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2g / L, calcium chloride 1g / L, magnesium sulfate 4g / L.
[0051] The seed...
Embodiment 2
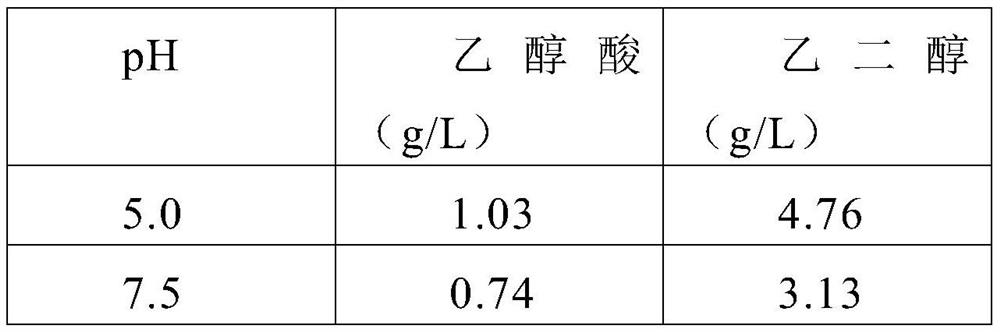
[0056]Production of ethylene glycol and / or glycolic acid by Escherichia coli fermentation using xylose as carbon source. The Escherichia coli used was wild-type strain W3110.
[0057] Escherichia coli was inoculated into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed culture medium, and the shaker cabinet was rotated at 200 rpm and kept at a constant temperature of 37°C for seed cultivation.
[0058] The composition of the fermentation medium is: xylose acid 30g / L, corn steep liquor 50g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2g / L, calcium chloride 1g / L, magnesium sulfate 4g / L.
[0059] The seeds were cultured for 12 hours, inoculated into a 5L fermenter, which contained 3L fermentation medium or control medium, kept ventilation and stirring during the fermentation process, and the fermentation temperature was 37°C. During the fermentation process, the pH of the fermentation liquid was adjusted by adding ammonia solution. Stabilized at 5.0 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com