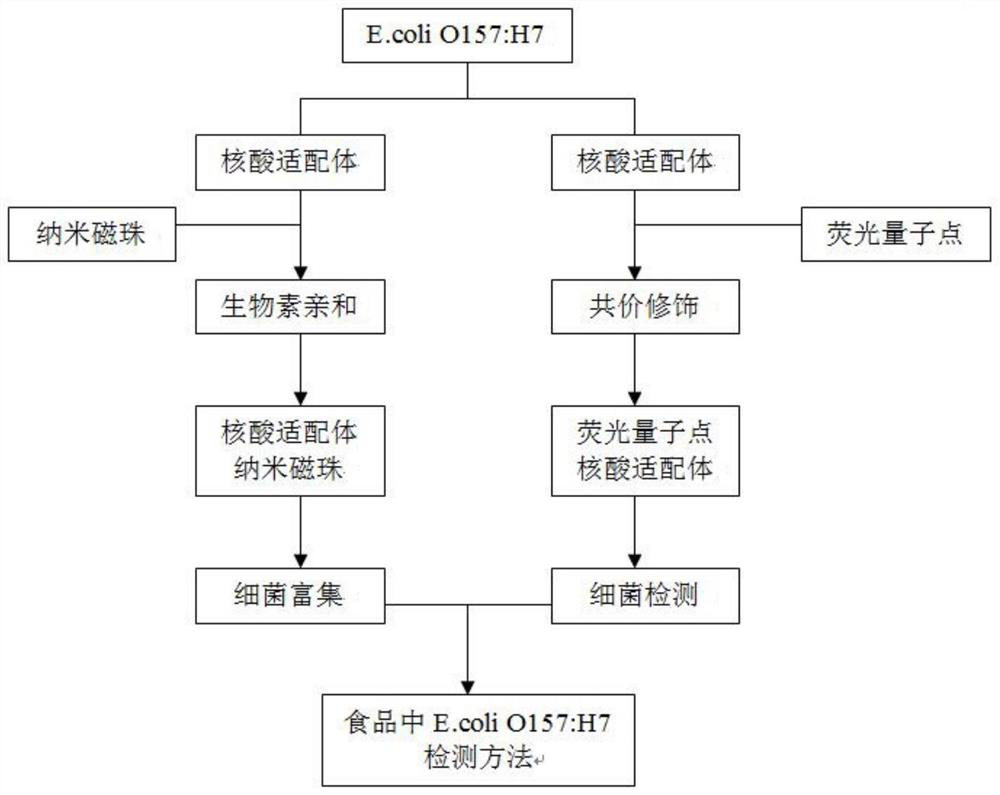
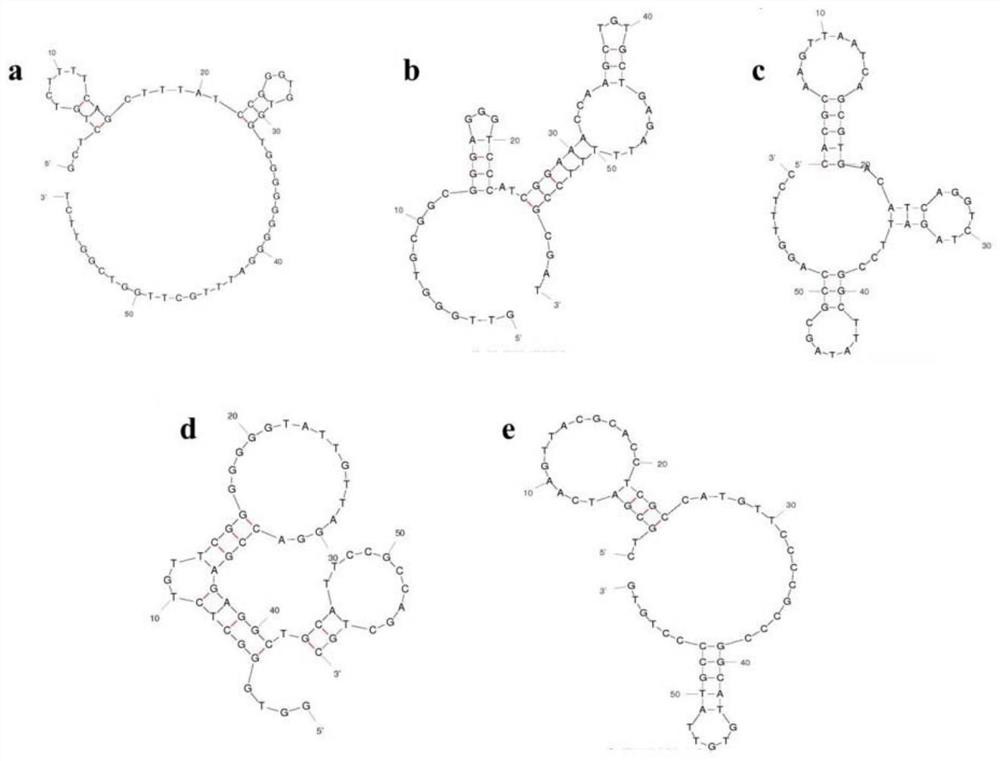
Method for detecting food-borne enteropathogenic bacteria O157: H7 based on nucleic acid aptamers, nanoparticles and quantum dot markers
A nucleic acid aptamer and nanoparticle technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity and specificity, complicated operation process, and time-consuming Long and other problems, to achieve the effect of wide range of target molecules, high sensitivity and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Construction and screening of nucleic acid aptamers of Escherichia coli O157:H7
[0036] 1. Coarse screening of nucleic acid aptamers of Escherichia coli O157:H7
[0037] The specific screening steps are as follows:
[0038] (1) For the first round of screening, take 200 pmol single-stranded random DNA oligonucleotide templates, dilute to 500 μL with binding buffer (pH=7.6), heat denature at 95°C for 10 minutes, and quickly place in ice water at 0°C Ice-bathed for 10 minutes, then placed at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0039] (2) Mix the single-stranded random DNA oligonucleotide template after ice bathing with 200 μL of Escherichia coli O157:H7, and shake at room temperature for 60 minutes. Centrifuge at 6000rmp for 5min and discard the supernatant. Wash three times with 400 μL wash buffer. The purpose is to wash away the single-stranded random DNA oligonucleotide template that does not bind E. coli O157:H7.
[0040] (3) Take the precipitate obtai...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2. Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles and functionalization of nucleic acid aptamers
