Method for preparing iron silicon from molten salt electric deoxidised copper slag
A technology of molten salt electric deoxidation and molten salt electrolyte is applied in the field of copper slag resource utilization, which can solve the problems that elements cannot be fully utilized, easily pollute groundwater, damage soil environment, etc., so as to improve electron transfer efficiency and realize efficient comprehensive recovery. Utilization, the effect of low reaction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
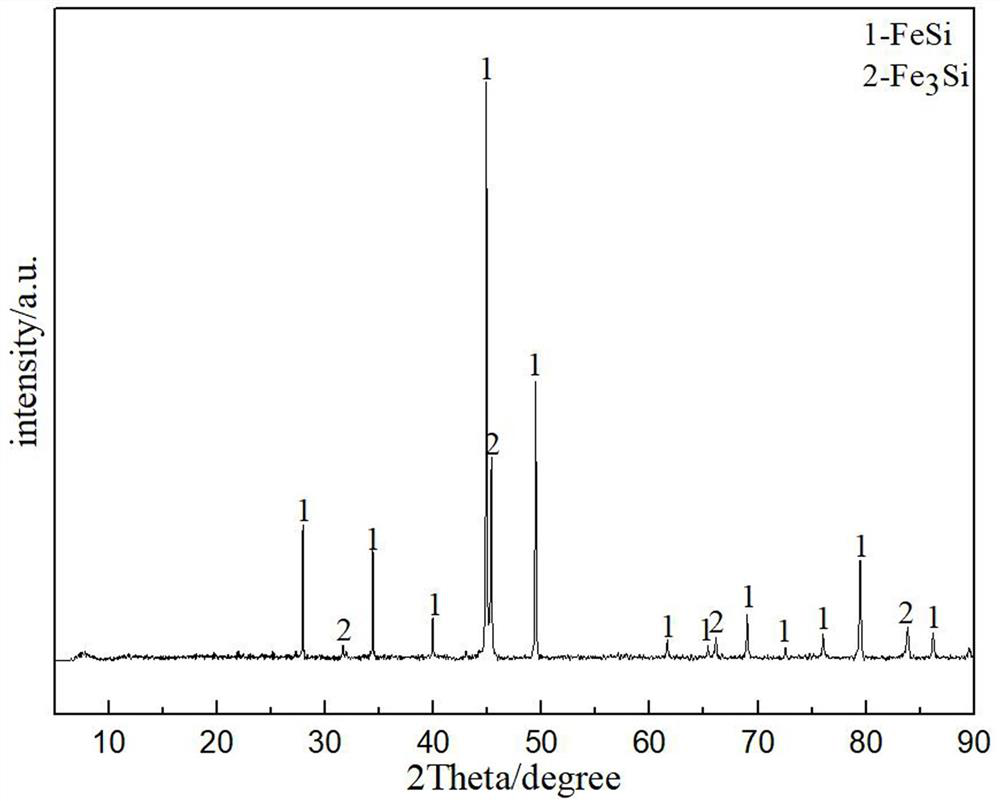
[0033] Example 1 A method for preparing iron-silicon from molten salt electro-deoxidation copper slag
[0034] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0035] S1, placing copper slag in a ball mill and performing mechanical ball milling for 10 hours at a speed of 150 rpm to obtain copper slag powder with a particle size of 15 μm to 25 μm;
[0036] S2, take 0.2kg copper slag powder and carry out magnetic separation treatment under the electric current of 1.0A, obtain 0.126kg magnetic separation tailings, get 0.0008kg magnetic separation tailings and press into sheet under 10MPa pressure condition and prepare as cathode sheet, and Under the protection of an inert gas, the cathode sheet was sintered at a temperature of 800°C for 5 hours, and the cathode sheet was wrapped with a metal iron mesh cloth and fixed on the iron rod of the cathode current collector with an iron wire;
[0037] S3, 0.18kg of electrolyte CaCl with a molar ratio of 1:1 2 , NaCl was dried in a drying...
