Preparation method of low-chlorine composite PAE wet strength agent
A PAE wet-strength agent and composite technology, which is applied in the direction of reinforcing agent addition, non-fiber pulp addition, papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of high dosage of low-chlorine wet-strength agent, achieve rapid aging speed, stable appearance and color, and good weather resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
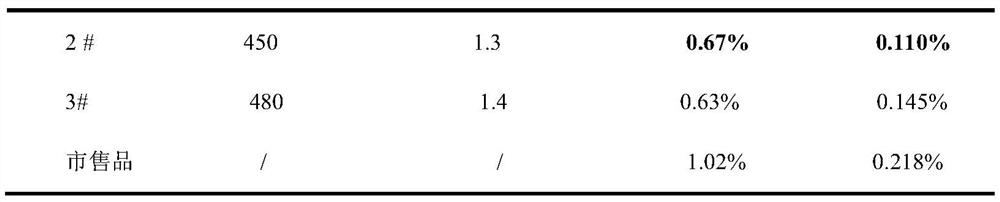
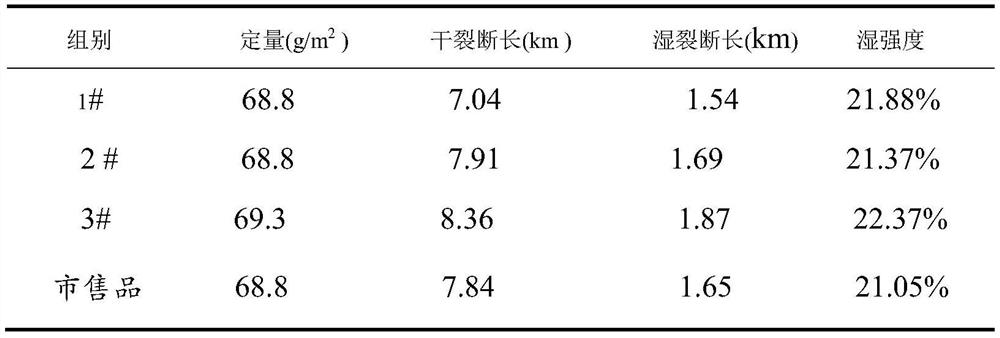
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Weigh 146 grams of adipic acid (1.0mol) and 50 grams of deionized water into a four-necked flask, stir to form a slurry, and then feed nitrogen after vacuuming, then add 104 grams of diethylenetriamine (1.01mol) in sequence, and heat up by electric heating Heat it at 180°C for 2 hours, collect about 86.5 grams of water released during the reaction, and add 215 grams of deionized water to obtain a polyamide intermediate with a solid content of 50%, a viscosity of 340 cps, and a pH of 10.2.
[0034] 100 grams (0.232 mol) of the above-mentioned polyamide aqueous solution, 50 grams of deionized water, 0.2 g of triethanolamine, and 1.0 g of potassium carbonate were heated to 25 ° C during the stirring process, and 26 grams (0.281 mol) of epichlorohydrin was added dropwise. The dripping time is 2 hours. During the whole epichlorohydrin dripping process, it is necessary to continuously add potassium carbonate solution to control the pH of the reactant in the kettle to be above ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Weigh 132 grams of glutaric acid (1.0mol) and 75 grams of deionized water into the four-neck flask, stir to form a slurry, and then feed nitrogen after vacuuming, then add 103 grams of diethylenetriamine (1.0mol) in turn, and heat Raise the temperature to 175°C, keep it warm for 2 hours, collect about 112 grams of water released during the reaction, and add 200 grams of distilled water to obtain a polyamide intermediate with a solid content of 50%, a viscosity of 450 cps, and a pH of 9.8.
[0037] With 100 grams (0.248mol) of the above-mentioned polyamide aqueous solution, 65 grams of deionized water, 0.2 g of hexamethylenetetramine, and 1.0 g of sodium carbonate, the temperature was raised to 25 ° C during the stirring process, and 30 grams of epichlorohydrin ( 0.324mol), the dropping time is 2h. During the whole epichlorohydrin dripping process, sodium carbonate solution needs to be continuously added to control the pH of the reactant in the kettle to be above 9.0. Aft...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Weigh 146 grams of adipic acid (1.0mol) and 120 grams of deionized water and add them to a four-necked flask, stir to form a slurry, vacuumize and feed nitrogen, then add 102 grams of diethylenetriamine (0.99mol) and heat up to 180°C, keep warm for 2.0 hours, collect about 137 grams of water released during the reaction, add 212 grams of distilled water to obtain a polyamide intermediate, and its indicators are 50% solid content, 480 cps viscosity, and 9.8 pH.
[0040]With 100 grams (0.228mol) of the above-mentioned polyamide aqueous solution, 80 grams of deionized water, 0.6 g of hexamethylenetetramine, and 1.0 g of sodium carbonate, the temperature was raised to 25 ° C during the stirring process, and 30 grams of epichlorohydrin ( 0.324mol), and the dropping time is 2h. During the whole epichlorohydrin dripping process, sodium carbonate solution needs to be continuously added to control the pH of the reactant in the kettle to be above 9.5. After 30 minutes of epichloro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com