SNP locus combination for detecting resistance of tomato gray leaf spot disease and application thereof
A tomato gray leaf spot and site technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve problems such as linkage burden, insufficient versatility of SNP sites, and invalid selection of target genes, to achieve accurate detection, reduce field transplanting workload, and improve The effect of breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] The screening of embodiment 1 SNP site combination
[0085] 1. Experimental materials
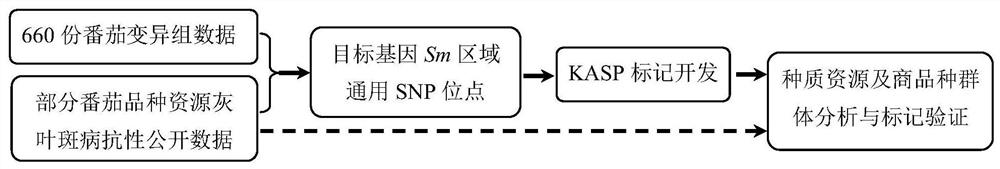
[0086] The variant group data of 660 representative tomato germplasm resources from different sources worldwide were selected for SNP site screening in this embodiment. The tomato variant group data is mainly based on the previous work of the project team where the inventor works ( Lin,T.,Zhu,G.,Zhang,J.et al.Genomic analyzes provide insights into the history of tomato breeding[J].Nat Genet,2014,46:1220~1226; Tieman D,Zhu G,Resende M F R, et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6323): 391). Among them, the genotype data of some tomato germplasm resources and the resistance phenotype data of the Sm gene come from the existing public database (https: / / solgenomics.net / ).
[0087] 2. Screening of SNP site combinations
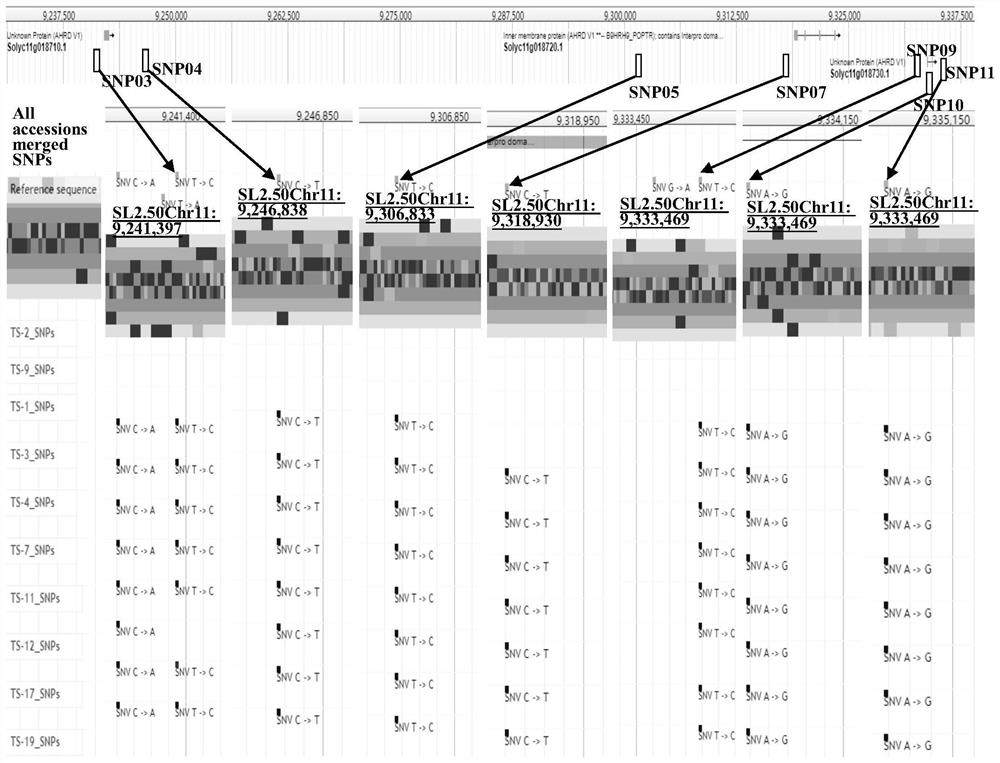
[0088] Use the target gene Sm (Solyc11g018710, Solyc11g018720 and Solyc11g018730, database source: https: / / solgenomics.net / ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 Primer Synthesis and Kit Preparation
[0093] 1. Primer design and screening
[0094] According to the flanking sequences of the SNP01 site to SNP11 site provided in Example 1, for each SNP site, according to the KASP marker design and development principle (target product 80-150bp, primers that specifically match the target region on the reference genome and are located in non- SNP-intensive regions, avoid complex sequence regions with high A\T or G\C content, etc.), use Primer3.0 software to design two forward primers upstream of the SNP site, and design a reverse primer downstream.
