Extracellular matrix-imitated hydrogel dressing for diabetic foot ulcer and preparation method
A technology for diabetic foot ulcers and extramatrix, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problem of no diabetic foot ulcers, avoid toxicity and side effects, keep the wound moist, and improve the wound healing rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an extracellular matrix-like hydrogel dressing for diabetic foot ulcers, including:
[0052] Step 1, preparing polydopamine nanoparticles (M@D) loaded with deferoxamine mesylate, specifically including:
[0053] Step 101, dissolving 0.36 g of surfactant Pluronic F-127 and 417 μL of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) in 64 mL of deionized water, then adding 60 mL of absolute ethanol, stirring to mix evenly, to obtain a TMB solution; The stirring time can be 30min;
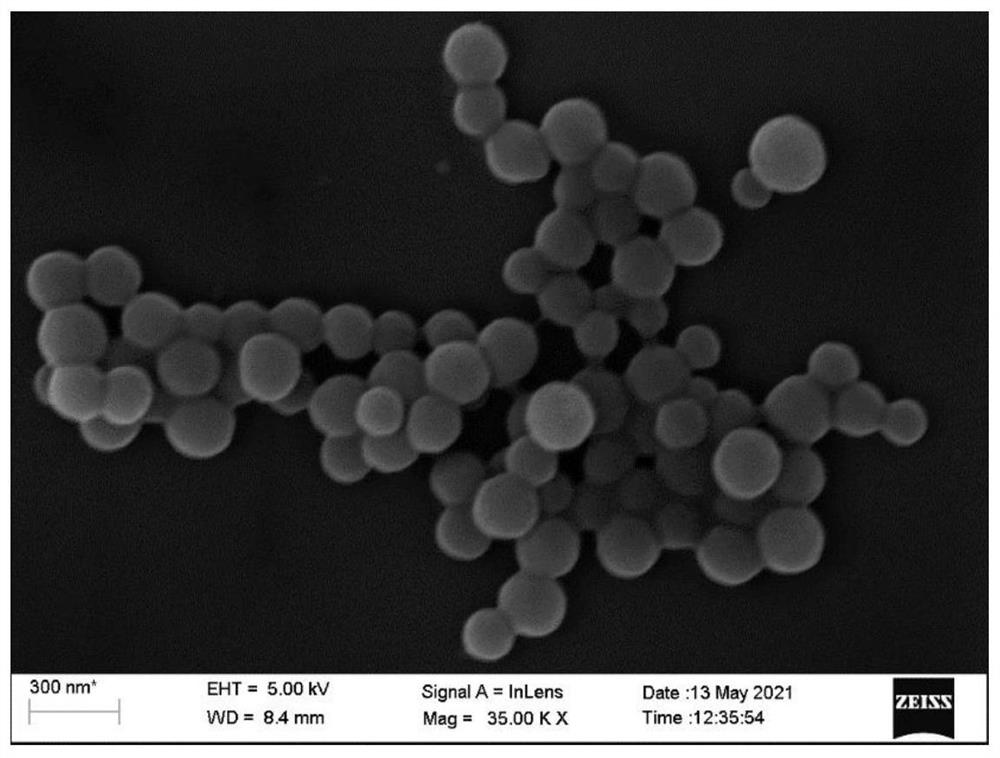
[0054] Step 102, adding 60 mg of dopamine hydrochloride and 90 mg of tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane (Tris) into the TMB solution described in step 101, stirred and reacted for 24 hours at room temperature, centrifuged, washed, and freeze-dried to obtain polydopamine nanoparticles (MPDA ); said cleaning is cleaning with a volume ratio of absolute ethanol and acetone mixed solution of 2:1, and the number of times of said cleaning is 3 times;
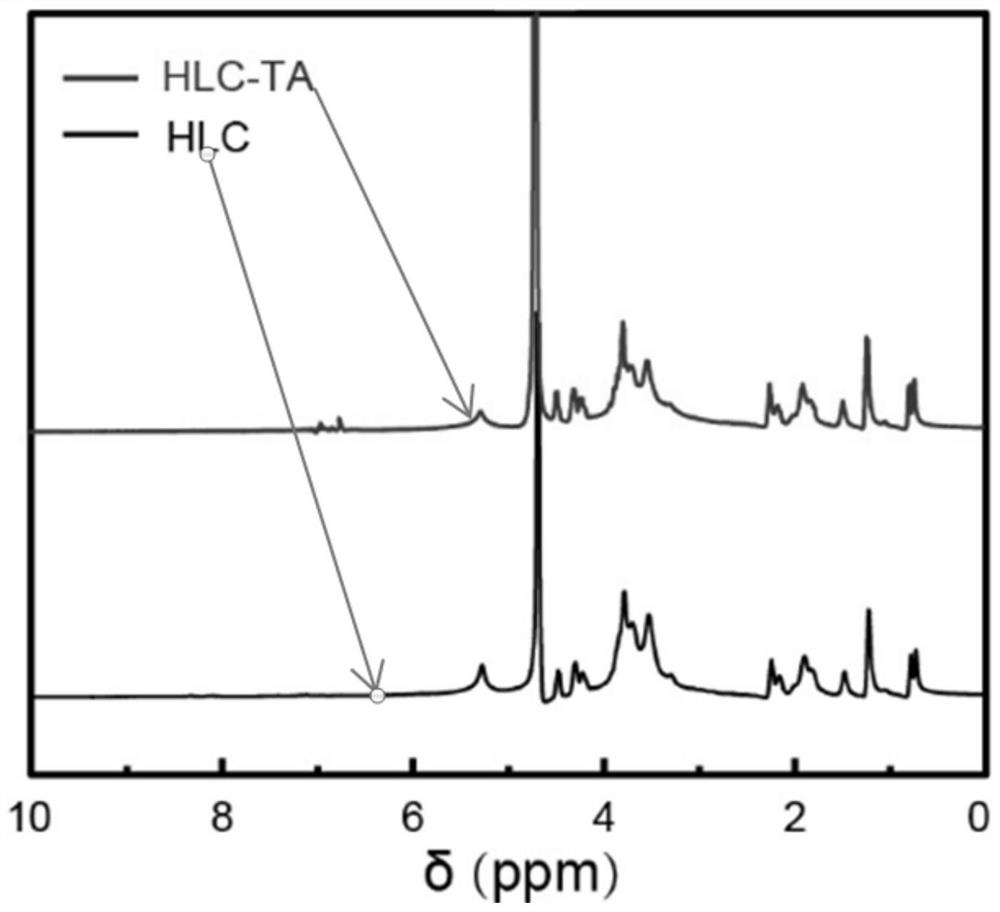
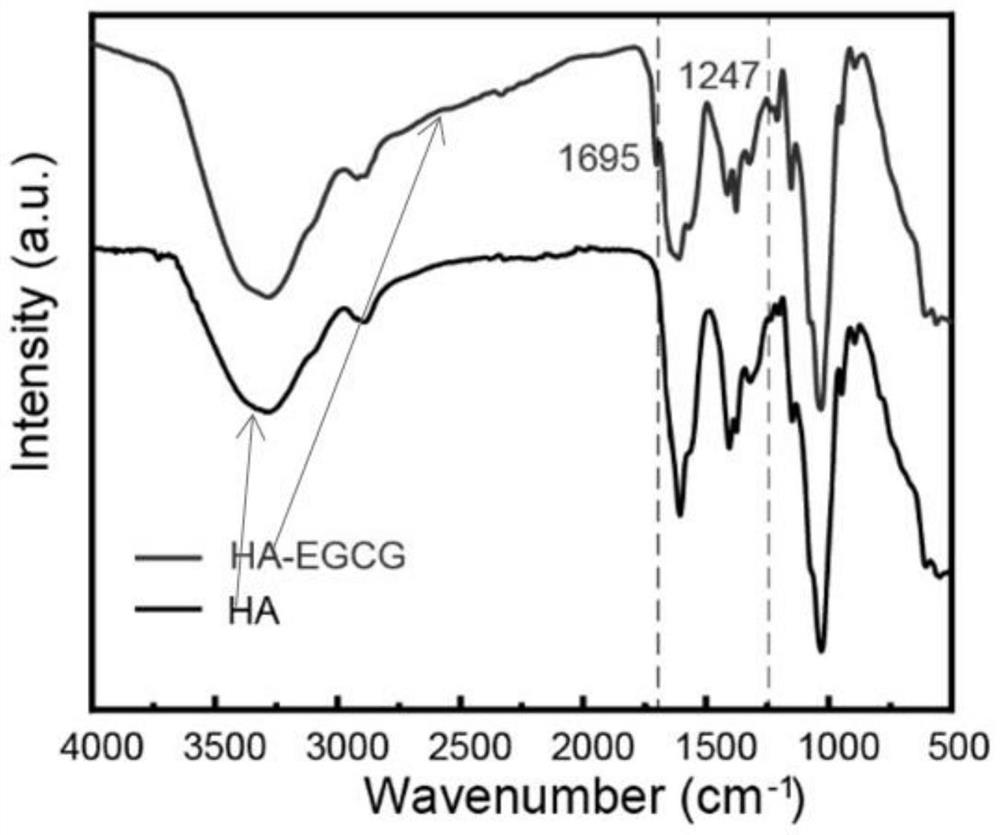
[0055] Step 103, addi...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an extracellular matrix-like hydrogel dressing for diabetic foot ulcers, including:
[0082] Step 1, preparing polydopamine nanoparticles (M@D) loaded with deferoxamine mesylate, specifically including:
