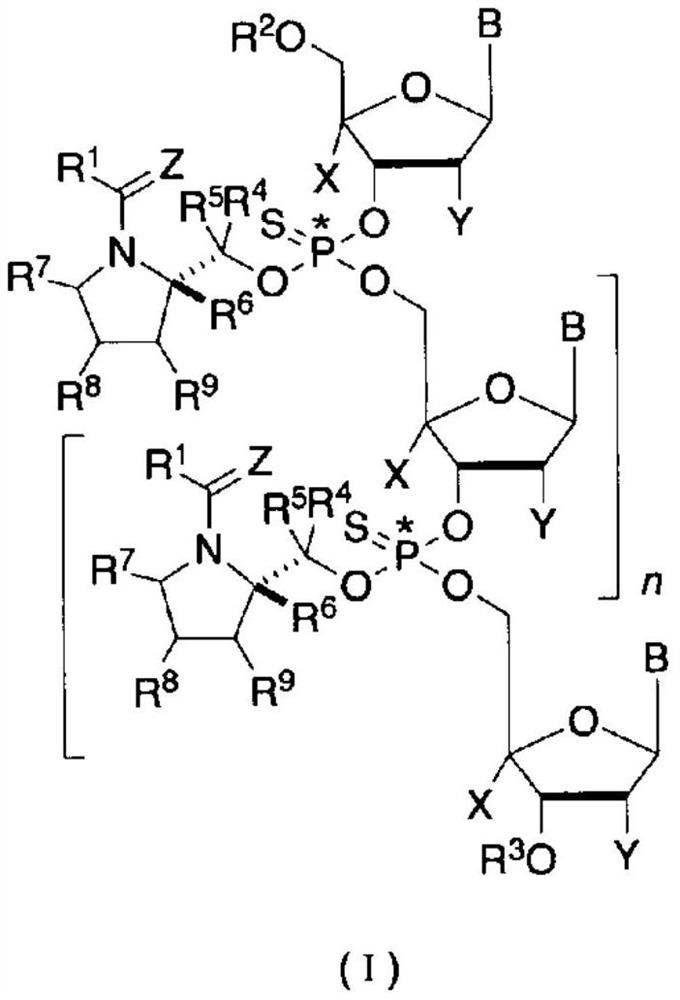
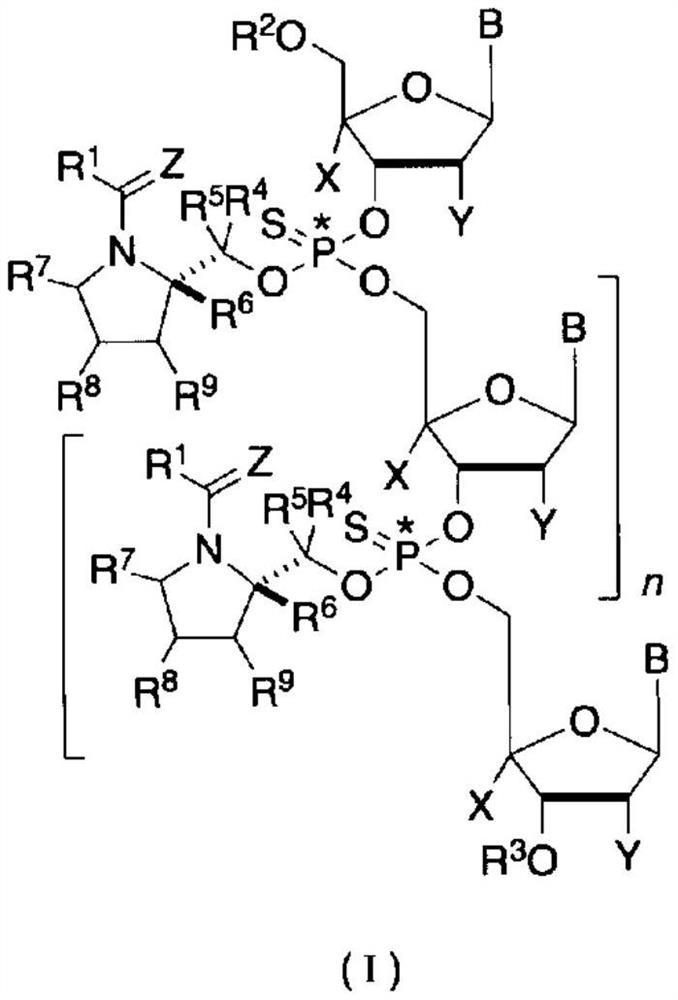
Optically active fragment for synthesizing stereocontrolled oligonucleotide, method for producing same, and method for synthesizing stereocontrolled oligonucleotide using same
An oligonucleotide and optically active technology, which is applied in the field of synthesis of phosphorus atom-modified oligonucleotides, can solve problems such as excessive dosage and side effects, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of procedures and purification load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] (Step 1: Synthesis of Optically Active Phosphorylating Agents)
[0084] [chemical 9]
[0085]
[0086] Phosphorus trichloride (3.5 mL, 5.5 g, 40 mmol) was dissolved in toluene (50 mL) at -78°C. Separately, L-prolinol (3.9 mL, 4.0 g, 40 mmol) and triethylamine (12 mL, 8.9 g, 88 mmol) were dissolved in toluene (50 mL), and added dropwise to phosphorus trichloride over 1 hour. After directly stirring for 12 hours, return to 0° C. and stir for another 1 hour. After the reaction, a precipitate formed as a by-product was filtered off with celite, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product. This was distilled under reduced pressure (65° C., 1.0 mmHg) to obtain the target phosphorous oxychloride 1 (3.2 g, 19 mmol, yield 48%).