[0095] Tomato samples to be tested include 21 randomly selected germplasm resources and breeding materials with known genotypes and phenotypes as resistant, susceptible or heterozygous controls, and finally add 3 ddH 2 O is used as the NTC blank control, a total of 24 copies.
[0096] DNA extraction Genomic DNA was extracted from the leaves of tomato samples by conventional C...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Example 3 Verification and Breeding Application of Tomato Gray Leaf Spot Resistance Gene Sm High Efficiency KASP Marker
[0112] In this example, based on the SNP loci provided in Example 1, the kit (including primer combinations) provided in Example 2 was used to carry out the verification and breeding application of the tomato gray leaf spot resistance gene Sm high-efficiency KASP marker.
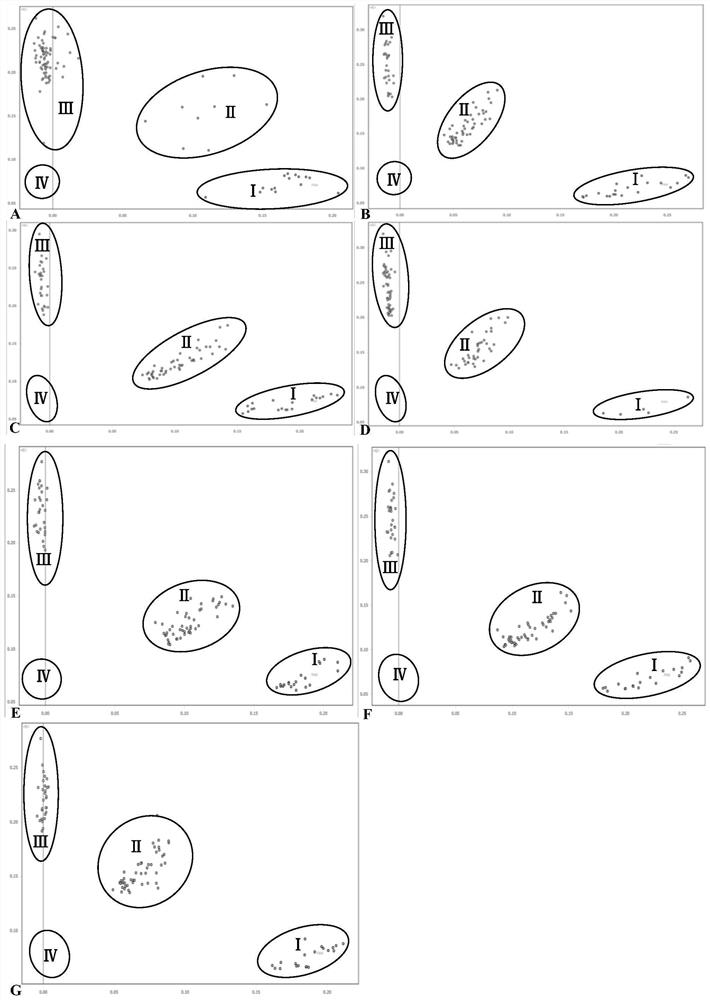
[0113] Select 381 representative tomato samples including mainstream commercial varieties, core public germplasm of the National Resource Bank, breeding intermediate materials, new hybrid combinations, etc., involving large fruit tomatoes, cherry tomatoes, cluster tomatoes, fresh tomatoes, processed tomatoes and Among cultivated tomatoes of different types and origins such as farm species (landraces), 162 of them have obtained Sm genotype data through third-party commercial institutions using closely linked InDel markers (including 15 with known ash leaf spot resistance phenotypes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com