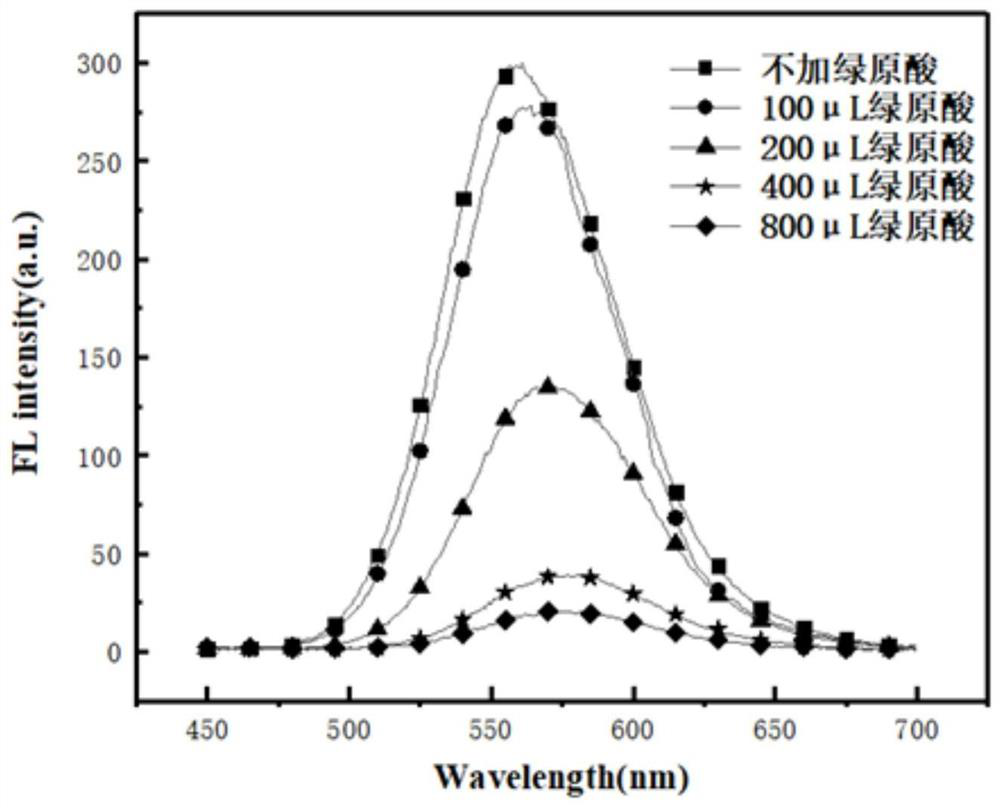
Fluorescent blotting membrane for in-situ visual detection of root exudates as well as preparation and application of fluorescent blotting membrane
A technology of root exudates and imprinted membranes, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, analytical materials, nano optics, etc., can solve problems such as root damage, inconvenient assembly, cumbersome steps, etc., and achieve wide application and operation Convenience and high specific response value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] (1) Preparation of CdTe quantum dots
[0063] Mix 1.6g sodium borohydride and 1.6g tellurium powder evenly, then disperse in 100mL distilled water, and react in the dark for 6h at room temperature to obtain the Te precursor NaHTe solution in CdTe quantum dots. Dissolve 0.4g of cadmium chloride and 0.5mL of thioglycolic acid (TGA) in 50mL of distilled water, add a 5% NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 10, and add 25mL of the precursor NaHTe solution to the In the mixed solution, the mixed solution was heated in a water bath to 90° C. for reflux reaction for 3 h to obtain a CdTe QDs solution, which was washed three times with absolute ethanol, centrifuged and freeze-dried for 12 h to obtain a CdTe QDs powder.