[0077] In this paper, sodium hydroxide solution was used to hydrolyze ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O) and ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) mixed solution to prepare Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles, also known as co-precipitation method to prepare MNP, its chemical principle is 2Fe 3+ +Fe 2+ +8OH - → Fe 3 o 4 ↓+4H 2 O, iron ions Fe3+ and ferrous ions Fe should be strictly controlled 2+ The ratio is 2:1.
[0078] Synthesis of Fe by Co-precipitation 3 o 4 The steps of magnetic nanoparticles are as follows: the concentration is 0.12mol / L FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and concentration is 0.2mol / L FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in deionized aqueous solution, mechanically stirred and mixed, and nitrogen gas was passed through to fully remove the dissolved oxygen in the solution, and then a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 2.5mol / L was added dropw...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3. Preparation of avidinized nano-magnetic beads and functionalized quantum dots
[0082] The specific method of preparing avidinated amino magnetic beads based on the glutaraldehyde method refers to the method of Wu et al., with slight changes, as follows: Weigh 5 mg of aminated magnetic beads and dissolve them in 5 mL of 10 mM phosphate buffer for 20 min; Add 1.25mL of 25% glutaraldehyde, shake slowly at room temperature for 1h, enrich and separate Fe under the action of magnet 3 o 4 And washed 3 times with PBS to remove the physically adsorbed glutaraldehyde; 3 o 4 Add 500ul 1mg / mL streptavidin to the magnetic particles, shake slowly at room temperature for 6h; enrich and separate the avidinized amino magnet under the action of a magnet, discard the supernatant containing free avidin, and wash repeatedly with PBS; Add 5mL of 10mg / mL BSA to the primed amino magnetic beads and shake slowly at room temperature for 6h to block unreacted and non-specific bindin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com