Preparation method and application of copper modified molecular sieve catalyst
A catalyst and molecular sieve technology, applied in the field of catalytic chemistry, can solve the problems of discontinuous reaction process, low methanol yield, uneconomical oxidant and catalyst, etc., to achieve optimized methane activation effect, excellent catalytic activity, and good hydrothermal stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
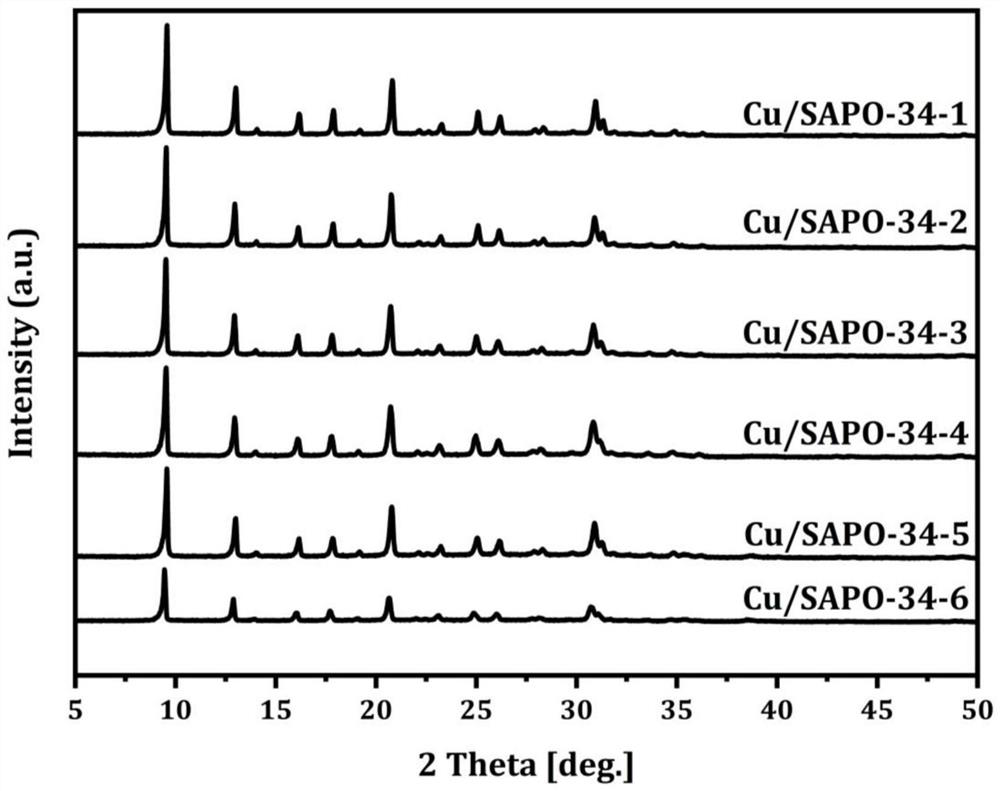
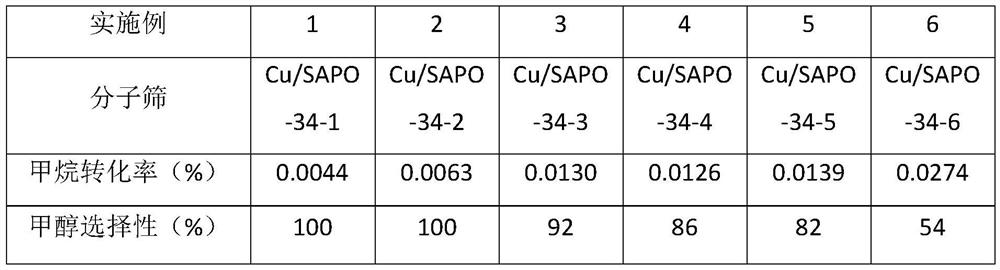
Embodiment 1-6
[0030] This embodiment provides the preparation method of the copper-modified molecular sieve catalyst that is used for the selective oxidation of methane to produce methanol,
[0031] Step 1. Mix 85% orthophosphoric acid as the phosphorus source in water, stir for five minutes, add 67% pseudo-boehmite and stir for 1.5 hours at room temperature to obtain the first mixed solution;
[0032] Step 2, another CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O is mixed in a certain amount of water, and after it is completely dissolved, tetraethylenepentamine is added and stirred for 30 minutes, then morpholine is added for stirring, and 50% silica sol is added after 30 minutes to obtain a second mixed solution;
[0033] Step 3. The second mixed solution is mixed with the first mixed solution, stirred at room temperature for 6-12 hours, mixed evenly, put into a stainless steel reactor lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and crystallized at 200°C for 2-4 hours. day; after the crystallization was completed, the reactor...
Embodiment 7-12
[0045] The above-mentioned Cu / SAPO-34-3 was used as the catalyst. Except that the reaction temperature was controlled at 200-400° C., other operating conditions were the same as in Examples 1-6. See Table 3 for specific analysis results.
[0046] Table 3 Effect of reaction temperature on the reaction of methane selective oxidation to methanol
[0047] Example 7 8 9 10 11 12 Reaction temperature (°C) 200 250 270 300 350 400 Methane conversion rate (%) 0 0.0017 0.0045 0.0126 0.0416 0.0505 Methanol selectivity (%) 0 100 100 86 52 19 Methanol productivity (μmol / g / h) 0 20 62 176 503 196
[0048] As can be seen from Table 3, as the reaction temperature increases, the conversion rate of methane increases and the selectivity of methanol decreases. At 270 ° C, the selectivity of methanol is 100%, after which the peroxidation product carbon dioxide appears, lead to a decrease in selectivity.
Embodiment 13-16
[0050] The catalyst is the above-mentioned Cu / SAPO-34-3. Take 0.1-0.3g sample and put it into a quartz reactor. After pretreatment, feed methane gas, water vapor, and oxygen reaction gas. Carry out below, the total flow of control inlet gas is 60ml / min, change the ratio of feeding reaction gas, wherein the volume content of methane is 99% in the reaction gas of example 13, without oxygen; The volume content of methane in the reaction gas of example 13 98%, the volume content of oxygen is 0.04%; the volume content of methane in the reaction gas of example 14 is 78%, and the volume content of oxygen is 0.2%;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com