[0083] Step 101. Dissolve 0.38 g of surfactant Pluronic F-127 and 435 μL of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) in 64 mL of deionized water, then add 60 mL of absolute ethanol, stir to mix evenly, and obtain a TMB solution; The stirring time can be 30min;
[0084] Step 102, adding 65 mg of dopamine hydrochloride and 90 mg of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) into the TMB solution described in step 101, stirred and reacted for 24 hours at room temperature, centrifuged, washed, and freeze-dried to obtain polydopamine nanoparticles (MPDA ); said cleaning is cleaning with a volume ratio of absolute ethanol and acetone mixed solution of 2:1, and the number of times of said cleaning is 3 times;
[0085] Step 103, adding 100 mg ...
Embodiment 3
[0105] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an extracellular matrix-like hydrogel dressing for diabetic foot ulcers, including:
[0106] Step 1, preparing polydopamine nanoparticles (M@D) loaded with deferoxamine mesylate, specifically including:
[0107] Step 101. Dissolve 0.40 g of surfactant Pluronic F-127 and 450 μL of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) in 120 mL of deionized water, then add 60 mL of absolute ethanol, stir to mix evenly, and obtain a TMB solution; The stirring time can be 30min;
[0108]Step 102, adding 70 mg of dopamine hydrochloride and 90 mg of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) into the TMB solution described in step 101, stirred and reacted for 24 hours at room temperature, centrifuged, washed, and freeze-dried to obtain polydopamine nanoparticles (MPDA ); said cleaning is cleaning with a volume ratio of absolute ethanol and acetone mixed solution of 2:1, and the number of times of said cleaning is 3 times;
[0109] Step 103, adding 100 mg ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| load ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com