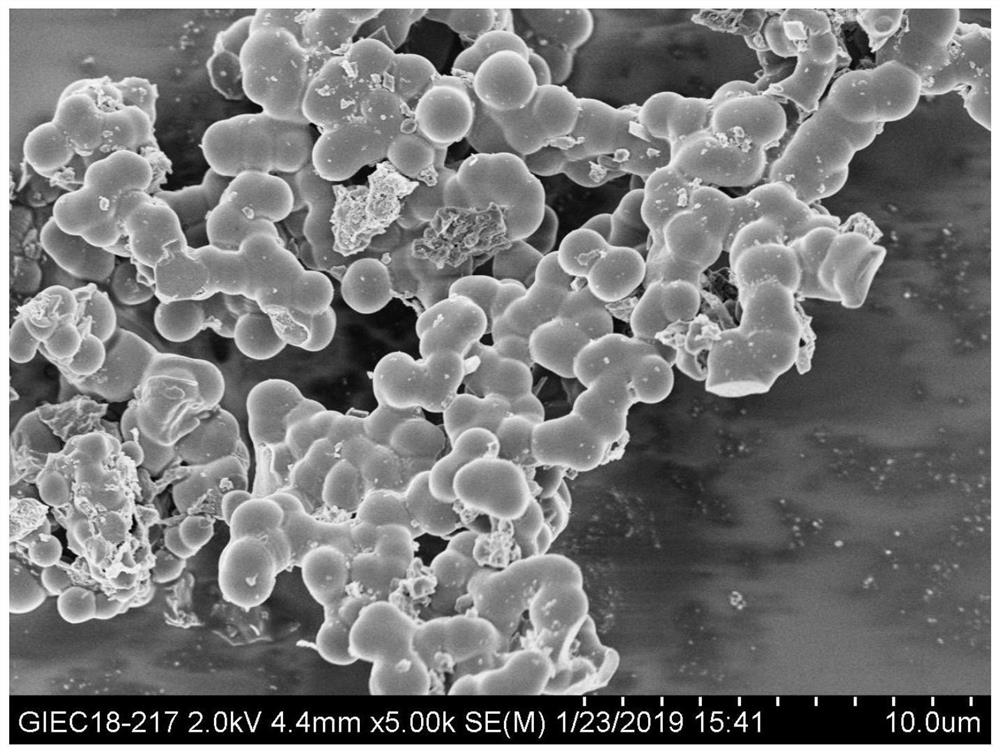
[0064] (2)CdTe@SiO 2 Preparation of @MIPs Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
[0065] Preparation of CdTe@SiO by Inverse Microemulsion Method 2 @MIPs: Add 100mL cyclohexane, 10mL NP-10, and 1mL distilled water into a round bottom flask, and sonicate for 20min to form...
Embodiment 2
[0069] (1) Preparation of CdTe quantum dots
[0070] 1.6g sodium borohydride (NaBH 4 ) and 3.2g of tellurium powder were mixed evenly, then dispersed in 100mL of distilled water, and reacted in the dark for 6h at room temperature to obtain the Te precursor NaHTe solution in CdTe quantum dots. Dissolve 0.5g of cadmium chloride and 0.5mL of thioglycolic acid (TGA) in 50mL of distilled water, add a 5% NaOH solution to adjust the pH to 10, and then add 17mL of the precursor NaHTe solution to the In the mixed solution, the mixed solution was heated in a water bath to 120° C. for reflux reaction for 3 h to obtain a CdTe QDs solution, washed three times with absolute ethanol, centrifuged and freeze-dried for 12 h to obtain a CdTe QDs powder.
[0071] (2)CdTe@SiO 2 Preparation of @MIPs Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
[0072] Preparation of CdTe@SiO by Inverse Microemulsion Method 2 @MIPs: Add 100mL cyclohexane, 14mL NP-10, and 1mL distilled water into a round bottom flask, and son...
Embodiment 3
[0076] (1) Preparation of CdTe quantum dots
[0077] 3 g sodium borohydride (NaBH 4 ) and 3g of tellurium powder were evenly mixed, then dispersed in 100mL of distilled water, and reacted in the dark for 12h at room temperature to obtain the Te precursor NaHTe solution in CdTe quantum dots. 0.5g cadmium chloride (CdCl 2) and 1.5 mL of thioglycolic acid (TGA) were dissolved in 50 mL of distilled water, and a 5% NaOH solution was added to adjust the pH to 10. After 0.5 h of nitrogen deaeration, 75 mL of the precursor NaHTe solution was added to the mixed solution, The mixed solution was heated to 90°C in a water bath for reflux reaction for 9h to obtain a CdTe QDs solution, washed with absolute ethanol for 3 times, centrifuged and freeze-dried for 12h to obtain CdTe quantum dot powder.
[0078] (2) CdTe@SiO 2 Preparation of @MIPs Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
[0079] Preparation of CdTe@SiO by Inverse Microemulsion Method 2 @MIPs: Add 100 mL of cyclohexane, 10 mL of NP-10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com