Recycling method of waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode powder
A lithium iron phosphate and positive electrode technology, which is applied in the field of recycling waste lithium iron phosphate positive electrode powder, can solve problems that restrict the popularization and application of lithium iron phosphate batteries, battery capacity attenuation, and cannot be used normally, so as to solve the difficulty of tailings disposal , the content of impurities is reduced, and the product appearance is good
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073]Method for recycling the recovery method of waste phosphate lithium positive electrode powder, including the following steps:
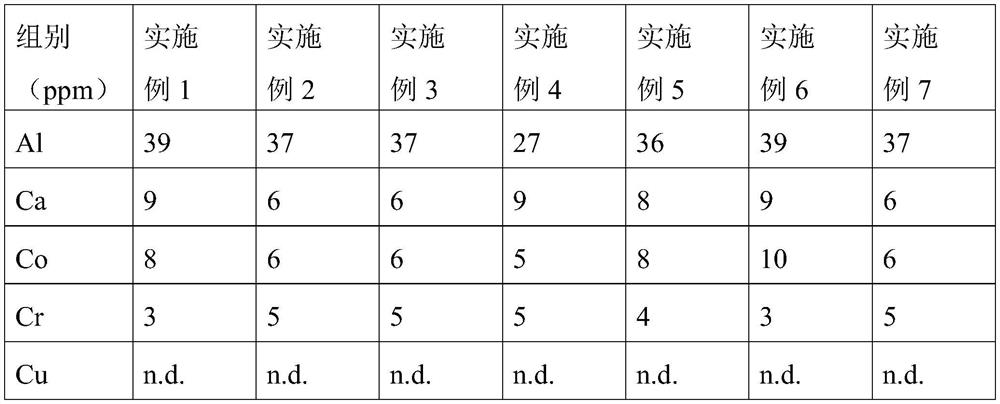
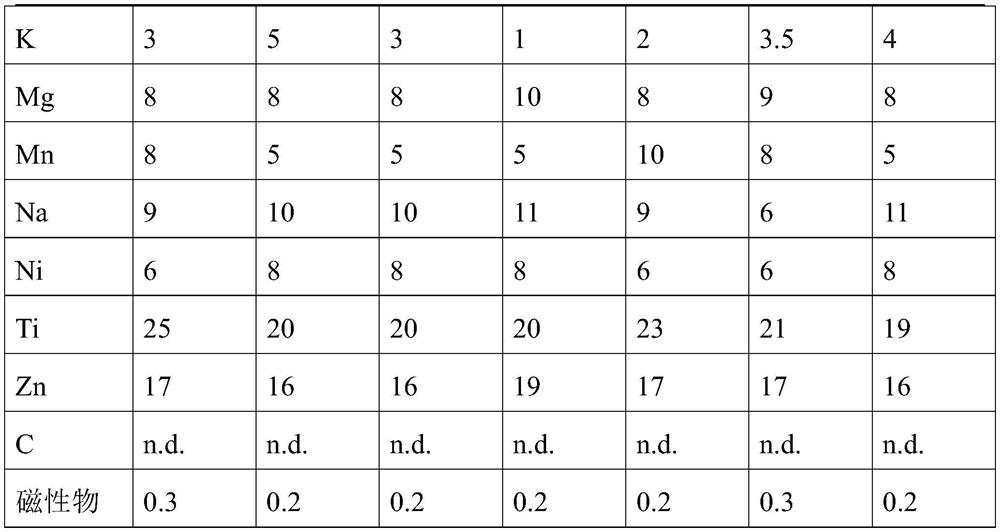
[0074](1) Weigh 100g waste phosphate cell positive powder in the reaction kettle, add 200 ml of distilled water to 0.053 g (0.02 mol) concentrated hydrochloric acid, 11g (0.05 mol) Hedp, stirred at 20R / min, constantly stirring The temperature was warmed to 80 ° C, the reaction was 2 h, and the lithium iron phosphate containing <100 ppm was filtered. 100 g of a tubic iron phosphate battery positive electrode powder and a substance of lithium iron phosphate content of 100 ppm of 100 ppm is about 0.54 mol.
[0075](2) In the reaction kettle, 200 ml of distilled water, 55 g (0.55 mol) concentrated hydrochloric acid was added, and the lithium iron phosphate was pulp, the stirring speed was 20 r / min, and 47 g (0.38 mol) dioxygen (content: 27.5%), control The reaction temperature was <70 ° C. The oxidation is completely oxidized with an adjacent phytoprine, an...
Embodiment 2
[0082]Method for recycling the recovery method of waste phosphate lithium positive electrode powder, including the following steps:
[0083](1) Weigh 100g used phosphate positive electrode powder in the reactor, add 200 ml of distilled water, add 0.5 g (0.005 mol) concentrated sulfuric acid, 15.7 g (0.053 mol) EDTA, stirring speed of 20R / min, constantly agitation The lower temperature was 80 ° C, the reaction was 3 h, and the lithium iron phosphate containing <100 ppm was filtered. 100 g of a tubic iron phosphate battery positive electrode powder and a substance of lithium iron phosphate content of 100 ppm of 100 ppm is about 0.54 mol.
[0084](2) In the reactor, 200 ml of distilled water, 27 g (0.27 mol) concentrated sulfuric acid was added, and the lithium iron phosphate was pulp and the stirring velocity was 20 R / min, and 47 g (0.38 mol) dioxygen (content: 27.5%), control The reaction temperature was <70 ° C. The oxidation is completely oxidized with an adjacent phytoprine, and the...
Embodiment 3
[0091]Method for recycling the recovery method of waste phosphate lithium positive electrode powder, including the following steps:
[0092](1) Weigh 3000 g of waste phosphithium phosphate positive electrode powder in the reaction kettle, add 60 g of concentrated sulfuric acid, 300 g of EDTA, stirred at a stirring speed of 20 r / min, and stir up to 90 ° C, reaction for 3 h, filtrate Lithium lithium iron phosphate containing <100 ppm was obtained. 100 g of a tubic iron phosphate battery positive electrode powder and a substance of lithium iron phosphate content of 100 ppm of 100 ppm is about 0.54 mol.
[0093](2) 6000 ml of distilled water, 810 g of concentrated sulfuric acid was added, and the lithium iron phosphate was pulp and the stirring velocity was 20 R / min, and 1410 g of dual oxygen (content: 27.5%) was added dropwise, and the reaction temperature was <70 ° C. The oxidation is completely oxidized with an adjacent phytoprine, and the reaction is 1 h, which is a lithium sulfate so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com