Gordonia rubripertincta, application and pigment production method
A technology of Gordonia crimson and Gordonia, which is applied in the field of microorganisms and its applications, can solve the problems of limited strains and achieve the effects of good stability and simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Isolation and Identification of Carotenoid-producing Gordonia Rubus (GH-1)
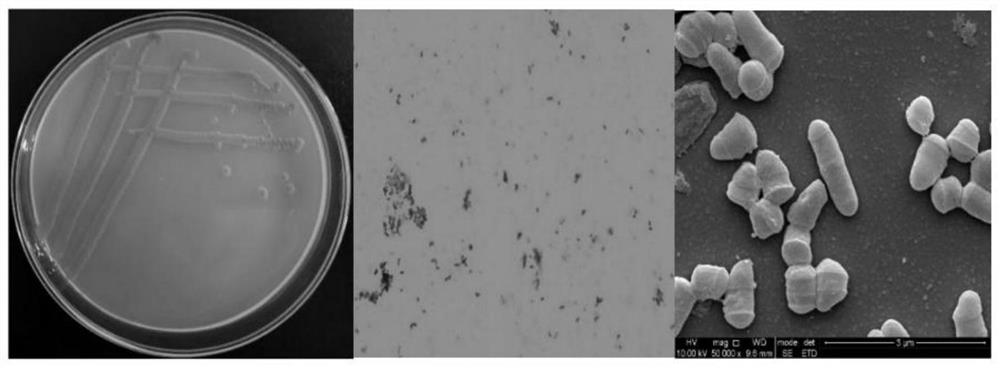
[0046] (1) Isolation and purification of carotenoid-producing strains: Take 2 g of Pixian watercress (collected in Pidu District, Chengdu City) in the traditional brewing process in 100 mL of GD medium (GD medium: sucrose 20 g / L; potassium nitrate 4 g Magnesium sulfate 0.4g / L; Ferrous sulfate 0.015g / L; Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2g / L; Disodium hydrogen phosphate 3g / L; Sodium citrate 2g / L), light, 30 ℃ enrichment culture 5d. Afterwards, 200 μL of bacterial liquid was diluted and spread on GD solid medium, and cultured at 30°C for 3 days. The single colonies that produced pigment were picked and streaked and purified in GD solid medium ( figure 1 Middle panel a), after 3 days of culture at 30°C, single colonies were picked for enrichment culture, and stored in glycerol at -50°C.
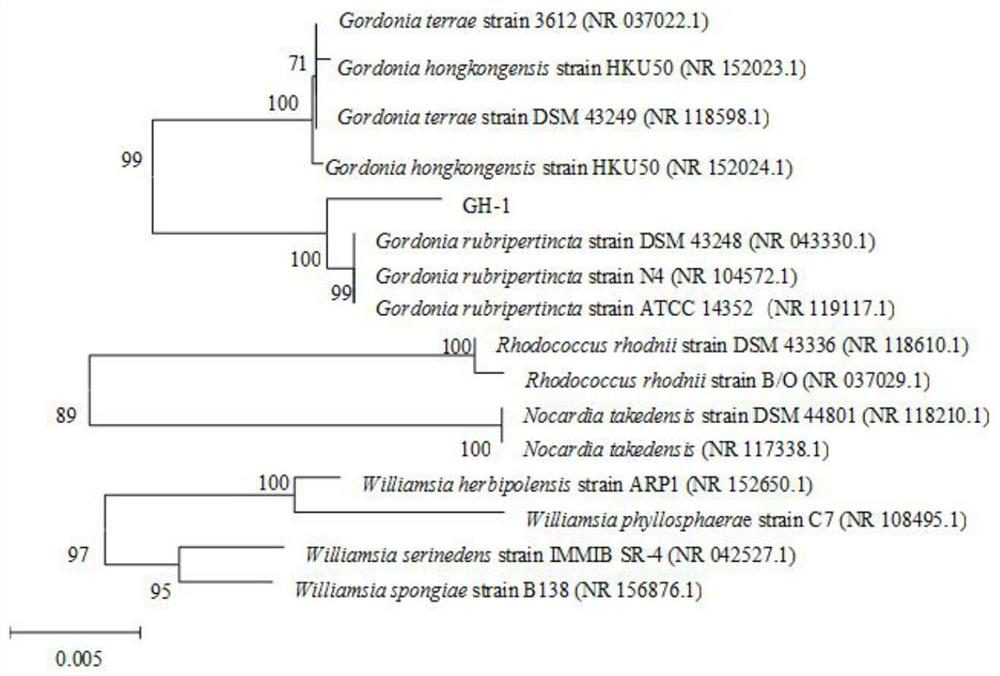
[0047] (2) Identification of carotenoid-producing strains: 16S rRNA was used to carry out molecular...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Colony morphology and physiological and biochemical characteristics of bacterial strain GH-1
[0052] The bacterial strain GH-1 (Gordonia rubripertincta) isolated by the present invention has a yellow colony on the GD agar medium, is round in shape, opaque, and has bulges and wrinkles. Observed under a microscope, the strain is long rod-shaped. After morphological identification and 16S rRNA sequence developmental tree analysis, the strain was named Gordonia rubripertincta (Gordonia rubripertincta) GH-1.