[0087] (Step 2: Synthesis of Optically Active Phosphoramidite 2)
[0088] [chemical 10]
[0089]
[0090] 5'-DMTr-protected thymidine (11 g, 21 mmol, manufactured by Shanghai Zhaowei Technology Developme...
Embodiment 2
[0117] (Step 9: Synthesis of Optically Active Dinucleotides (N-Acetyl Termination))
[0118] [chemical 17]
[0119]
[0120] Optically active phosphoramidite 2 (2.7 g, 4.0 mmol) and 5'-hydroxyl unprotected nucleoside 3 (1.0 g, 3.1 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile (20 mL), to which was added benzimidazolium triflate Salt (1.2 g, 4.6 mmol). After 30 minutes, N-methylimidazole (0.49 mL, 510 mg, 6.2 mmol) was added, followed by acetic anhydride (0.73 mL, 790 mg, 7.7 mmol), followed by stirring for 30 minutes. Finally, phenylacetyl disulfide (1.9 g, 6.2 mmol) was added and stirred for 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was partitioned between dichloromethane (100 mL) and saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (100 mL), and the organic layer was recovered. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine (50 mL), and dried over sodium sulfate to obtain a crude product. This was purified by column chromatography using hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol as an eluting solvent to obt...
Embodiment 3
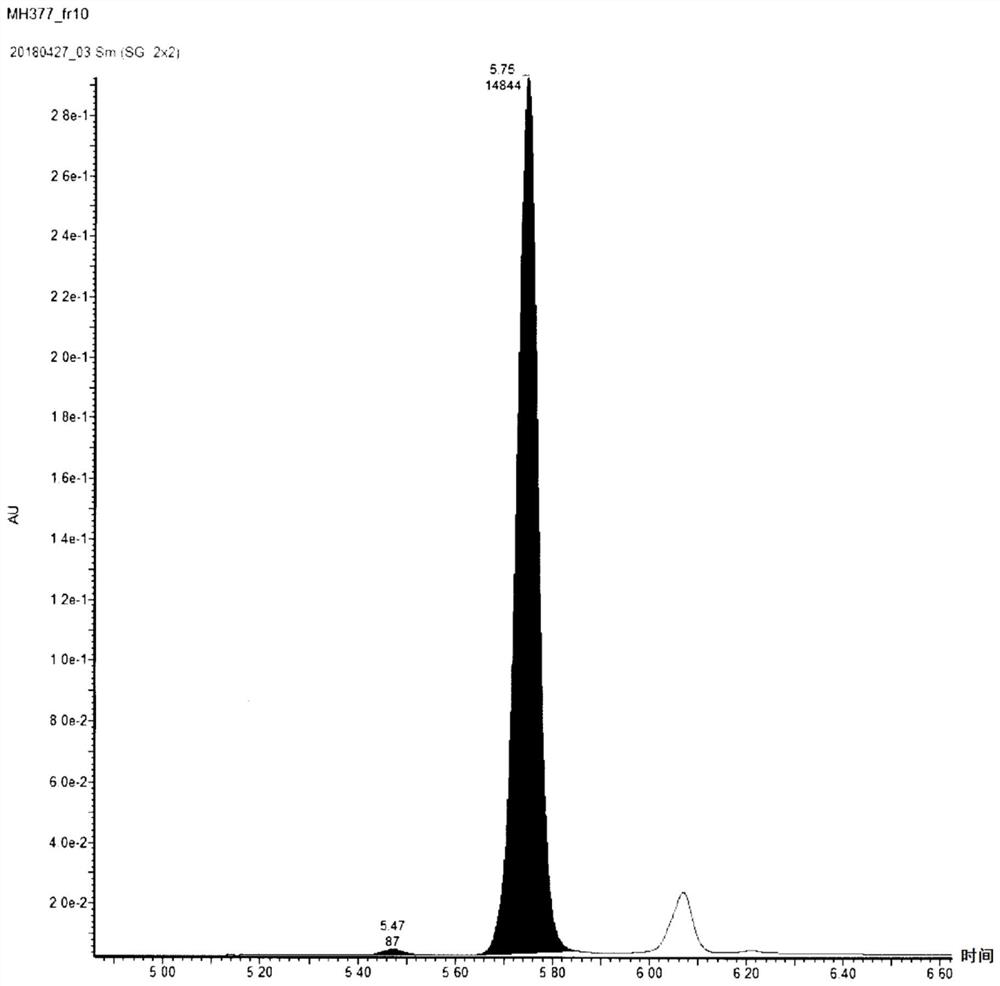
[0147] (oligonucleotide synthesis)
[0148] The optically active phosphoramidite obtained in this embodiment was used in the oligonucleotide solid-phase synthesis apparatus to synthesize stereocontrolled oligonucleotides. After carrying out condensation reaction, end-capping reaction, and oxidation or sulfuration reaction according to the standard experimental protocol of the device, the solid phase carrier is taken out, the obtained oligonucleotide is cut out from the solid phase carrier, and deprotected with concentrated ammonia water.
[0149] Based on the above results, the optically active fragment for synthesizing a stereocontrolled oligonucleotide according to this embodiment uses L- or D-prolinol derivatives as one of the raw materials as a chiral source, and can have multiple Stereo-controlled phosphorothioate groups, not limited to one. Therefore, the number of steps required for synthesizing a stereocontrol oligonucleotide of the same length can be reduced compared...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com