Device for on-line selective separation of organic acid from anaerobic digestion liquid
An anaerobic digestion and selective technology, which is applied in anaerobic digestion treatment, separation methods, and separation of dispersed particles, can solve the problems of difficult separation of mixed salt solutions, low product purity, and reactor failure, and achieve the reduction of chemicals Use, wide application scenarios, and avoid toxicity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] Further, the preparation method of the microporous membrane filled with the organic extractant is as follows: immerse the microporous membrane in the organic extractant, and treat it with ultrasonic (25kHz-30kHz, 240W) for 15min-30min so that the extractant can fully fill the micropores, take it out and absorb To remove residual organic solvents on the surface, wherein the extractants used to fill the microporous membrane include: conventional oxygen-containing extractants, such as esters and ethers; organic phosphorus extractants, such as trioctylphosphine oxide and tributyl phosphate; Aliphatic amine extractant, such as trioctylamine, dodecylamine.
[0030] In addition, the breathable microporous membrane has high permeability to highly volatile short-chain fatty acids, and the microporous membrane filled with extractant has a high permeability to C 4 The above fatty acids have higher selectivity and can be selected according to needs, such as choosing a gas-permeable...
Embodiment 1
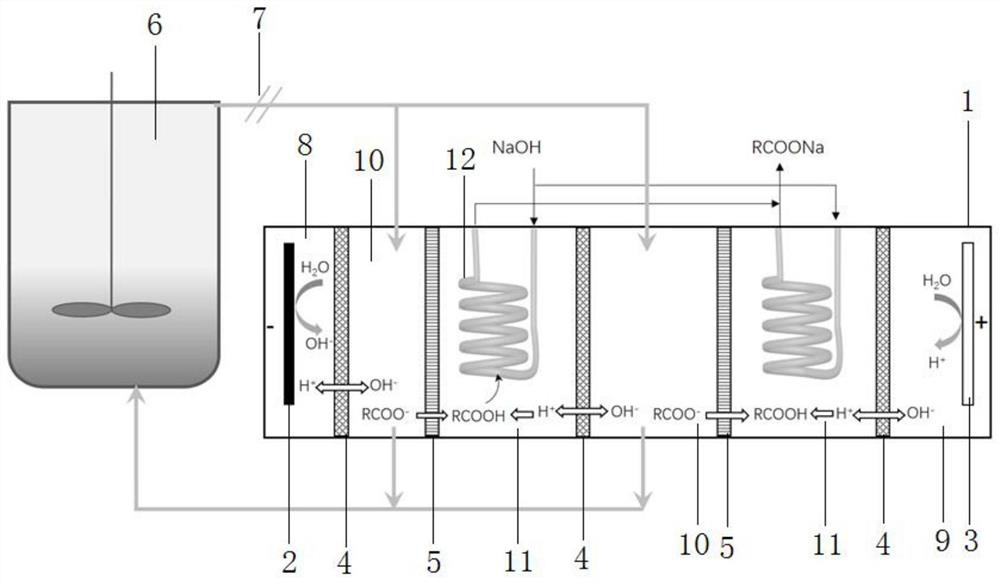
[0039] In this embodiment, the volatile fatty acids are extracted from the simulated solution prepared in the laboratory, and a polytetrafluoroethylene gas-permeable membrane is selected for the microporous membrane for the volatile small molecular fatty acids; the simulated VFAs solution prepared in the laboratory is 2L in total, containing: acetic acid 1000mg / L, propionic acid 1000mg / L, butyric acid 1000mg / L, valeric acid 1000mg / L, and NaCl 3000mg / L. The pH was adjusted to 7.0 using 2M NaOH and 2M HCl. Since the simulated solution prepared does not contain suspended solids (Suspended Solid, SS), no microfilter is used, and it is directly circulated in the electrodialysis module of the experimental device through a magnetic pump. The electrodialysis module uses two sets of membrane stacks, such as figure 1 As shown, the circulation flow rate is set to 40L / h, the acid chamber 11 circulates with the same circulation flow rate, the NaOH in the microporous membrane contactor 12 ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The experimental device of this embodiment is different from that of Reference Example 1. The difference is that the microporous membrane contactor is replaced by the microporous membrane contactor soaked and filled by the extractant trioctylamine, and the simulated solution is additionally added: caproic acid 1000mg / L, lactic acid 1000mg / L, other operating conditions are consistent with embodiment 1, the final recovery of each organic acid: acetic acid 39%, propionic acid 76%, butyric acid 85%, valeric acid 89%, hexanoic acid 91%, lactic acid 42% .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com