[0053] The physiological and biochemical results of the isolated bacterial strain GH-1 of the present invention are shown in Table 1 below:
[0054] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical results of strain GH-1
[0055]
[0056] Note: Physiological and biochemical test results ("+" means positive, "-" means negative)
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: the identification process of the pigment produced by bacterial strain GH-1
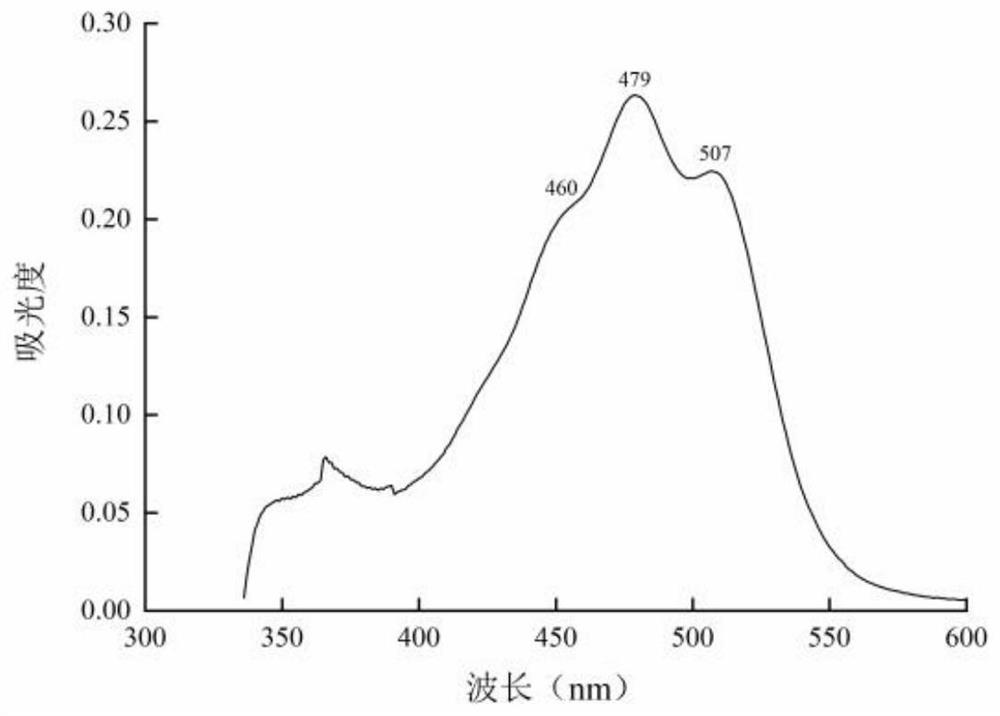
[0058] (1) Strain GH-1 was inserted into GD medium and cultured at 30°C for 120h. Take the bacterial liquid in a refrigerated centrifuge and centrifuge at 8000rpm for 10min. Wash the cells twice with sterile normal saline, then add acetone reagent to sonicate for 20 minutes, centrifuge, extract, and take the supernatant, which is the crude pigment.
[0059] (2) The purification of crude pigment is carried out by silica gel column chromatography, and the column is packed by petroleum ether wet method. Petroleum ether: acetone = 4:1; petroleum ether: acetone = 1:1; petroleum ether: acetone = 1:4 Gradient elution. The separation effect was tested by thin layer chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography. TLC conditions: developing solvent is petroleum ether: acetone = 1:4. HPLC conditions: C18 chromatographic column, mobile phase A is pure methanol, mobile phase B ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com