Embodiment 2
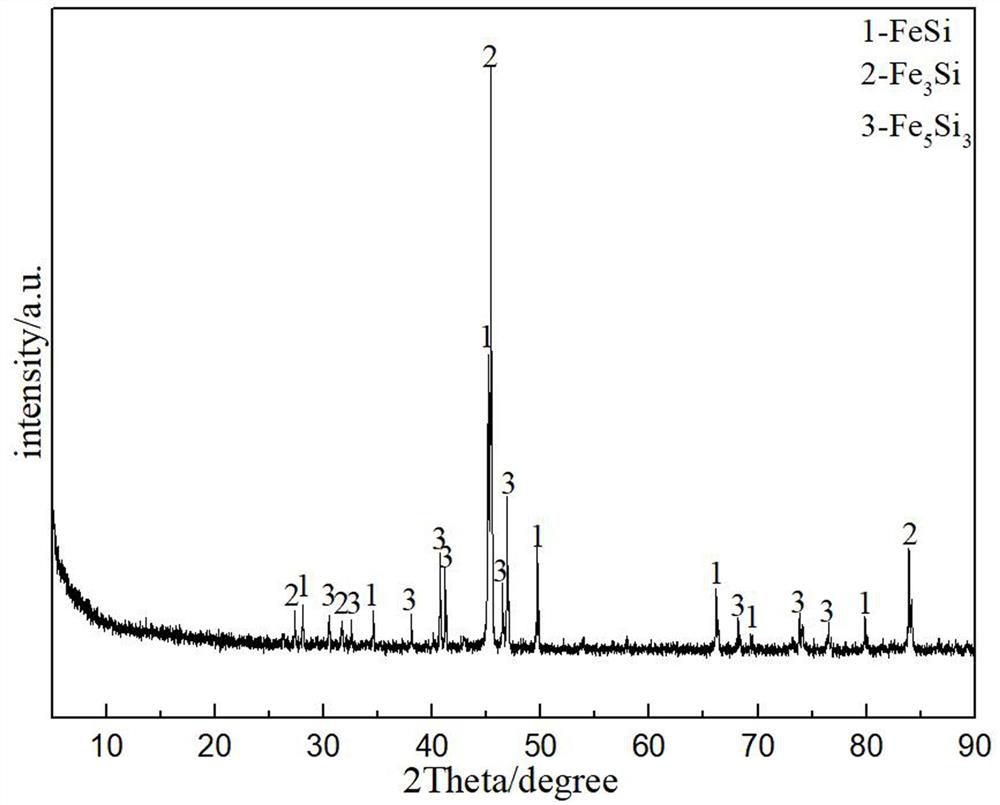
[0041] Example 2 A method for preparing iron-silicon from molten salt electro-deoxidation copper slag
[0042] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0043] S1, placing copper slag in a ball mill and performing mechanical ball milling for 6 hours at a speed of 180 rpm to obtain copper slag powder with a particle size of 15 μm to 25 μm;
[0044] S2, take 0.32kg copper slag powder and carry out magnetic separation process under the electric current of 1.1A, obtain 0.184kg magnetic separation tailings, get 0.0008kg magnetic separation tailings and press into sheet under 15MPa pressure condition and prepare as cathode sheet, and Under the protection of inert gas, the cathode sheet was sintered at a temperature of 700°C for 5 hours, and the cathode sheet was wrapped with metal iron mesh cloth and fixed on the cathode current collector iron rod with iron wire;
[0045] S3, 0.18kg of electrolyte CaCl with a molar ratio of 1:1 2, NaCl was dried in a drying oven at 230°C for...
Embodiment 3
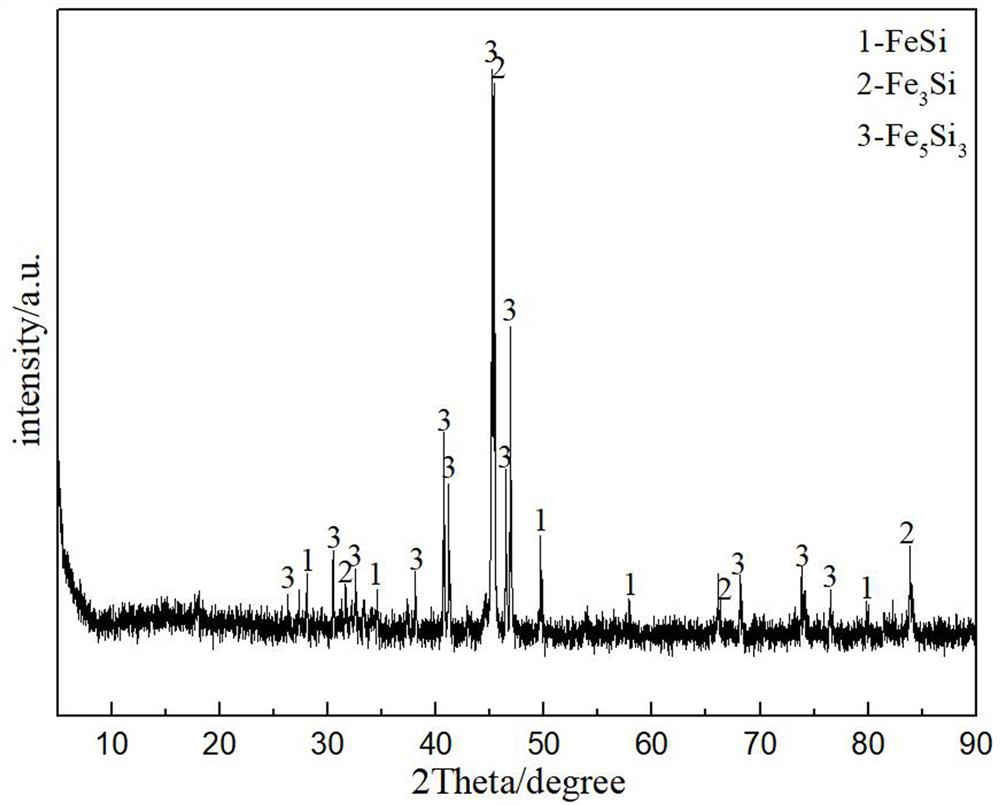
[0049] Example 3 A method for preparing iron-silicon from molten salt electro-deoxidation copper slag
[0050] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0051] S1, placing the copper slag in a ball mill for 8 hours of mechanical ball milling at a speed of 200 rpm to obtain copper slag powder with a particle size of 15 μm to 25 μm;
[0052] S2, take 0.2kg copper slag powder and carry out magnetic separation process under the electric current of 1.2A, obtain 0.121kg magnetic separation tailings, get 0.0008kg magnetic separation tailings and press into sheet under 13MPa pressure condition and prepare as cathode sheet, and Under the protection of an inert gas, the cathode sheet was sintered at a temperature of 800°C for 5 hours, and the cathode sheet was wrapped with a metal iron mesh cloth and fixed on the iron rod of the cathode current collector with an iron wire;
[0053] S3, 0.18kg of electrolyte CaCl with a molar ratio of 1:1 2 , NaCl in a drying oven at 240°C for 26...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com